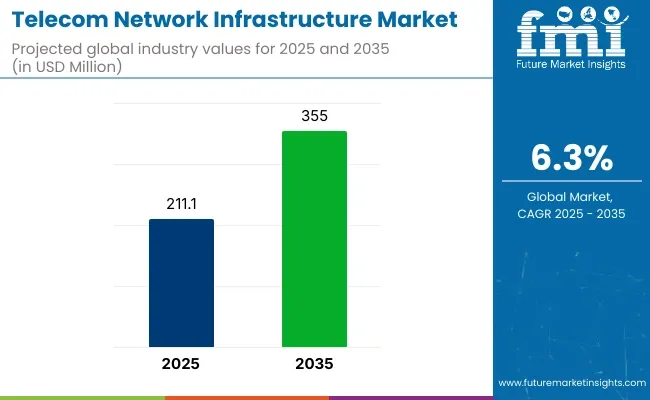
The telecom network infrastructure market is estimated to generate a market size of USD 211.10 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 355.00 billion by 2035, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% during the forecast period.
This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for high-speed internet connectivity, the ongoing rollout of 5G networks, and the rising need for robust infrastructure to support data-intensive applications. Telecom network infrastructure includes various components such as routers, switches, antennas, base stations, and fiber optic cables that are essential to ensure the efficient functioning of communication networks worldwide.
A key driver of the market's growth is the rapid deployment of 5G networks, which require the upgrade and expansion of existing telecom infrastructure. 5G technology promises to deliver faster data speeds, low latency, and higher capacity, which are crucial for emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and smart cities. The global race to build 5G networks has spurred significant investments in telecom network infrastructure, particularly in regions with high demand for next-generation communication capabilities.
Recent developments in the telecom network infrastructure market reflect a growing focus on upgrading legacy systems and adopting new technologies. Telecom companies are increasingly investing in fiber optic networks, small cells, and distributed antenna systems (DAS) to enhance network coverage and capacity. Additionally, the deployment of edge computing, which brings data processing closer to end-users, is improving network efficiency and enabling faster delivery of services.
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 211.10 Billion |
| Market Size in 2035 | USD 355.00 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.3% |
On June 12, 2025, Ericsson introduced Ericsson On-Demand, a groundbreaking 5G core network platform offered as a true SaaS service, developed in collaboration with Google Cloud-as per Ericsson’s press release . This solution enables communication service providers to deploy full core networks in minutes, scale elastically on-demand, and transition from upfront capex to consumption-based billing.
It integrates AI-enabled operations, 24/7 SRE support, and cloud-native reliability across global Google Cloud regions. “A radical step-change in agility and efficiency,” stated Ericsson’s press release, underscoring a new paradigm in telecom infrastructure management. This service positions Ericsson at the forefront of cloud-native, on-demand telecom deployment.
As the demand for high-speed connectivity continues to increase and new technologies such as 5G and IoT become more prevalent, the telecom network infrastructure market is expected to experience sustained growth. Ongoing advancements in network design, efficiency, and scalability will play a critical role in shaping the future of telecom infrastructure.
Leading telecom infrastructure companies are integrating smart technologies such as AI-based network management, edge computing, software-defined networking (SDN), and 5G automation to improve network performance, scalability, and reliability. These innovations are transforming global connectivity across consumer, enterprise, and industrial applications.
Huawei Technologies:
Huawei integrates AI, machine learning, and autonomous network operations into its telecom infrastructure. Its "Autonomous Driving Network" initiative enables self-optimizing and self-healing networks. The company is also a key player in 5G core and RAN (Radio Access Network) deployments, offering end-to-end smart infrastructure solutions.
Ericsson:
Ericsson uses AI and automation in its intelligent RAN systems and dynamic spectrum sharing technologies. It offers cloud-native 5G core solutions and leverages machine learning for real-time network traffic optimization, predictive maintenance, and energy efficiency improvements in telecom infrastructure.
Nokia:
Nokia incorporates AI and analytics into its "Cognitive Networking" approach, enabling automated network slicing and dynamic traffic management. Its Digital Operations Center offers smart orchestration and assurance for 5G networks, supporting cloud, edge, and IoT deployments.
Cisco Systems:
Cisco deploys smart technologies through software-defined networking (SDN), network function virtualization (NFV), and AI-based telemetry. Its "Crosswork Network Automation" platform enables closed-loop automation, real-time analytics, and intent-based networking across multi-domain telecom infrastructures.
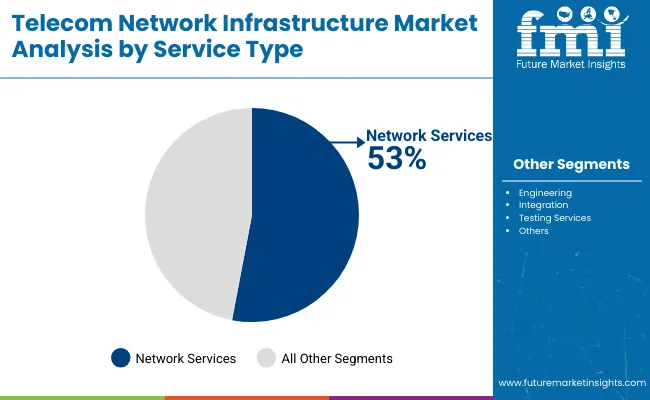
Telecom network infrastructure is widely used for network services due to its extensive coverage, reliability, and scalability. It provides the backbone for voice, data, and internet communications, supporting both wired and wireless technologies.
With established infrastructure like fiber optics, cellular towers, and satellite links, telecom networks enable high-speed connectivity across urban and rural areas. Their ability to handle large volumes of data traffic ensures seamless service delivery for businesses and consumers alike.
Additionally, telecom providers offer consistent maintenance, security, and upgrades, making them a dependable choice for delivering essential network services in today's connected world.
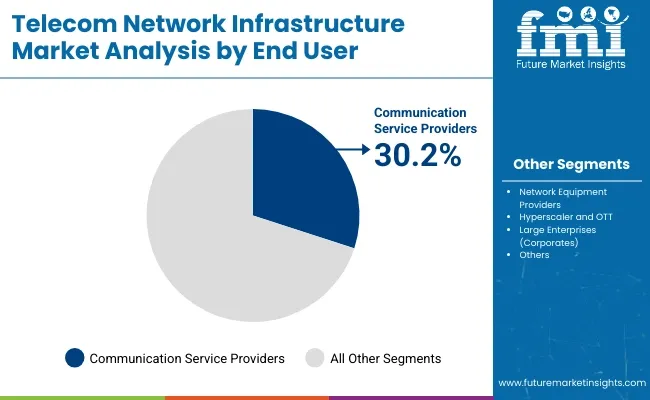
Communication service providers are major end users of telecom network infrastructure because they depend on it to deliver essential services such as internet access, voice communication, messaging, and video streaming.
They use components like fiber optic networks, mobile towers, routers, and data centers to ensure fast, reliable, and wide-reaching connectivity. This infrastructure supports the transmission of large volumes of data across long distances, enabling providers to meet growing customer demands.
By leveraging telecom infrastructure, communication service providers can offer high-quality services, expand into new markets, and maintain strong network performance, which is critical in a digitally connected world.
| Company | Nokia and AT&T |
|---|---|
| Contract/Development Details | Signed a multi-year expansion agreement to upgrade AT&T's voice carriage and 5G network automation in the USA, enabling new 5G functionalities, AI, and machine learning capabilities for voice services. |
| Date | February 2025 |
| Contract Value (USD Million) | USD 3,400 |
| Renewal Period | Multi-year |
| Company | Nokia and Deutsche Telekom |
|---|---|
| Contract/Development Details | Secured a contract to deploy a mobile network using Open Radio Access Network (ORAN) technology across more than 3,000 sites in Germany, replacing existing equipment from Huawei. |
| Date | November 2024 |
| Contract Value (USD Million) | USD 2,432 |
| Renewal Period | Multi-year |
| Company | Bharti Airtel and Ericsson |
|---|---|
| Contract/Development Details | Entered a multi-billion dollar agreement to enhance 4G and 5G coverage in India, deploying centralized radio access network (RAN) and Open RAN-ready solutions. |
| Date | December 2024 |
| Contract Value (USD Million) | USD 6,423 |
| Renewal Period | Multi-year |
Increasing investments in 5G infrastructure drive telecom network upgrades
World-wide telecom sector is undergoing a transformation with major money activity in 5G infrastructure and network evolution, making it a perfect match for growth propulsion. 5Gs critical role in economic development and technological innovation has not escaped the attention of Governments worldwide. For example, based on estimates, the 5G economy will add USD 1.4 trillion to USD 1.7 trillion to America’s GDP by 2030, creating around 3.8 to 4.6 million jobs in the same period.
Such expected growth has emphasized the need for strong 5G infrastructure investments. On the other hand, China also has impressive achievements with 5G base stations, which had exceeded 2.3 million by the end of 2022 and demonstrated the country's efforts in fast-tracking 5G installations. They will not only be made in urban centers; we will also target rural and underserved areas to bridge the digital divide.
Adoption of SDN and NFV reduces costs and improves scalability
As networks become more complex, the telecommunications industry is adopting Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) to improve operational efficiency and scalability. RFC 7929 defines how to delegate an administrative validation Key Management Order (KMO) to a new Key Management Entity (KME). SDN and NFV can help telecom operators in reducing the capital expenditure incurred in setting up hardware-centric networks and also reduce operational costs through automated network management.
This change helps with deploying new services quickly, and enhances the ability to scale network resources according to varying demand. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic has made remote work and online activities become commonplace; enterprise networks need to keep pace with traffic growth, and it would be easier to adapt to changes with SDN and NFV. On top of that, these technologies allow for the convergence of the emerging services of edge computing and network slicing, which would be essential to enable the nailing of diverse 5G applications.
Integration of satellite connectivity for remote and rural areas
The penetration and growth of telecom and telecommunication satellite system and broadband internet satellite are very desirable, as it combines both satellite connectivity into existing infrastructure. In these regions, traditional terrestrial networks can often suffer from economic and logistical challenges, resulting in digital divides. Recent advances in satellite technology, particularly Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites, have made high-speed, low-latency internet services now capable of reaching underserved communities.
Satellite communications, for example, have already begun deploying gigabit-capable speeds at a price point that is competitive with terrestrial providers across the United Kingdom through various initiatives.
Touted as a first-of-a-kind solution, the Nomadic Multi-orbit User Terminal Demonstrator would be a portable capable of receiving signals from multiple LEO and geostationary orbit (GEO) satellites to provide a carrier-grade broadband service. In Australia, the government is also investigating the capability of combining satellite technologies to deliver mobile voice and SMS services across Australia, particularly during disasters.
Increasing cyberattacks on telecom networks raise security concerns
Telecom network infrastructure is being targeted more and more by cyberattacks, with potentially devastating impacts to global communications. As networks evolve with the introduction of 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud integration, the attack surface expands and telecom operators become more susceptible to sophisticated cyber-attacks.
"Cybercriminals are leveraging gaps in network protocols, cloud-based services, and connected devices to bring down operations, steal sensitive information, or execute large scale DDoS attacks. Telecom networks provide the physical infrastructure for essential services such as emergency services, financial systems, and government communications. A single breach can cause widespread disruptions, impacting millions of users and leading to economic loss.
As state-sponsored cyber warfare rises, telecom networks have become prime targets for the espionage, and sabotage. Nation-state actors and cybercriminal organizations target the networks to intercept communications, alter data traffic, or implant malware that can disrupt the integrity of the network.
Tier 1 vendor are market leaders in telecom network infrastructure with their global reach, large product portfolio, and mature technology. At its heart are dozens of companies, such as telecom equipment vendors and services providers, which provide unified telecom infrastructure, core network equipment or end-to-end radio access networks (RAN) or optical transport or cloud-based network management systems.
They have solid relationships with large telecom providers and governmental organizations that allow them to win contracts for large masses. Their financial robustness enables them to invest heavily in research and development, which results in consistent innovation around 5G, cloud-native automation, and software-defined networking (SDN). These vendors also play an important role in global telecom standards and regulations, leading to a high level of deployment of their technologies.
Tier 2 vendors have a solid regional footprint and focus in one or more area of telecom network infrastructure. While their global presence may not reach the scale of the Tier 1 vendors, their influence on particular technology segments like small cell rollout, private 5G networks, and software-oriented infrastructure is far-reaching.
Many of these companies work with telecom carriers to deliver customized solutions to meet regional demand. Other Tier 2 vendors target specific geographic markets, and others are focused on new technologies like Open RAN to help telecom operators diversify their supply chain. Vendors that compete with Tier 1 players on niche offerings usually offer low-cost, flexible solutions.
Tier 3 vendors are generally smaller companies that concentrate on local or specific telecom infrastructure solutions. Typically, these companies build network parts, software programs, or integration services that help complement the services of bigger suppliers.
They act as a catalyst for innovation, leading the way in emerging technologies such as IoT connectivity, network security, and edge computing, creating huge value. Tier 3 vendors often serve particular industry verticals or regional telecom operators that need tailored networking infrastructure solutions. Although they have difficulties to achieve economies of scale on their own, they can grow their market share through partnerships with larger vendors or telecom operators.
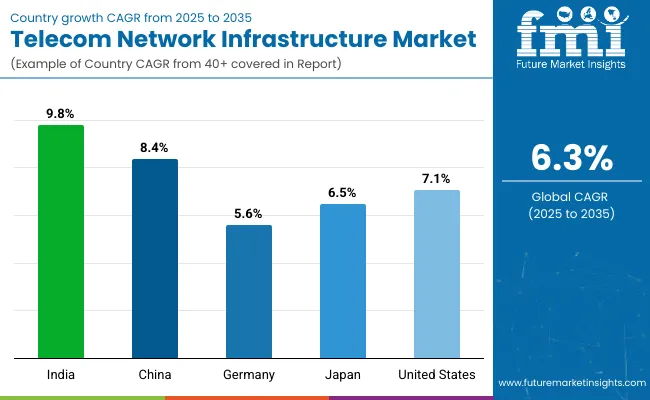
The section highlights the CAGRs of countries experiencing growth in the Telecom Network Infrastructure market, along with the latest advancements contributing to overall market development. Based on current estimates China, India and USA are expected to see steady growth during the forecast period.
| Countries | CAGR from 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| India | 9.8% |
| China | 8.4% |
| Germany | 5.6% |
| Japan | 6.5% |
| United States | 7.1% |
India has seen record-breaking growth in mobile data consumption, fueled by affordable data plans, increased smartphone penetration, and digital transformation initiatives. The rapid growth of video streaming, online gaming, and web-based applications has put unprecedented stress on existing telecom networks, leading operators to scale out and upgrade their backbone. In response, telecom companies are quickly rolling out more spectrum, growing fiber-optic networks, and improving 4G and 5G coverage to accommodate the massive number of users.
In India, government initiatives like Digital India and BharatNet are speeding up the network expansion across rural and semi-urban populations. Apart from this, as the government drives towards better internet connectivity and bringing down the digital gap by implementing more internet linking programs, data consumption is only going to increase.
Also, the continuous deployment of 5G services is likely to improve the network performance, and provide faster speeds offering lower latency to both consumer and enterprise customers. India is anticipated to see substantial growth at a CAGR 9.8% from 2025 to 2035 in the Telecom Network Infrastructure market.
Private 5G networks are gaining traction in the United States, providing enterprises with more control, security, and efficiency over their connectivity needs. Private networks, unlike public 5G networks, give individual users exclusive access to bandwidth and low-latency communication, which are ideal for sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and health care. To improve operational efficiencies, faster automation and real-time data processing many organizations are leveraging private 5G solutions.
The USA government has already begun facilitating the deployment of private 5G networks with allocated spectrum as well as policy backing. All types of businesses, from smart factories to airports to hospitals, are deploying private 5G networks to streamline their operations. Private networks are also anticipated to facilitate improvements across the various sectors for autonomous vehicles, robotics, and industrial internet of things applications. USA Telecom Network Infrastructure market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR 7.1% during this period.
Telecommunications network modernization has become a critical component of China’s digital transformation strategy. The government has also been investing heavily in 5G infrastructure, the expansion of fiber-optic networks, and smart city projects. In October 2023, the 5G network was underpinned by new developments, which drive connectivity, assist industrial automation and promote innovation in sectors. In turn, China has created the world’s largest 5G network, providing widespread coverage in urban and rural areas.
There was coverage of projects backed by the government that sped up the deployment of next-generation telecom technology such as AI network management and edge computing. Not just for consumer connectivity but also for forming industrial applications like smart manufacturing, autonomous transport, and AI-powered analytics.
With ongoing support from policymakers, telecom operators are expanding their infrastructure to satisfy the demand for high-speed, low-latency communication. Telecom Network Infrastructure market in China accounts for 43.4% of global market share and continues to grow at a high CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
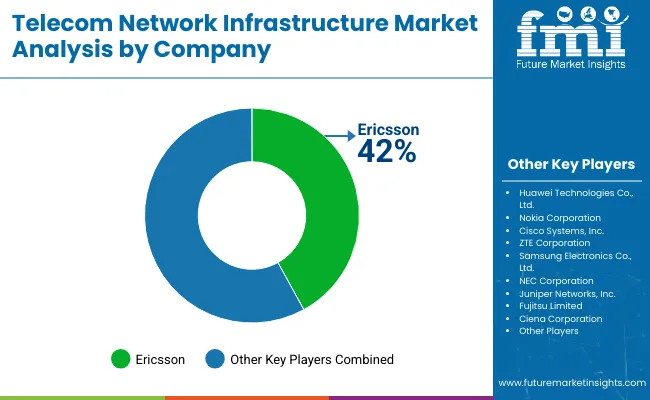
The telecom network infrastructure industry faced intense competition with continuous technological developments and changing consumer demands. In 5G, fiber optics, and cloud-based networking, innovation, scalability, and cost-efficiency are key focus areas for companies to differentiate offerings.
Expanding market presence and technology via strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions Heightening government regulations and cybersecurity threats create complexities, leading enterprises to upgrade their security and compliance infrastructure.
| Report Attributes | Details |
|---|---|
| Current Total Market Size (2025) | USD 211.10 billion |
| Projected Market Size (2035) | USD 355.00 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.3% |
| Base Year for Estimation | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2020 to 2024 |
| Projections Period | 2025 to 2035 |
| Quantitative Units | USD million for value |
| Service Types Analyzed (Segment 1) | Network Services, Engineering, Integration & Testing Services |
| End Users Covered (Segment 2) | Telecom Operators, Communication Service Providers, Network Equipment Providers, Hyperscalers & OTT, Large Enterprises, Content Delivery Networks, Government, Others |
| Regions Covered | North America; Latin America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Middle East & Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, China, Germany, India, Japan, UK, Brazil, South Korea |
| Key Players Influencing the Market | Huawei, Nokia, Ericsson, Cisco Systems, ZTE, Samsung Electronics, NEC, Juniper Networks, Fujitsu, Ciena Corporation |
| Additional Attributes | Dollar sales by service type and end user, government funding impact, 5G and fiber deployment trends, CSP market dominance, innovation in SDN and cloud networks |
In terms of Service Type, the segment is divided into Network Services and Engineering, Integration and Testing Services.
In terms of end user, the segment is segregated into Telecom Operators, Communication Service Providers, Network Equipment Providers, Hyperscaler and OTT, Large Enterprises (Corporates), Content Delivery Networks, Government and Others.
A regional analysis has been carried out in key countries of North America, Latin America, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, Western Europe, Eastern Europe and Middle East and Africa (MEA), and Europe.
The Global Telecom Network Infrastructure industry is projected to witness CAGR of 6.3% between 2025 and 2035.
The Global Telecom Network Infrastructure industry stood at USD 211.10 billion in 2025.
The Global Telecom Network Infrastructure industry is anticipated to reach USD 355.00 billion by 2035 end.
South Asia & Pacific is set to record the highest CAGR of 8.1% in the assessment period.
The key players operating in the Global Telecom Network Infrastructure Industry Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Nokia Corporation, Ericsson, Cisco Systems, Inc., ZTE Corporation, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., NEC Corporation, Juniper Networks, Inc., Fujitsu Limited, Ciena Corporation.
Figure 1: Global Market Value (USD Million) by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 2: Global Market Value (USD Million) by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 3: Global Market Value (USD Million) by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 4: Global Market Value (USD Million) by Region, 2025 to 2035
Figure 5: Global Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Region, 2020 to 2035
Figure 6: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2025 to 2035
Figure 7: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2025 to 2035
Figure 8: Global Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Component, 2020 to 2035
Figure 9: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 10: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 11: Global Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Type, 2020 to 2035
Figure 12: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 13: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 14: Global Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by End-Use , 2020 to 2035
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 17: Global Market Attractiveness by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 18: Global Market Attractiveness by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 19: Global Market Attractiveness by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 20: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2025 to 2035
Figure 21: North America Market Value (USD Million) by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 22: North America Market Value (USD Million) by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 23: North America Market Value (USD Million) by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 24: North America Market Value (USD Million) by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 25: North America Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Country, 2020 to 2035
Figure 26: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 27: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 28: North America Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Component, 2020 to 2035
Figure 29: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 30: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 31: North America Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Type, 2020 to 2035
Figure 32: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 33: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 34: North America Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by End-Use , 2020 to 2035
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 37: North America Market Attractiveness by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 38: North America Market Attractiveness by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 39: North America Market Attractiveness by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 40: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 41: Latin America Market Value (USD Million) by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 42: Latin America Market Value (USD Million) by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 43: Latin America Market Value (USD Million) by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 44: Latin America Market Value (USD Million) by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 45: Latin America Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Country, 2020 to 2035
Figure 46: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 47: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 48: Latin America Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Component, 2020 to 2035
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 50: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Type, 2020 to 2035
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 53: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 54: Latin America Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by End-Use , 2020 to 2035
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 57: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 58: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 59: Latin America Market Attractiveness by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 60: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 61: Europe Market Value (USD Million) by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 62: Europe Market Value (USD Million) by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 63: Europe Market Value (USD Million) by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 64: Europe Market Value (USD Million) by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 65: Europe Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Country, 2020 to 2035
Figure 66: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 67: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 68: Europe Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Component, 2020 to 2035
Figure 69: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 70: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 71: Europe Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Type, 2020 to 2035
Figure 72: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 73: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 74: Europe Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by End-Use , 2020 to 2035
Figure 75: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 76: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 77: Europe Market Attractiveness by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 78: Europe Market Attractiveness by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 79: Europe Market Attractiveness by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 80: Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 81: South Asia Market Value (USD Million) by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 82: South Asia Market Value (USD Million) by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 83: South Asia Market Value (USD Million) by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 84: South Asia Market Value (USD Million) by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 85: South Asia Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Country, 2020 to 2035
Figure 86: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 87: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 88: South Asia Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Component, 2020 to 2035
Figure 89: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 90: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 91: South Asia Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Type, 2020 to 2035
Figure 92: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 93: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 94: South Asia Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by End-Use , 2020 to 2035
Figure 95: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 96: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 97: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 98: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 99: South Asia Market Attractiveness by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 100: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 101: East Asia Market Value (USD Million) by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 102: East Asia Market Value (USD Million) by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 103: East Asia Market Value (USD Million) by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 104: East Asia Market Value (USD Million) by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 105: East Asia Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Country, 2020 to 2035
Figure 106: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 107: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 108: East Asia Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Component, 2020 to 2035
Figure 109: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 110: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 111: East Asia Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Type, 2020 to 2035
Figure 112: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 113: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 114: East Asia Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by End-Use , 2020 to 2035
Figure 115: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 116: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 117: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 118: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 119: East Asia Market Attractiveness by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 120: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 121: Oceania Market Value (USD Million) by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 122: Oceania Market Value (USD Million) by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 123: Oceania Market Value (USD Million) by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 124: Oceania Market Value (USD Million) by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 125: Oceania Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Country, 2020 to 2035
Figure 126: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 127: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 128: Oceania Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Component, 2020 to 2035
Figure 129: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 130: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 131: Oceania Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Type, 2020 to 2035
Figure 132: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 133: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 134: Oceania Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by End-Use , 2020 to 2035
Figure 135: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 136: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 137: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 138: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 139: Oceania Market Attractiveness by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 140: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 141: MEA Market Value (USD Million) by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 142: MEA Market Value (USD Million) by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 143: MEA Market Value (USD Million) by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 144: MEA Market Value (USD Million) by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 145: MEA Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Country, 2020 to 2035
Figure 146: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 147: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2025 to 2035
Figure 148: MEA Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Component, 2020 to 2035
Figure 149: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 150: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 151: MEA Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by Type, 2020 to 2035
Figure 152: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 153: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 154: MEA Market Value (USD Million) Analysis by End-Use , 2020 to 2035
Figure 155: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 156: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 157: MEA Market Attractiveness by Component, 2025 to 2035
Figure 158: MEA Market Attractiveness by Type, 2025 to 2035
Figure 159: MEA Market Attractiveness by End-Use , 2025 to 2035
Figure 160: MEA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2025 to 2035






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Telecom Tower Power System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Mounting Hardware Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Billing And Revenue Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Testing Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Analytics Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Internet Of Things (IoT) Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Tower Power System Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Generator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Power Rental Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Millimeter Wave Technology Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
telecom-expense-management-market-market-value-analysis
Telecom Order Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Cloud Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Power Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Wireless Data Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Telecom Managed Service Market Trends - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Telecommunications Services Market - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Telecom Enterprise Services Market Analysis - Growth & Forecast through 2034
Telecom Service Assurance Market Trends – Size, Demand & Forecast 2023-2033

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA