The global weft feeder industry is valued at USD 726.4 million in 2025. As per FMI’s analysis, the weft feeder market will grow at a CAGR of 5.2% and will reach USD 1.23 billion by 2035. Weft feeders are an integral part of textile production today, providing accurate and uninterrupted weft yarn supply to weaving machines.
During 2024, the weft feeder industry underwent a transformative phase led by the accelerated development in textile automation and increased demand for accurate weaving. The direction of the industry was influenced by an increasing focus on energy-saving feeders, reduced yarn wastage, and improved synchronization with high-speed looms.
As the industry ventures into 2025, growth is set to pick up pace, fueled by the broadening adoption of IoT-based feeders and adaptive control systems. The drive towards environmentally friendly textile production is urging stakeholders to invest in green weft feeder solutions, minimizing energy usage and cutting down on operational inefficiencies. As worldwide textile production ramps up, the need for sophisticated weft management technology is set to reshape efficiency standards, driving a more nimble and reactive supply chain.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Value (2025E) | USD 726.4 Million |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 1.23 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.2% |
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
Weft feeder industry is witnessing continued traction, driven by the extensive application of smart weaving technologies and rising demand for accuracy-driven textile production. Advanced technological innovations in sensor-integrated feeders and Internet-of-Things-based automation are transforming efficiency levels, enabling textile manufacturers to deliver increased throughput along with reduced wastage of material. On the other hand, companies that adopt traditional feeder technologies stand to get left behind with the industry transitioning towards next-gen, high-speed solutions.
Accelerate Automation and Smart Weaving Integration
Investments in AI-powered and IoT-integrated weft feeders will be the top priority for stakeholders to maximize operational accuracy, minimize downtime, and maximize yarn utilization. A transition to smart feeders will be essential for retaining competitiveness in high-speed textile manufacturing.
Align with Sustainability and Circular Textile Trends
Conforming to the world's move toward environmentally friendly production, stakeholders ought to incorporate energy-saving designs and recyclable material into weft feeder manufacturing. Partnership with sustainable textile programs will strengthen industry position and address changing regulatory requirements.
Develop Strategic Partnerships and Regional Industry Penetration
Strengthened partnerships with loom makers and textile mills will provide friction-free integration opportunities for next-generation weft feeder solutions. Increased presence in high-growth sectors via customized distribution networks and localized R&D will yield new revenue opportunities.
| Risk Factor | Probability & Impact |
|---|---|
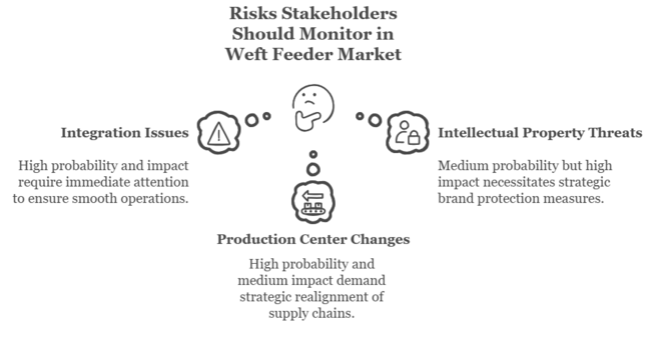
| Integration Issues with High-Speed Looms: Incompatibility of older weft feeders with newer generation high-speed looms can prevent smooth operations, causing inefficiency and higher maintenance expenditure. | High Probability, High Impact |
| Intellectual Property & Counterfeit Goods: New low-cost, counterfeit weft feeders on the emerging sectors pose a threat to established brands, cutting into profit margins and producing quality inconsistencies in the supply chain. | Medium Probability, High Impact |
| Changes in Textile Production Centers: Realigning textile manufacturing to low-cost areas can disturb established supply chains, and partners would have to re-strategize distribution channels and form new regional alliances. | High Probability, Medium Impact |
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Enhance Operational Resilience Amid Supply Chain Uncertainty | Diversify the sourcing plans for key feeder parts to reduce risks of material shortages and geopolitical tensions. |
| Optimize Feeder Performance for Complex Textile Blends | Invest in R&D to create adaptive weft feeders that can process varied yarn compositions, such as recycled and technical high-performance fibers. |
| Strengthen Cybersecurity in Digitized Weaving Processes | Incorporate strong cybersecurity measures to safeguard IoT-connected weft feeders against data breaches and operational interference. |
To stay ahead, companies must redefine their competitive edge by pioneering ultra-responsive weft feeder technologies that anticipate the evolving demands of high-velocity textile production. The roadmap needs to ensure microsecond-level accuracy in yarn delivery, self-tuning tension management, and adaptive feeder architecture that harmonizes with dynamic weaving patterns.
Supply chains need to be protected against geopolitical and raw material volatilities by multi-sourcing initiatives and nearshoring programs. In addition to operational resilience, leadership needs to infuse regulatory forward thinking, maintaining compliance with stringent sustainability requirements while being positioned for first-mover benefits from next-gen eco-certified textiles.
Mechanical and electronic weft feeders continue to be the giants of contemporary weaving operations, serving varied production requirements. With their rigidity and reliability, mechanical versions continue to be applied in traditional weaving operations where cost-effectiveness and longevity are the priorities.
Electronic weft feeders, however, are leading the industry's transition, providing high-precision control and real-time yarn tension manipulation. Their interface with high-speed looms and computerized weaving systems is augmenting production quality, minimizing waste, and speeding up production.
Between 2025 and 2035, the electronic weft feeder category will surpass the mechanical one at a CAGR of 5.2%. This upsurge is driven by the need for intelligent textile production and digitally optimized weaving techniques.
Manual and auto weft feeders serve different operational needs and contribute to the direction of industry development. Manual feeders will continue to remain relevant in small-sized weaving units and in traditional textile clusters where automation investment is limited. Such feeders provide affordable solutions for artisans and niche manufacturers engaged in producing customized fabrics.
Automatic weft feeders are leading the way towards smart weaving ecosystems, smoothly integrating with high-speed looms to maximize yarn flow and remove production bottlenecks. Sophisticated sensors, self-regulating mechanisms, and IoT connectivity are fueling their uptake in large-scale mills and industrial textile factories. With automation driving the textile manufacturing of today, the automatic weft feeder segment will exhibit a CAGR of 6.4% between 2025 and 2035, standing as the leading growth driver in the industry.
Weaving mills remain the largest buyers of weft feeders, using both mechanical and electronic models to ensure smooth production cycles. Mills prefer feeders that ensure operational stability to deliver consistent fabric quality with reduced defects. As textile producers invest in high-performance looms, demand for accuracy-oriented feeders is likely to grow steadily, driving growth in this segment.
Textile production factories are adopting next-gen feeders to optimize mass-scale fabric production. AI-powered monitoring automated systems are becoming the norm, enhancing material efficiency and lowering downtime. The packaging sector is also increasingly using weft feeders in the production of woven sacks and industrial fabric.
With myriad applications across these industries, the combined demand for weft feeders in industrial and commercial applications will register a industry CAGR of 5.4% from 2025 to 2035.
The United States continues to be a leader in weft feeder technology, led by the high-speed uptake of smart textile technology and automated weaving solutions. Demand for high-speed, precision-driven feeders is growing as domestic producers focus on efficiency and minimizing waste. Increasing investments in green textile manufacturing are also driving the move towards energy-efficient weft feeders with real-time monitoring.
The increasing relevance of nearshoring in clothing manufacturing is reconstructing supply networks, boosting demand for sophisticated feeder systems for production close to clients. As the demand is for fine cloth production, the USA industry can anticipate consistent growth. FMI opines that the CAGR of this country is approximately 5.5% between 2025 and 2035.
India's textile sector is undergoing fast-paced modernization, causing demand for economical yet technologically sophisticated weft feeders. The transition to high-speed weaving looms in large mills is opening doors for automation-based feeders that maximize productivity with minimal defects. Further, the increased usage of technical textiles in auto, medical, and defense applications is broadening the scope for the use of weft feeders beyond general textile production.
Small and medium-scale textile mills are also starting to use electronic feeders steadily in order to increase operational efficiency. This shift, along with a rapidly growing export sector, puts India firmly in the midst of the sector's future expansion. FMI forecasts that the CAGR of this country is around 5.8% between 2025 and 2035.
China leads the world in the production of textiles, and thus it is one of the largest sectors for weft feeders. The country's robust industrial sector and fast progress in digital textile production are creating the demand for precision feeders equipped with AI and IoT. Big textile mills are investing in completely automated weaving systems, lowering dependency on labor and increasing the efficiency of production.
In addition, the emergence of smart plants in China's textile bases is creating sector demand for real-time monitoring technologies in feeder technology. As the nation reinforces its position as an export champion, its investments in next-generation weft technologies will further influence industry dynamics. FMI projects that the CAGR of this country is expected to reach approximately 5.9% between 2025 and 2035.
The United Kingdom's weft feeder industry is changing with increasing demand for high-value, high-specialization textile manufacturing. Revival of domestic textile production, especially in luxury and technical textiles, is fueling the installation of precision-based feeder systems. Textile mill automation is speeding up the conversion from mechanical to electronic feeders, improving production efficiency and minimizing flaws.
The government's initiative to reshore textile manufacturing to build stronger local supply chains is also driving demand for high-end weaving solutions. With the industry going digital, UK textile manufacturers are focusing on feeder innovations that support automation trends. FMI forecasts that the CAGR of this country is expected to be around 5.4% between 2025 and 2035.
Germany leads in textile machine innovation, stimulating the need for technologically advanced weft feeders. Germany's focus on Industry 4.0 is revolutionizing the textile industry with far-reaching implementations of automated feeders with built-in predictive maintenance. German textile companies are centering on high-precision engineering, incorporating top-of-the-line feeder systems for optimized weaving performance.
Growing demand for technical textiles in automotive, aerospace, and medical applications is further fueling industry growth. Sustainability is still a top agenda item, and investments in energy-efficient and recyclable feeder parts are being made. FMI opines that the CAGR of this country is projected to be approximately 5.6% between 2025 and 2035.
South Korea's weft feeder industry is booming as a result of the speedy adoption of smart manufacturing and digital weaving technologies. The robust textile R&D environment in the country is fueling innovation in electronic feeders with artificial intelligence-driven tension control and real-time performance monitoring. South Korea's technical textile competitiveness, such as protective textiles and functional clothing, is also boosting demand for high-end feeder systems.
With increased emphasis on automation, textile producers are increasingly using new-generation manual feeders to replace old models that enhance efficiency and minimize fabric inconsistencies. FMI projects that the CAGR of this country is estimated to be around 5.5% between 2025 and 2035.
Japan's weft feeder industry is progressing with technological advancement and automation-driven textile manufacturing. The nation's focus on precision manufacturing is creating demand for high-performance feeders that provide error-free yarn handling and high-quality weaving.
Japan's top textile machinery makers are leading the development of sensor-based feeder systems, which allow real-time adjustments and low wastage. Increased usage of digital looms is driving the shift towards electronic feeders from mechanical ones, enabling enhanced production efficiency.
With an established textile machinery industry and quality focus, Japan's weft feeder industry will continue to witness steady growth. FMI forecasts that the CAGR of this country will be approximately 5.4% between 2025 and 2035.
France's weft feeder industry is transforming with the nation's luxury and haute couture textile industry. The need for precision-based feeders is increasing as high-end fabric producers look for cutting-edge solutions to ensure superior weaving quality. The trend towards digital weaving technologies is also driving the use of electronic feeders in high-end textile manufacturing.
Furthermore, increasing demand for technical textiles, such as performance clothing for fashion and industry, is broadening the industry for custom feeder systems. Sustainability continues to be a sector driver, which is driving investment in energy-efficient and low-waste weaving technology. FMI projects that the CAGR of this country is expected to be around 5.3% between 2025 and 2035.
Italy's rich experience with textile machinery and upscale fabric making is influencing the growth of its weft feeder business. Its emphasis on artistry and fine-quality textiles is fuelling the need for technologically advanced feeders with perfect weaving quality. Automated feeder systems are increasingly being incorporated into Italian textile manufacturers to add efficiency to upmarket and fashion textiles production.
Furthermore, the growth of technical textiles in industrial and automotive uses is also driving market expansion. FMI forecasts that the CAGR of this country will be approximately 5.5% between 2025 and 2035.
Australia and New Zealand's weft feeder industry is experiencing consistent growth as more investments are made in sustainable and technical textile production. There is a growing demand for advanced feeder systems due to regional textile manufacturers' need to upgrade operations to meet global quality levels. With the high emphasis on wool and natural fiber-based fabrics, feeder manufacturers are launching specialized products that meet distinctive fabric needs.
Moreover, the transition to automated and sustainable production processes is promoting the use of energy-saving electronic feeders. The increasing involvement of the region in international textile supply chains is also fueling demand for advanced weaving technologies. FMI opines that the CAGR of this region is estimated to be around 5.2% between 2025 and 2035.
Surveyed Q4 2024, n=450 stakeholder participants evenly distributed across manufacturers, distributors, textile mills, in the USA, Western Europe, Japan, and South Korea
Regional Variation
High Variance
Convergent and Divergent Perspectives on ROI
68% of USA stakeholders concluded automation was "worth the investment," while 41% of Japan's textile mills continue to use manual feeders.
Consensus:
Aluminum-Alloy Feeder Parts:
62% overall preferred them due to corrosion resistance and lightweight durability.
Variance:
Shared Challenges
85% mentioned rising raw material prices (steel up 28%, advanced alloys up 16%) as a key concern.
Regional Differences
Manufacturers
Distributors
End-Users (Textile Mills)
Alignment
72% of world manufacturers intend to invest in AI-driven feeder controls.
Divergence
Regulatory Influence
High Consensus
Automation, energy efficiency, and cost volatility are universal issues.
Key Variances
Strategic Insight
A "one-size-fits-all" solution will not be effective. Regional adaptation (AI-based feeders in the USA, eco-friendly materials in Europe, and space-saving feeders in Asia) is necessary to penetrate the market.
| Countries | Government Regulations |
|---|---|
| United States | Strict OSHA safety standards and EPA energy regulations are influencing the uptake of effective weft feeders. |
| India | The PLI program is compelling local production, lessening reliance on imports. BIS certification guarantees safety norms compliance, while GST policies determine procurement. |
| China | Government CCC certification mandates stringent quality adherence, while carbon-neutral programs are propelling the transition to energy-efficient feeders. |
| United Kingdom | UKCA marking after Brexit imposes additional compliance challenges. Energy efficiency policies in textile manufacturing are stimulating the demand for intelligent feeders, while changes in import duties influence supplier strategy. |
| Germany | CE marking is required for textile machinery, in line with EU Green Deal legislation that focuses on emissions management. |
| South Korea | KCs marking is required for imported machinery. Automation grants supported by the government promote the use of AI-based weft feeders to improve productivity. |
| Japan | JIS safety standards regulate import requirements, raising compliance expenses. |
| France | Tough labor regulations require worker-friendly and ergonomic machinery. The EU sustainability model is driving the transition towards energy-efficient weft feeders in textile production. |
| Italy | The EU Machinery Directive regulates operational safety, while government-initiated digital transformation programs promote more use of automated feeder technology. |
| Australia-NZ | AS/NZS safety standards regulate textile machinery imports, while country-level carbon-neutral targets are driving demand for low-energy feeders in the sector. |
The industry for weft feeders is moderately fragmented with many regional and global players. Major players are competing based on technological advancements, competitive pricing, strategic alliances, and geographical expansion to establish strong market positions.
Leading players in the weft feeder industry are aggressively investing in the creation of innovative, energy-efficient feeders to address the changing needs of the textile sector. They are collaborating through strategic alliances and partnerships to develop technological competence and increase industry share.
In November 2024, the leading textile machinery company KARL MAYER introduced its WEFT GRID ECO products at ITMA ASIA + CITME 2024. The reception to these introductions validated that KARL MAYER's Business Unit Technical Textiles is heading in the correct direction, though impulses for growth from the building industry were below expectations.
Market Share Analysis
Growing labor shortages and need for high-speed precision weaving are driving increased adoption of automated feeders at textile centers worldwide.
Changing supply chain tactics and regional trade policies are inducing manufacturers to diversify sourcing and invest in local production capabilities.q
Industry leaders are incorporating IoT and AI-powered analytics to make feeders more efficient, minimize wastage of yarn, and allow predictive maintenance.
Tighter eco-compliance regulations are compelling manufacturers towards energy-efficient design and recyclable material usage to keep pace with changing regulatory standards.
Firms are focusing R&D on adaptive tension control, precision yarn feeding, and automation to meet increasing demand for high-performance textile machines.
Mechanical, Electronic Weft Feeder
Manual Weft Feeder, Automatic Weft Feeder
Weaving Mills, Textile Manufacturing Plants, Garment Manufacturing, Packaging Industry, Others
North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, Middle East and Africa (MEA), East Asia, South Asia and Pacific
Power Tool Gears Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Surge Tanks Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
External Combustion Engine Market Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Motor Winding Repair Service Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Industrial Linear Accelerator Market Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Vision Guided Robots Market - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.