Solar district heating will experience a significant growth during the period from 2025 to 2035 primarily due to increased use of renewable sources the distributed grid is heating. The government's pledge to green infrastructure and the improvements received in solar thermal technology would represent the key factors for the market's expansion.
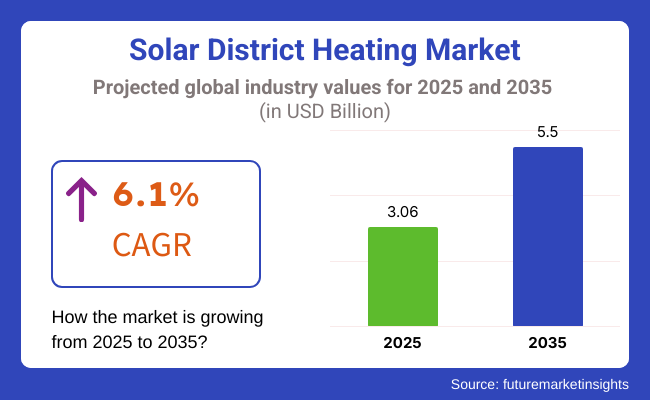
The market is expected to be valued at USD 3.06 billion in 2025 and will go up to about USD 5.5 billion in 2035, which corresponds to a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1%. Solar district heating (SDH) systems draw resources from large solar thermal collectors that are employed for production and distribution of heating energy for residential, commercial buildings and industries, thereby, promoting a reduction of carbon emissions and consequently the reliance on fossil fuels.
In addition to the stringent energy efficiency regulations, the growing financial investments in green infrastructure, and the soaring energy prices that have reached new records, the peak demand for solar-assisted centralized heating is due to all these factors. The major missions of changing the way energy is heated, and the demand for urban heat in the transition to energy sovereignty are power sources for the market.
The establishment of the solar central heat plants, thermal storage systems, and distribution networks requires the mobilization of significant capital, which can be the main liability after price-sensitive markets. Also, the integration of SDH with the already existing district heating needs regulatory approval, political support, and financing.
Public-private collaborations (PPPs) and new funding projects have been carried out to enhance SDH systems' accessibility and affordability. The thermal energy storage (TES) technology development also stands to bolster the market further because it brings seasonal heat storage whereby extra heat collected during summertime can be used during the winter.
Underground thermal energy storage (UTES) and major storage tanks are not only boosting the reliability of the system but also enhance system performance. Additionally, the SDH setup with digital monitoring, AI-based heat demand forecasting, and smart grid solutions is delivering the optimized system functionality which can lower the operational cost.
With the focus on carbon-neutral heating in urban areas, many cities have started promoting SDH which is, of course, a sustainable heating alternative to coal and gas heating especially in crowded population areas. The governments along with the utilities are pushing the green contracts, tightening the building code, and increasing the clean heating subsidies.
The advancement of solar thermal efficiency, regulatory support, and investment in energy efficiency urban planning are believed to be the three driving forces that will facilitate the fast-tracked market growth over the coming decade.
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
Between 2020 and 2024, the solar district heating (SDH) market grew natably. Some key reasons are rising investments in renewable energy, government subsidies for decarbonization, and thermal energy storage innovations. Demand for low-carbon urban heating systems fueled the growth of large-scale solar thermal plants coupled with district heating networks. Europe, China, and North America dominated SDH uptake through solar collectors that are efficient.
Nonetheless, these issues like solar resource fluctuation, heavy costs while starting, and land scarcity prevented its wide use. Between 2025 and 2035, the SDH market will progress as AI gets used in solar management. Work is being put into developing high-temperature thermal storage tanks, and hybrid solar integration of wind and thermal energy.
Predictive energy dispatch through AI will maximize grid-smart heating networks to deliver efficient energy distribution. Modular and decentralized SDH systems will make it penetrate urban and rural communities. With governments tightening carbon reduction policies, SDH will emerge as a key element in global sustainable district energy solutions.
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Governments supplemented clean heating legislation and carbon price support for phasing out coal- and gas-based district heating. | Increased climate policy calls for comprehensive decarbonisation of district heating systems, accelerating solar district heating power plant investment with thermal storage. Development of heat-as-a-service (HaaS) business models. |
| SDH stations increasingly became linked with district heating networks in Scandinavia, Germany, and China to reduce natural gas dependency. | Sector coupling between electric heat pumps, green hydrogen production, and solar district heating on a full scale makes 100% renewable urban heating possible. |
| Solar heat duration beyond sun peak hours was made possible through hot water tanks and underground thermal energy storage (UTES). | Use of PCMs and molten salt heat storage improves efficiency for seasonal heat storage, rendering SDH economically attractive even in low-climate locations. |
| Solar thermal systems frequently included supplemental reserve heating based on biomass or gas combustion for provision through the winter period. | Large-scale hybrid SDH is coupled with heat pumps, excess wind/solar power electricity, and backup systems that can operate using hydrogen. |
| Idea-level IoT-based monitoring facilities made the SDH plants more efficient at an improved reduced operation cost. | Artificial intelligence-based heat demand prediction, block chain-based energy monitoring, and real-time grid balancing maximize energy dispatch and cost-effectiveness. |
| Urban areas and industrial parks increasingly utilized SDH in order to reduce heating emissions. Fossil-fuel-fired heat reserve was employed in some locations. | Smart city district heating expansion with smart metering, AI-optimized heat dispatch, and decentralized thermal micro grids optimizes urban heating efficiency. |
| High land values and solar collector costs limited project size in some locations. Governments provided grants and subsidies to expand SDH. | Modular and prefabricated SDH systems, low-cost vacuum tube collectors, and rooftop solar thermal collectors with space-saving designs improve affordability and ease of deployment. |
| Governments implemented clean heating regulations and carbon pricing policies to phase out district heating based on coal and gas. | Market expansion driven by net-zero heating ambitions, AI-powered energy systems, and hybrid renewable district heating networks. Higher adoption of hydrogen-compatible solar heating grids. |
In district heating systems, solar thermal can collaborate instead of competing with other renewable technologies. One method that is proving to be effective is to integrate solar heat with biomass or biogas boilers where solar arrays generate heat when the sun shines, decreasing the use of biomass fuels and decreasing air pollution.
Biomass, in turn, becomes a backup during cloudy spells or peak winter demand. In another synergy-large-scale heat pumps and electric boilers-solar heat is utilized first when available, and a heat pump uses surplus wind or off-peak electricity when solar output is low. This integration allows thermal networks to act as a storage facility and balancing agent for the grid, thus helping stabilize renewable energy supply.
Solar thermal can also be combined with industrial waste heat, resulting in hybrid district heating networks that integrate multiple RE sources. (Now, some European towns are operating networks powered almost entirely by solar, biomass, geothermal and heat pumps, substantiating the possibility of all-renewable heating.)
Another major opportunity is to expand district heating infrastructure. Many cities design new networks or upgrade fossil-based systems among sustainability goals. These new-age networks are designed for enhanced renewable integration, with modular low-temperature designs. Many municipalities in Europe are preparing or building solar district heating projects, and interest is increasing in North America and Asia.
| Category | Investment Level |
|---|---|
| European Union (EU) | High |
| Germany (BEW fund, €3 billion through 2026) | High |
| France (Newheat and other private investors) | High |
| China (Large-scale installations, government push) | High |
| Middle East (Saudi Arabia’s large solar heating plant) | Medium |
| North America (Slow uptake, early pilot projects) | Low |
The USA is witnessing development of gigantic-scale renewable heat schemes with increasing urbanization and energy-efficient infrastructure requirements. Public policies and incentives have led to paradigm shifts in clean energy.
Solar collector efficiency and affordability have also become better with enhanced efficiency and reduced costs. As demand for green heat continues to grow, most residential and commercial properties are switching to green energy solutions with the vision of ending the use of fossil fuels and reducing carbon footprints.
Growth Factors in The USA
| Growth Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Urbanization | Rapid urban growth necessitates efficient and sustainable heating solutions. |
| Government Initiatives | Policies supporting renewable energy adoption bolster market expansion. |
| Technological Advancements | Innovations in solar thermal technologies enhance system efficiency. |
UK focuses its efforts on developing sustainable heat networks to meet its ambitious climate neutrality goals. The government helps finance the rollout of renewable heat mass-scale networks through grants and funding programs.
Solar solutions are being integrated into more residential and commercial schemes on the premise of reducing the application of gas boilers. Public education about the virtues of renewable energy is also making the market pull.
Growth Factors in The UK
| Growth Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Government Support | Initiatives offering grants and affordable loans for solar installations encourage adoption. |
| Environmental Goals | Commitment to reducing carbon emissions drives the shift towards renewable heating solutions. |
| Public Awareness | Increased awareness of sustainable energy benefits fuels market demand. |
Germany paces the world in renewable heat with strong environmental policy and advanced clean energy infrastructure to back it. Cutting-edge carbon emissions policy and aggressive climate policy have seen robust investment in solar-thermal technology. Business leadership in collector efficiency and energy storage devices drives growth in residential, commercial, and municipal markets.
Growth factors in Germany
| Growth Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Environmental Policies | Strict regulations on carbon emissions promote the adoption of solar-based heating systems. |
| Technological Leadership | Advances in solar thermal technologies position Germany as a market leader. |
| Public Awareness | Growing recognition of environmental benefits and increase demand for sustainable heating solutions. |
Japan is increasingly turning to renewable sources of heat in a wide-ranging policy to reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels. Japan's dense, high-density urban development facilitates centralized heating schemes with energy efficiency in consumption and heat supply.
Research in advanced solar energy integration and new heat storage technology is driving overall improvement in efficiency. Growing focus on energy security and sustainability will convert into investment expansion in large-scale heating schemes over the next two years.
Growth Factors in Japan
| Growth Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Energy Security | Efforts to reduce dependence on fuels drive the adoption of renewable energy sources. |
| Urban Development | High-density urban areas benefit from centralized heating systems. |
| Technological Innovation | Continuous innovation in solar energy technologies enhance performance. |
Australia's vast solar resources are a suitable market for large thermal power systems. The government's attempts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have developed policy support and financing prospects for renewable heat projects.
Solar-heating networks are emerging as a viable alternative in industrial, commercial, and residential areas because of high energy requirements and long-term approach towards sustainability. More attention given to decarburization would tend to favor momentum in utilization of new thermal storage technologies within the next couple of years.
Growth Factors in Australia
| Growth Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Abundant Solar Resources | Australia’s High solar irradiance levels make thermal-based heating highly efficient. |
| Government Policies | Supportive regulations and incentives encourage the adoption of renewable energy solutions. |
| Sustainability Goals | National commitments to reducing greenhouse gas emissions drive market growth. |
This type of solar district heating is growing, especially in locations that experience variable solar irradiation over the course of the year. These Hybrid systems incorporate solar thermal energy as well as conventional heating sources such as biomass, natural gas, or waste heat recovery, which gives us the ability to provide heating without interruption even when solar energy availability is decreased.
Hybrid systems are extensively adopted in commercial and industrial continue to provide operational efficiency while helping to reduce energy costs. They also help diversify energy sources and support initiatives addressing climate change by integrating energy storage and smart grid technology that increases system resilience.
This element makes such layouts particularly advantageous for hybrid adoption in well-patterned new smart cities or mixed-use areas, where energy demand can be quickly scaled up and down as energy needs vary throughout the day.
Centralized solar district heating is the highest one in the market share; it is cheap and makes larger heating possible. These systems concentrate solar thermal energy at a central plant and deliver via an insulated pipeline network to residential, commercial and industrial end-users.
Centralized systems (which offer high efficiency, low carbon emissions, and which can be complemented with other renewable energy resources such as biomass and geothermal energy) are more favorable in terms of government and municipal decision-making.
Countries with strong sustainability commitments and cold climates, such as Germany, Denmark, and Sweden are the early adopters of centralized solar district heating systems. Utility providers and urban planners advocate for these systems for their potential to cut fossil fuel reliance, air pollution, and operational costs for end-users. Centralized systems also harness advanced energy storage, maintaining heat supply during intervals lacking solar radiation, contributing to their preferred global status.
The largest potential demand in the solar district heating market stems from the residential sector. Growing environmental concerns and interest in renewable energy have resulted the adoption of solar-based systems in apartment complexes and housing communities. As part of this effort, governments are promoting solar water heaters and integrating solar thermal energy into district heating networks to diversify their energy sources and move towards carbon neutrality.
Solar district heating is cost-competitive against fossil fuels, can account for a month or more of accumulated heat for the winter months, which benefits residential buildings. But these systems cannot run on solar energy directly without the use of thermal storage options which once again can lead this technique to be used to fix the solar-based energy consumption as a replacement for a gas or oil-based systems. Solar district heating is a sustainable solution for new build residential developments due to these characteristics.
Solar district heating adoption is gaining traction in the industrial sector, as companies look to cut carbon emissions and hit tough sustainability targets. Advanced solar thermal solutions with heat storage and hybrid configurations are enabling industries like food processing, chemical manufacturing and textiles to harness the forced potentialities of solar thermal heating for high-temperature processing requirements.
In Europe, China, and North America, governments and regional authorities are encouraging businesses to invest in solar district heating systems. These systems can save a lot of energy and allow industries to adhere to tight emissions regulations.
The corporate sector is increasingly prioritizing energy efficiency and green initiatives while solar district heating is a scalable, long-term solution that supports the achievement of sustainability benchmarks and the reduction of fossil fuel dependency.
Global warming and burning fossil fuels are forcing societies worldwide towards cleaner forms of energy. This, in turn, has given rise to the solar district heating market. Major players in this market are Aalborg CSP, Fortum, Göteborg Energi, Kelag Energy, Keppel DHCS, Korea District Heating Corporation, Logstor, NRG Energy, Ramboll Group, RWE, Savosolar, Shinryo, Statkraft, STEAG, and Vattenfall.
These companies have shown to partake in developing and innovating in the area of solar district heating. The growth strategies adopted by these major players dictate them to focus on many aspects, such as technological innovation, strategic alliances, and investment in renewable energy infrastructure.
For example, Aalborg CSP designs integrated energy systems based on the use of concentrated solar power technology for providing efficient and sustainable heating. Fortum has partnered with Microsoft to capture surplus heat from data centers that is then directed into district heating networks to provide energy efficiency. Likewise, Göteborg Energi has teamed up with Kamstrup to implement intelligent demand-side management solutions that can optimize the utilization of energy in the city's district heating network.
Market Share Analysis by Company
| Company Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| ENGIE SA | 14-16% |
| Danfoss A/S | 12-14% |
| Veolia Environnement S.A. | 10-12% |
| Fortum Oyj | 8-10% |
| Vattenfall AB | 6-8% |
| Other Companies (combined) | 40-50% |
| Company Name | Key Offerings/Activities |
|---|---|
| ENGIE SA | Develops high-capacity district heating grids using solar thermal power plants and CHP and heat storage to supply energy-efficient city heating. |
| Danfoss A/S | Offers district heating control systems, heat exchangers, and smart energy management solutions, optimizing solar thermal integration. |
| Veolia Environnement S.A. | Provides sustainable district energy solutions such as solar heating, waste heat recovery, and hybrid district heating grids. |
| Fortum Oyj | Carbon-neutral heating experts, combining solar district heating with bioenergy and geothermal heat networks. |
| Vattenfall AB | Comes forth with solar-heated district networks, specifically focused on low-emission city heating and renewable infrastructure. |
Key Company Insights
ENGIE SA
ENGIE is a global leader in district energy solutions, investing in large-scale solar district heating projects across Europe, North America, and Asia. The company integrates solar thermal plants with CHP (Combined Heat and Power) and seasonal heat storage to enhance district heating efficiency. ENGIE is also involved in smart energy grid innovations, optimizing solar thermal energy utilization in urban areas.
Danfoss A/S
Danfoss is a leading supplier of district heating components and control systems, providing heat exchangers, substations, and smart heating management solutions. The company focuses on optimizing solar district heating networks, ensuring efficient distribution and minimal energy loss. Danfoss plays a key role in digitizing district heating systems, enabling real-time monitoring and automation.
Veolia Environment S.A.
Veolia is a major player in sustainable urban heating solutions, integrating solar thermal energy, industrial waste heat, and hybrid district heating grids. The company focuses on low-carbon district heating projects, implementing solar-powered and energy-recovery-based heating networks in cities across Europe and Asia.
Fortum Oyj
Fortum specializes in carbon-neutral district heating solutions, combining solar thermal, biomass, and geothermal energy. The company is actively involved in solar district heating developments in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe, integrating large-scale heat storage for year-round efficiency. Fortum is expanding its renewable district heating projects, focusing on future-proof energy systems.
Vattenfall AB
Vattenfall is a leading provider of renewable district heating, developing solar-powered heating grids and low-emission urban heating networks. The company is investing in heat storage and smart heating technologies, ensuring optimized solar energy distribution for residential and commercial applications.
The estimated market valuation for 2025 is USD 3.06 billion.
The market is estimated to reach USD 5.5 billion by 2035.
ENGIE SA, Danfoss A/S, Veolia Environments S.A., Fortum Oyj, Vattenfall AB, and others these are some key players of the market.
By configuration, Solar District heating market can be segmented in to Centralized, Decentralized & Hybrid.
By application, Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Greenhouse Heating & Government Institutions
The capacity is another segment Small Scale, Medium Scale & Large Scale.
By region, North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, South Asia & Pacific, East Asia, Middle East & Africa.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Swellable Packers Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Sustainable Aviation Fuel Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
CNG Tanks Cylinders Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Green Building Materials Market Analysis by Type, Application, End-user and Region: Forecast for 2025 and 2035
Sand Control Screens Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.