The textile recycling market is projected to witness stable growth from 2025 to 2035 due to increasing awareness about the environment, stringent waste management regulations, and rising demand for sustainable fashion. The industry is estimated to grow at about 3.2% CAGR during the forecast period to reach approximately USD 5.1 billion by 2025, supported by the increasing adoption of environmentally sustainable practices to reach USD 7.0 billion by 2035.
In 2024, the growth was driven by heightened regulatory scrutiny of fashion brands to take on sustainable practices, especially in Europe and North America. Some countries implemented mandatory textile waste collection systems, resulting in more recycling.
Meanwhile, the introduction of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs further motivated brands to incorporate recycled fibres into their offerings. The green-driven demand for mechanical and chemical recycling technologies skyrocketed, leading to breakthroughs in polyester and cotton fibre regeneration, making recycled textiles more competitive.
The increase will be driven by improvements in recycling technologies, greater incorporation of recycled materials into mainstream fashion, and movement to minimize textile waste in landfills. Nevertheless, high operating and maintenance costs, along with limited textile recycling infrastructure, pose significant barriers.
However, the future of the overall textile recycling Market still looks promising, with increasing focus on developing sustainable consumption models driven by factors such as consumer awareness and changing legislation. Governments, brands, and consumers will come together even more to lead the way in the implementation of recycling systems.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2025E) | USD 5.1 billion |
| Market Value (2035F) | USD 7.0 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 3.2% |
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
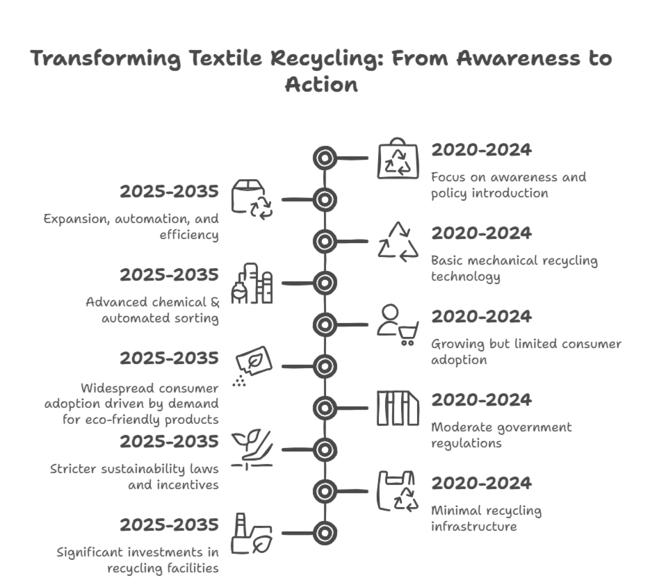
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Focus on awareness and policy introduction | Expansion, automation, and efficiency |
| Basic mechanical recycling technology | Advanced chemical & automated sorting |
| Growing but limited consumer adoption | Widespread consumer adoption is driven by demand for eco-friendly products |
| Moderate government regulations | Stricter sustainability laws and incentives |
| Minimal recycling infrastructure | Significant investments in recycling facilities |
| Fashion brands experimenting with recycled materials | Widespread use of recycled textiles in mainstream fashion |
| High textile waste in landfills | Increased circular economy adoption, reducing landfill waste |
| Regional recycling initiatives | Global collaborations for textile waste management |
Future Market Insights (FMI) has carried out a comprehensive survey of key stakeholders, including manufacturers, recyclers, policymakers, sustainability experts involved in the textile recycling industry. The survey showed that 73% of stakeholders believe technological improvements, such as chemical recycling and fiber-to-fiber recycling, will drive the bulk of industry growth between 2025 and 2035.
Also, 65% of respondents considered the demand for sustainable fashion to be one of key trends driving the industry. Stakeholders also highlighted the necessity of collaboration between brands, governments, and recycling firms to scale up infrastructure and enhance collection systems.
Of the challenges they faced, 60% indicated that high operational costs and low levels of consumer awareness remain major barriers to industry growth. But stakeholders were optimistic about the potential for government regulations and incentives to help overcome those challenges.
For example, 75% of respondents feel that extended producer responsibility (EPR) and recycling process tax benefits will help propel the industry forward. In essence, the survey highlighted the importance of concerted action from all stakeholders to realize a circular economy in the textile sector.
| Countries | Regulations |
|---|---|
| European Union | The EU’s Circular Economy Action Plan mandates textile waste reduction targets and promotes recycling through Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) schemes. |
| United States | Several states have introduced EPR laws for textiles, and federal tax incentives support recycling initiatives. |
| India | India is in the process of implementing an EPR framework” to avoid misrepresenting current regulations. |
| China | China’s 14th Five-Year Plan emphasizes green development, including textile recycling and waste management. |
| United Kingdom | The UK’s Waste Prevention Programme includes specific targets for textile recycling and bans on landfill disposal of textiles. |
Leading players in the textile recycling industry compete through pricing strategies, technological advancements, strategic collaborations, and geographic expansion. Firms are directing efforts toward cost-effective recycling processes to position recycled textiles at the same price levels as virgin textiles.
Innovation also plays an important role, with firms investing in state-of-the-art chemical recycling processes to enhance fiber quality and yield. Further, partnerships among fashion brands and textile recyclers have been on the rise, which provides constant access to recycled fibers and aligns with sustainability goals.
In expansion, major players are expanding their operations and venturing into new geographies. Firms are establishing regional recycling centers, with Asia being a key focus area where textile waste is readily available, and governments are changing policies to support sustainability.
Some companies are acquiring small recycling startups to gain exclusive access to advanced recycling technologies. Investment in artificial intelligence-based sorting mechanisms and blockchain to track material origin is also turning into a differentiator.
Market Share Analysis of Leading Companies
| Company | Industry Share |
|---|---|
| Lenzing AG | 18%, primarily due to its dominance in fiber innovation and closed-loop recycling. |
| Martex Fiber | 12%, specializing in industrial textile waste recycling, produces recycled fibers for insulation, automotive, and nonwoven applications. |
| Unifi, Inc. | 10%, largely due to its well-known REPREVE® recycled polyester, which is widely used in sportswear, automotive textiles, and consumer goods. |
| Pure Waste Textiles | 9%, producing garments made from 100% recycled materials |
| Boer Group | 8%, post-consumer textile collection and sorting, supplying recyclers with high-quality textile waste |
| Circ | 7%, a key player in chemical textile recycling, specializing in converting discarded clothing into new fibers |
| Renewcell AB | 6%, players in chemical textile recycling, converting discarded clothing into new fibers |
| I:CO (I Collect) | 5%, a global clothing collection system, partners with major retailers for take-back programs |
| Evrnu | 4%, a newer player, focuses on high-tech fiber regeneration |
| Others | 21%, local initiatives, and emerging startups innovating within the industry |
Key Developments (Mergers, Acquisitions, Partnerships) in 2024
The textile recycling industry is a segment of the larger waste management and recycling Industry, and it falls under the sustainable textiles and circular economy umbrella. It targets turning textile waste into something reusable, cutting reliance on landfilling and strengthening eco-friendly utilization.
As the fashion industry is also one of the biggest polluters, producing 8-10% of the earth’s total carbon emissions, national and non-governmental organizations are advocating for circular economy models. Macro-economic factors including strict waste management regulations, increasing consumer awareness regarding sustainable fashion, and growing acceptance of extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies are fueling growth of the industry.
As an example, the European Union’s Circular Economy Action Plan and other such initiatives in the USA and Asia are laying out a regulatory environment conducive to such practices. Moreover, technological progress in recycling, including chemical and mechanical recycling that increases efficiency, and scalability is contributing to the growth of the industry.
The increasing demand for recycled textiles from sectors such as fashion, automotive, and home furnishings is also contributing to Industry growth. Nonetheless, high operational costs and inadequate infrastructure for the collection and sorting of textiles remain challenges.
The textile recycling Industry is segmented into cotton, polyester, wool, polyamide, and others. The leading recyclers of cotton are those that recycle the cotton used for apparel and home textiles, as cotton is ubiquitous in these products, and is biodegradable and easy to process.
Polyester recycling is on the rise as it accounts for a large portion of fast fashion and can help combat a large source of plastic waste. Wool has niche but valuable recycling opportunities, because its durability and high-quality applications make it popular in luxury and winter wear. As strength and elasticity are essential, polyamide recycling is gaining traction as the most important Industry, especially in sportswear and automotive textiles.
The report segments the industry by source into apparel waste, home furnishing waste, automotive waste, and others. Apparel waste is the biggest segment, fueled by the fast-fashion Industry and consumers throwing away more clothes. Household textiles, including curtains and upholstery, have started to come under the spotlight due to the sheer volume of waste they create and their potential for reuse as construction and insulation materials.
The automotive segment, which includes things like seat covers and carpets, is growing as the auto Industry becomes more focused on sustainable practices. Niche recycling sources are available from other textiles, including industrial and medical textiles. The diversification in textile waste generation necessitates the need for customized recycling solutions that address these varied forms of textile waste.
Process-wise, the industry is segmented into mechanical and chemical recycling. The traditional method, mechanical recycling, involves shredding and re-spinning textiles into new fibers; this is cost-effective but cannot cope with blended fabrics. Chemical recycling is a new and disruptive technology that breaks textiles down into raw materials which can be used for high-grade fiber production, particularly for polyester and polyamide.
Both textile recycling and upcycling must address the complexity of textile waste. Chemical recycling service is expected to gain prominence due to its ability to process blended and synthetic materials. In fact, it is this Interconnection of those processes that will be important to scale up textile recycling and achieve Sustainability targets.
Indeed, the textile recycling Industry could reap huge benefits as it contributes to the demand for sustainable practices and increases demand for new business models based on circularity. Some of the biggest additional technological improvements are seen in how we recycle our unwanted textiles.
Chemical recycling in particular gives us the chance to be able to deal with blended & complex textiles. Greater capacity for collection and sorting infrastructure will expand opportunities to tap into untapped sources of post-consumer and post-industrial textile waste.
Industries that do use recycled content - such as fashion, automotive, and home furnishings - are increasingly committed to sourcing recycled materials, and this demand is expected to continue growing. Growth can be better accelerated by a joint camp of brands, recyclers, and government,s which can work on creating a standard recycling structure and combining sustainable incentives.
Based on the Industry observations, several strategies can be adopted by stakeholders in the textile recycling Industry for the advancement of their businesses, capitalizing the emerging growth opportunities. There needs to be a significant investment in advanced recycling technologies such as chemical and mechanical recycling, to enhance efficiency and scalability for complex/mixed textiles.
It also calls on governments and the private sector to help build the necessary collection and sorting infrastructure to treat rising volumes of textile waste effectively. Collaboration between brands, recyclers, and policymakers is essential for implementing standardized recycling frameworks and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs.
Stakeholders must expand to new sectors, especially in emerging economies such as Africa and Asia where textile consumption rates are rapidly growing. Advocacy for participation in recycling programs, alongside consumer education and awareness campaigns, will further encourage recycling amongst the population, which would in turn drive demand for sustainable products.
The textile recycling industry in the United States is expected to grow steadily due to increasing awareness of sustainability and government initiatives promoting circular economy practices. However, the country faces challenges such as high operational costs and a fragmented recycling infrastructure.
The demand for recycled textiles is rising, especially in the fashion and home furnishing sectors, driven by corporate sustainability goals. Investments in advanced sorting and processing technologies will help improve efficiency in the coming years.
FMI opines that the United States textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 2.8% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 1.29 billion by 2035.
The UK textile recycling industry is projected to witness moderate growth, supported by strong government policies and consumer preference for eco-friendly products. The rising demand for sustainable fashion, combined with stricter waste management regulations, will drive industry expansion.
Additionally, collaborations between fashion brands and recycling firms are expected to enhance the adoption of recycled fibers. Challenges such as inconsistent waste collection systems still exist but are being addressed through technological advancements.
FMI opines that the United Kingdom textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 2.9% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.26 billion by 2035.
Germany is expected to have one of the highest growth rates in the textile recycling industry due to its well-established waste management infrastructure and stringent environmental regulations. The country is a leader in circular economy initiatives, with strong support from both the government and private sector.
The adoption of advanced chemical recycling methods and AI-based textile sorting systems is further driving industry growth. Germany's high recycling rates and strong corporate commitments to sustainability will continue to drive industry growth.
FMI opines that Germany’s textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 3.5% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and are expected to reach USD 0.96 billion by 2035.
France is making significant progress in textile recycling, backed by stringent sustainability policies and extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs. The country has banned the destruction of unsold textiles, pushing brands to invest in recycling solutions. Increased funding for textile waste management and innovative fiber recovery techniques will boost industry growth. Increasing consumer awareness is further driving demand for recycled and upcycled clothing.
FMI opines that the France textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 3.4% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.80 billion by 2035.
Italy’s textile recycling industry is benefiting from the country’s strong fashion and textile industries, which are increasingly embracing sustainability. Luxury and fast fashion brands are incorporating recycled materials into their production processes, while government initiatives are encouraging the development of circular economy models. However, Challenges such as a fragmented recycling infrastructure and high costs remain, which necessitates increased investment in technology and logistics by industry stakeholders.
FMI opines that the Italy textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 3.1% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.66 billion by 2035.
Australia and New Zealand are witnessing a gradual shift towards textile recycling, driven by government regulations and consumer demand for sustainable fashion. Both countries are investing in textile recovery programs and partnerships between fashion brands and recycling firms. However, logistical challenges due to their geographic location and lack of large-scale infrastructure may limit growth. Increased innovation in fiber recycling technologies is expected to improve industry prospects.
FMI opines that the Australia & New Zealand textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 2.7% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.32 billion by 2035.
China is emerging as a major player in the textile recycling Industry, supported by strong government policies aimed at reducing textile waste. The country’s vast manufacturing sector is integrating recycled materials into production, and advanced recycling technologies are being rapidly adopted.
Additionally, growing environmental awareness among consumers and stricter waste management regulations are accelerating Industry growth. Despite challenges like illegal textile waste dumping, increased investments in sustainable practices are expected to drive significant progress.
FMI opines that the China textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 3.8% a CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 1.49 billion by 2035.
South Korea’s textile recycling Industry is expanding as the country implements stricter sustainability regulations and promotes circular economy initiatives. Advanced textile processing technologies and AI-driven waste sorting systems are enhancing recycling efficiency.
Additionally, fashion brands are increasingly using recycled fibers, supported by government incentives. One of the key challenges is the high cost of textile collection and processing. Continued investment in research and development will be crucial for industry expansion.
FMI opines that South Korea's textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 3.6% CAGR from 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.37 billion by 2035.
Japan’s textile recycling industry is progressing steadily, driven by strong environmental consciousness and government-led sustainability initiatives. The country has a well-developed recycling infrastructure, but the adoption of textile recycling in mainstream fashion remains slow.
Traditional waste disposal methods still dominate, limiting the growth of textile recycling in Japan. However, rising interest in circular fashion and new developments in fiber-to-fiber recycling technology could help accelerate industry adoption in the long run.
FMI opines that the Japanese textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 2.9% CAGR from 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 1.28 billion by 2035.
The textile recycling market in India is well-positioned to grow significantly, fueled by increasing awareness of sustainability. India has prioritized circular economy and waste management initiatives due to the substantial amount of textile waste it generates annually from both domestic consumption and export production. With the government encouraging EPR in textiles and organized collection of textile waste systems, the market is witnessing substantial progress.
Finally, the development and acceleration of new fiber-to-fiber recycling technologies, particularly for cotton and polyester, are underway. Several startups and established players are working on mechanical and chemical recycling processes to transform textile waste into reusable fiber. Despite these challenges, collaborations between fashion brands, recyclers, and policymakers are helping steer the industry back on course.
FMI opines that the Indian textile recycling sales will grow at nearly 4.0% CAGR through 2025 to 2035 and is expected to reach USD 0.53 billion by 2035.
Textile recycling helps reduce landfill waste, conserves natural resources, lowers carbon emissions, and supports a circular economy by reusing materials for new products.
Commonly recycled materials include cotton, polyester, wool, polyamide, and blended fabrics. Advanced technologies also enable the recycling of synthetic fibers.
Challenges include high processing costs, contamination of materials, limited infrastructure, and difficulties in sorting blended fabrics for efficient recycling.
Mechanical recycling shreds and reprocesses textiles without altering their structure, while chemical recycling breaks fibers down into raw materials for higher-quality reuse.
Industries such as fashion, home furnishings, automotive, and sportswear benefit from textile recycling by incorporating sustainable materials into their products.
Precipitation Hardening Market Report - Demand, Growth & Industry Outlook 2025 to 2035
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) Market Growth - Innovations, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Sodium Bicarbonate Market Report - Demand, Growth & Industry Outlook 2025 to 2035
Plywood Market Growth - Innovations, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Phenylethyl Market Growth - Innovations, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
PP Homopolymer Market Report - Demand, Growth & Industry Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.