The yeast infection diagnostics market is valued at USD 470.5 million in 2025. As per FMI's analysis, the industry will grow at a CAGR of 6% and reach USD 805.2 million by 2035. In 2024, the industry for diagnostics of yeast infections saw increased momentum as a result of heightened diagnosis of recurring cases of vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC) in various clinical facilities.
Healthcare practitioners sought early diagnostic regimes, guided by a rise in complicated infections in Candida glabrata and Candida auris strains. Diagnostic laboratories also increased adoption of molecular testing kits compared to traditional cultures, enabling enhanced precision and quicker turnaround.
FMI’s findings suggest that public health initiatives in the United States and Europe were instrumental in raising clinical awareness of fungal infections, and as a result, increased diagnostic testing in outpatient gynecologic clinics.
Going forward in 2025, FMI’s findings indicate that the integration of technology-particularly point-of-care diagnostics, multiplex testing, and AI-based platforms-is going to revolutionize diagnostic workflows, particularly those based in hospitals.
In addition, the growth in antifungal resistance will put additional focus on accurate diagnosis; thus, diagnostic innovation will be a central driver of growth. Asia Pacific, driven by China and India, will likely be an important regional driver due to rising infection rates and growing healthcare infrastructure.
Market Forecast Table
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 470.5 Million |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 805.2 Million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6% |
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
The yeast infection diagnostics industry is on a consistent growth path, fuelled by increasing infection rates and worldwide demand for quicker, more precise diagnostic equipment. Expanded use of advanced molecular testing technologies is speeding early detection, particularly in drug-resistant Candida cases. As the industry evolves diagnostic technology suppliers and clinical labs will benefit most, while manufacturers dependent on legacy culture-based systems will lose industry share.
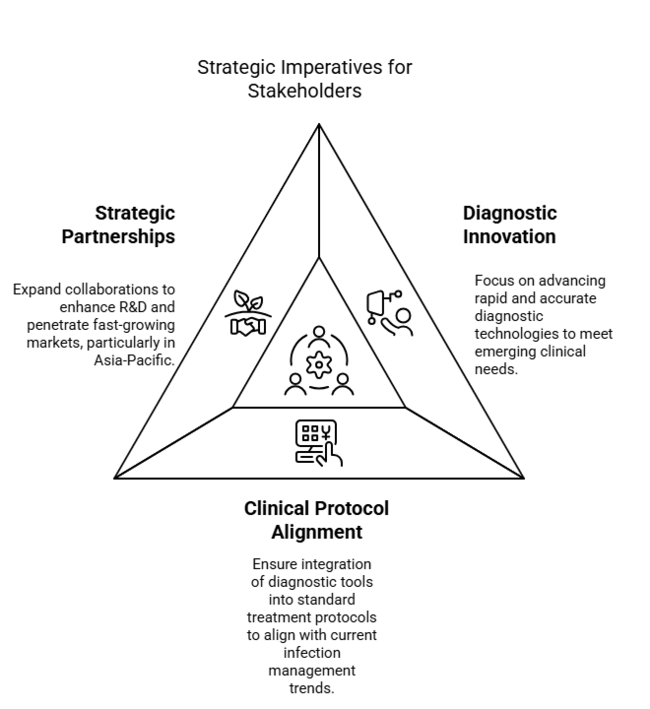
Accelerate Diagnostic Innovation
Invest in quick molecular and point-of-care diagnostic platforms to keep up with emerging fungal strains and address the growing clinical need for speedier, more precise results.
Align with Shifting Clinical Protocols
Work with healthcare facilities to include diagnostic devices in regular treatment plans, making sure the solutions match current infection management trends and the need to monitor resistance.
Broaden strategic partnerships and expand R&D efforts
Seek partnerships with educational institutions, biotechnology companies, and local distributors to upgrade R&D facilities and extend international presence, especially in untapped, fast-growing industries such as Asia-Pacific.
| Risk | Probability - Impact |
|---|---|
| Antifungal resistance outpacing diagnostic accuracy | Medium - High |
| Regulatory delays for advanced diagnostic tools | High - Medium |
| Limited adoption in low-resource healthcare settings | Medium - Medium |
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Expand Molecular Test Portfolio | Run feasibility on introducing low-cost PCR-based kits for outpatient clinics |
| Improve Clinical Adoption | Initiate hospital feedback loop on diagnostic tool usability and turnaround time |
| Strengthen Global Access | Launch distributor incentive pilot in Southeast Asia and Latin America |
To stay ahead, companies must focus on a shift toward fast, high-sensitivity diagnostic platforms that meet emerging antifungal resistance and changing clinical needs. Such insight supports the imperative to invest in next-generation molecular diagnostics and increase strategic partnerships, especially in rapidly growing geographies such as Asia-Pacific.
FMI research discovered that the traditional growth drivers are no longer sufficient; instead, companies will need to focus on innovation speed, regulatory adaptability, and the ability to deploy rapidly in diverse regions. Executives need to redefine their 12-18 month plan to encompass faster product development cycles, greater stakeholder interaction, and global access plans to achieve long-term leadership in the changing diagnostics industry.
Consensus and Divergence
Strategic Insight
| Countries | Policy and Regulatory Impact on Yeast Infection Diagnostics |
|---|---|
| United States | The CDC's diagnostic policy on fungal infections heavily informs hospital buying criteria. FDA clearance via 510(k) or De Novo pathways is required for commercial sale. Medicare/Medicaid reimbursement policies impact pricing strategy for tests. |
| United Kingdom | The MHRA requires compliance under UKCA marking for post- Brexit diagnostic devices. NHS procurement specifications highly dictate the uptake of diagnostics with established cost-effectiveness and digital connectivity. |
| France | Under the French Health Authority (HAS), diagnostics have to be CE-IVD certified and exhibit clinical utility. Public hospital adoption is consistent with national antimicrobial stewardship policies. |
| Germany | Strict application of the EU In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) requires third-party certification (Notified Bodies) and post- industry surveillance. Reimbursement needs to be added to the G-BA approved diagnostic catalog. |
| Italy | EU IVDR compliance is mandated. Regional public health procurement systems highlight the price-performance ratio. Public subsidization frequently accompanies locally certified molecular diagnostic tests. |
| South Korea | Regulatory approval by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is necessary for diagnostics. Government programs increasingly reward digital diagnostics, but controls on pricing are tight. |
| Japan | All diagnostics are required to obtain PMDA (Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency) approval. Stringent regulatory processes tend to hold back leading-edge diagnostics unless they demonstrate long-term cost-effectiveness. |
| China | The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) demands certification of Class II or III for molecular diagnostics. Domestic innovation is encouraged by policies, but import approvals are time-consuming and very intrusive. |
| Australia-NZ | The TGA in Australia and Medsafe in New Zealand need to be ARTG-listed and validated. Authorities are increasingly interested in point-of-care testing, especially for rural access. |
| India | The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) regulates diagnostic approvals. Critical diagnostics can apply for expedited approval, but regulatory consistency varies across states. Focus on public health deployment and affordability. |
Between 2025 and 2035, the panel test segment is expected to be the most profitable product segment, driven by the increasing clinical demand for multiplex detection formats that detect multiple pathogens simultaneously.
Amid growing regulatory clearances and cost reductions from miniaturization technologies, the segment is projected to increase at a CAGR of around 6.8% from 2025 to 2035, ahead of the global average. These tests simplify diagnostic workflows, enhance throughput, and provide more complete diagnostic results.
As clinicians shift away from one-pathogen-at-a-time testing approaches, panel tests are becoming increasingly popular in hospital laboratories as well as point-of-care applications. Additionally, their versatility for vaginal infections, STIs, and differential diagnosis fuels demand in high-prevalence geographies.
Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) will be the most lucrative segment because it is better at accurately finding Candida species and other infections. FMI research estimates that the NAAT segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 7.1%, making it the preferred diagnostic method in developed industries.
NAATs are rapidly superseding culture-based and pH tests, particularly in high-complexity laboratories as well as in clinical research environments. The convergence of AI-facilitated diagnostics and increasing investment in molecular diagnostic platforms are also driving the transition.
The vagina segment is likely to be the most profitable, driven by the worldwide burden of vulvovaginal candidiasis and recurrence rates. FMI suggeststhat the vaginal diagnostic segment will grow at a CAGR of around 6.3%, driven by product innovation and patient-focused delivery models.
Vaginal yeast infections continue to be the primary indication for diagnostic testing, particularly among women of reproductive age. With increased awareness, more gynecological screenings, and novel home-based diagnostics for this anatomical location, this industry is seeing fast adoption of NAATs and pH self-testing kits.
The vulvovaginal candidiasis will be the most profitable indication, as recurrent yeast infections cause most of these infections worldwide. According to FMI analysis, the segment will grow at a CAGR of about 6.5%, outpacing other infectious disease testing in the yeast-related segment.
Diagnostic differentiation from sexually transmitted infections and bacterial vaginosis is creating demand for high-precision platforms. Recurrence among immunocompromised individuals and those taking antibiotic therapy contributes to testing volume. Clinical guidelines for testing prior to treatment further establish diagnostic demand.
During the forecast period, diagnostics laboratories are expected to be the most profitable end-user segment, fuelled by centralized molecular testing, improved reimbursement structures, and growing private lab networks in developed and emerging economies. FMI suggests this segment will grow at a CAGR of nearly 6.7%, as strategic alliances and automation spending solidify its position as the leading diagnostic setting.
High-throughput capabilities and alliances with OB/GYNs and primary care physicians guarantee robust sample flow. As prices for NAAT-based platforms decrease, diagnostic laboratories are ramping up testing for multiplex vaginal panels and STI differentiation.
The industryin the USA is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.9% from 2025 to 2035. The USA still dominates diagnostic technologies due to robust reimbursement systems and the early adoption of molecular platforms. FMI analysis is of the opinion that strong awareness, active screening programs, and investment in digital health have led to the development of highly sensitive technologies for the early detection of Candida.
The CDC's fungal infection guidelines are redesigning hospital purchasing standards, particularly for immunocompromised patients. With FDA 510(k) approvals allowing advanced kits to be sold more easily, companies focusing on multiple, AI-supported solutions are in the best place to succeed and drive innovation.
UK’s salesis anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.3% during the assessment term. Regulatory changes following Brexit have seen diagnostics makers adapt to the new UKCA certification process in place of the EU's CE marking. FMI suggests that NHS guidelines on cost-effectiveness, infection control, and compatibility with digital record systems are restructuring the competitive dynamics.
Clinicians increasingly prefer quick point-of-care tests that minimize errors in prescriptions and are NICE compliant. Public health antimicrobial stewardship initiatives encourage the use of diagnostics to confirm infection before initiating treatment, making the UK an increasingly mature but policy-led industry.
The industryin France is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.7% from 2025 to 2035. Primary care physicians and public hospitals focus more and more on accurate diagnosis prior to starting antifungal therapy as part of government-supported initiatives to halt drug resistance. The FMI study revealed that France's healthcare environment is biased towards diagnostics approved by the French Health Authority (HAS) and conforming to CE-IVD in the EU's IVDR regime.
Investment in molecular diagnostics fuels the growth of the industryas part of national health reforms to modernize infectious disease care. Providers that are EHR compliant and economically priced can expect tremendous institutional backing in all French public and private healthcare sectors.
In Germany, the yeast infection diagnostic industryis projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% during the forecast period. Being one of the most regulated diagnostics environments in Europe, Germany requires strict clinical validation, complete IVDR compliance, and third-party notified body certification. FMI suggests that Germany's strong hospital system and government healthcare payments support the use of new diagnostic tools.
This is especially for those that provide faster results and help manage antibiotic use. Integration into national health information systems and conformity to the G-BA price catalog are a given. Suppliers with quick, accurate, and EHR-friendly solutions will enjoy a competitive advantage in this efficiency-driven but compliance-laden marketplace.
In Italy, the diagnostic industryfor yeast infections is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2025 to 2035. The Italian healthcare system is witnessing increasing demand for early-stage diagnostics that minimize empirical antifungal therapy, especially in obstetrics and geriatrics. Centralized digital health programs and rewards for technologies that meet CE-IVD standards are helping to balance out differences in healthcare facilities across regions.
FMI estimates indicate that government buying plays a big role in how widely devices are used, and devices that focus on being fast, accurate, and affordable are more likely to succeed. Italy's involvement in EU-level monitoring of antimicrobial resistance has also boosted investment in new diagnostic technologies, giving a strong advantage to companies with products that can be easily used at the point of care.
In South Korea, the yeast infection diagnostic industryis projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% during the forecast period. With the country developing its digital healthcare infrastructure, diagnostic accuracy becomes more of a priority in tertiary hospitals and women's health centers. The MFDS has strict regulatory requirements, but once cleared, products have the advantage of a well-organized healthcare delivery system.
FMI analysis indicates that Korean stakeholders are interested in AI-driven, portable diagnostics with real-time results, particularly for telehealth. Price regulation and reimbursement sensitivity are major impediments, but hybrid model providers (cloud reporting + on-site testing) are gaining traction in metropolitan and suburban industries.
In Japan, the industry is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.9% during the evaluation term. The landscape is conservative, preferring established practices and demanding rigorous validation by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA). FMI suggests that adoption of rapid or AI-based diagnostics is slower compared to the West because of regulatory conservatism and an aging clinical infrastructure.
However, demand is growing in urban hospitals, led by the fight against antifungal resistance and optimal prescribing. To be successful, firms need to provide clinically validated tools with localized data and be fully compliant with Japan's strict post-industry surveillance standards.
China’s sales is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.1% during 2025 to 2035. Increasing public investment in infectious disease testing, urbanization, and growing awareness of women's health are driving industry penetration. The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates tight approvals for diagnostic kits, particularly Class II and III devices, but encourages local innovation and scalability.
According to FMI's analysis, public hospitals in Tier I and Tier II cities are increasingly switching from culture-based techniques to molecular diagnostics. Companies offering cost-effective, scalable diagnostics tailored for high-volume testing are well positioned to dominate this high-growth but heavily controlled industry space.
In New Zealand and Australia, the yeast infection diagnostics industry is set to grow at a CAGR of 5.5% from 2025 to 2035. The two nations are investing in rural healthcare outreach, urging the move toward point-of-care and portable diagnostics. The TGA (in Australia) and Medsafe (in New Zealand) oversee diagnostic approvals through an ARTG listing with strict validation of performance and quality assurance.
FMI observes that adaptability to the environment, integration with clouds, and user-friendliness are more and more important for deployment in regions. Both private clinics and public health programs are backing AI-driven diagnostic systems that improve speed and lower uncertainty in diagnoses, creating a supportive environment for technology-based newcomers.
In India, the diagnostics industry for yeast infections is anticipated to grow at a 6.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035. The diagnostics segment is experiencing immense government support through the Ayushman Bharat program, with public-private collaborations promoting indigenous production of low-cost test kits.
Rural penetration is still a challenge according to FMI analysis, but Tier I and II cities are spearheading demand for quick, trustworthy diagnostics as antifungal resistance increases and women's health awareness grows. CDSCO regulates diagnostics device approvals with preferential approval of key diagnostics in the National List. Low-cost, low-infrastructure kit providers with support for validated performance data are set to experience high adoption.
In the diagnostics industry for yeast infections, leading players are competing on a competing by advancing innovation and optimizing cost structures, price flexibility, and strategic growth. Leading players are introducing multiplex molecular panels with faster turnaround times and higher diagnostic sensitivity while investing in to cater to the home-based diagnostics segment.
FMI analysis revealed that global players are also increasing regional penetration through distributor collaborations and acquisitions of local diagnostic laboratories. Partnership R&D with biotech companies and universities is speeding technology transfer and biomarker verification. Pricing competitiveness is still of prime importance, especially in the emerging industries where volume-based economies and reimbursement receptivity rule success.
Abbott Laboratories
Share: ~25-30%
Abbott is a leading competitor in the diagnosis of yeast infections, thanks to its extensive portfolio of molecular diagnostics and rapid tests. Abbott has a robust industry position through ongoing innovation and strategic alliances.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Share: ~20-25%
Roche boasts a strong presence with its highly advanced diagnostic platforms, such as PCR-based for fungal infections. The company lays emphasis on high-throughput and automation-based testing to improve the efficiency of labs.
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
Share: ~15-20%
Thermo Fisher is a major rival, offering a diversified portfolio of diagnostic assays and next-generation sequencing (NGS) solutions for the detection of yeast infection. Thermo Fisher lays significant emphasis on precision medicine and artificial intelligence-based diagnostics.
bioMérieux SA
Share: ~10-15%
Expertise in culture-based and automated diagnostic systems for fungal infections. Significant investments are made in R&D to achieve better sensitivity and shorter turnaround time.
BD (Becton, Dickinson, & Company)
Share: ~8-12%
BD specializes in sophisticated diagnostic instruments, such as automated identification and susceptibility testing systems for yeast infections. Strong distribution channels support its industry position.
Qiagen N.V.
Share: ~5-10%
In its molecular diagnostics products, Qiagen also offers PCR-based kits for Candida auris detection of infections. The corporation is strengthening its presence in growing industries.
Sales in the industry are being propelled mainly by increasing incidence of vulvovaginal candidiasis, increasing awareness regarding reproductive health, and the need for quick, home-based testing.
The industry is likely to experience steady growth owing to improvements in molecular diagnostics, increased healthcare access, and greater use of multiplex panels.
Some of the key companies are Hologic Inc., Becton, Dickinson and Company, Natureland Health, Stix's, PGYARD, myLAB Box, Juno Bio, Seroflora, PrivaPath Diagnostics, NutraBlast, Rite Aid Corporation, Home Health (UK) Ltd, Loyalbody, Savyon Diagnostics, BIOSYNEX SA, Quantbiome, Inc.
Panel test kits are likely to dominate as they can identify multiple pathogens at the same time with high sensitivity.
The industry will reach USD 805.2 million by 2035.
The market is categorized into strips, cassettes, panel test.
The industry is segmented into vaginal PH test, nucleic acid amplification testing (naat) and microbiome test.
The landscape is divided into vagina, penis, mouth, nail and skin folds.
The industry is segmented into vulvovaginal candidiasis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, bacterial vaginosis and others.
The landscape is segmented intohospitals, diagnostics laboratories, specialty clinics and homecare settings.
The market is studied across North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia, Oceania, The Middle East & Africa
Anti-hyperglycemic Agents Market: Growth, Trends, and Assessment for 2025 to 2035
Eyelid Scrub Market Analysis & Forecast by Product, Application and Region 2025 to 2035
CGRP Inhibitors Market Trends - Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Indolent Systemic Mastocytosis treatment Market Insights: Size, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Intraoperative Fluorescence Imaging Market Report - Demand, Trends & Industry Forecast 2025 to 2035
Cardiovascular Diagnostics Market Report- Trends & Innovations 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.