The global smart waste management market size reached USD 2,733.1 million in 2024. Worldwide demand for smart waste management recorded a Y-o-Y growth of 15.6% in 2024, and thus, the market is expected to reach USD 3,170.5 million in 2025. Over the projection period (2025 to 2035), global smart waste management sales are predicted to rise swiftly at 16% CAGR and climb to a market size of USD 13,986.4 million by 2035-end.
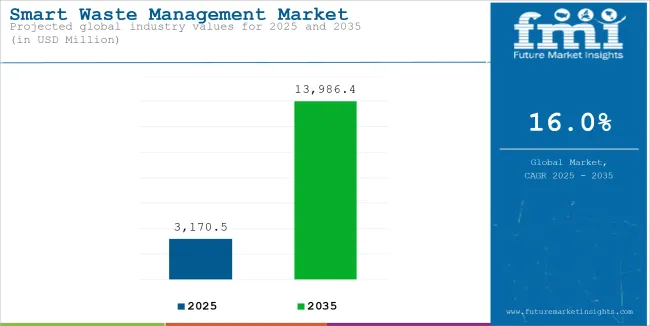
| Attributes | Key Insights |
|---|---|
| Estimated Size, 2025 | USD 3,170.5 million |
| Projected Size, 2035 | USD 13,986.4 million |
| Value-based CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 16% |
Increasing solid waste generation in various parts of the world has become a burden on the global economy. The World Bank has estimated that nearly 2.01 billion tons of waste are generated every day. More than 33% of this waste is not managed in an environmentally safe manner.
This number is expected to surge in the forthcoming years, which in turn is compelling governments and authorities in various countries to invest in smart waste management. The growing need for effective waste management in residential buildings, hospitals, commercial spaces, public places, and other institutions is expected to drive the market.
Smart waste management can potentially reduce the overall collection and transportation costs by 50%. They also reduce fuel and service costs. Backed by these factors, sales in the smart waste management market are forecast to increase at a prolific pace over the forecast period.
Further, the increasing adoption of connective-technology-based products in smart waste management is expected to bode well for the market. Technologies such as radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, sensor-based containers, vacuum containers, and disposal tags provide real-time management and tracking of solid municipal waste.
The table below presents the annual growth rates of the global smart waste management market from 2025 to 2035. With a base of 2024 and extended to the current year 2025, the report studied how the industry growth trajectory moves from the first half of the year-that is, January to June, (H1)-to the second half comprising July to December, (H2). This is an absolute comparison to offering the stakeholder's idea of how the sector has performed over time, with hints on developments that may emerge.
These figures indicate the growth of the sector in each half-year, between the years 2024 and 2025. The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.7% in H1-2024. In H2, the growth rate increases.
| Particular | Value CAGR |
|---|---|
| H1 2024 | 15.7% (2024 to 2034) |
| H2 2024 | 15.9% (2024 to 2034) |
| H1 2025 | 16.0% (2025 to 2035) |
| H2 2025 | 16.1% (2025 to 2035) |
Moving into the subsequent period, from H1 2025 to H2 2025, the CAGR is projected to slightly decrease to 16.0% in the first half and relatively increase to 16.1% in the second half. In the first half (H1), the sector saw an increase of 30 BPS while in the second half (H2), there was a slight increase of 20 BPS.
The section explains the Value Share of the leading segments in the industry. In terms of Smart Energy Recovery, the Waste-to-Energy will likely dominate and generate a share of around 40-45% in 2024.
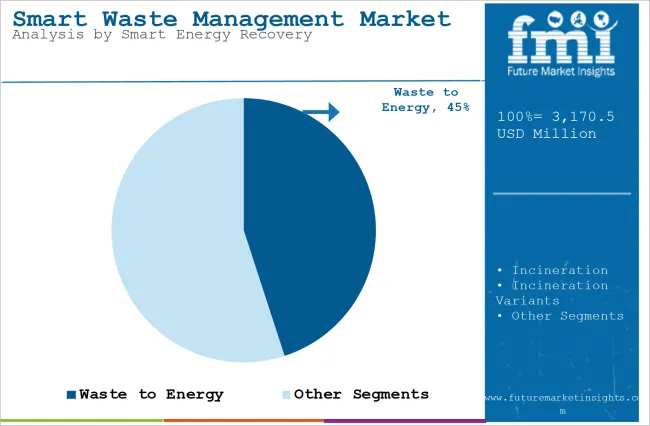
| Segment | Waste-to-Energy (Smart Energy Recovery) |
|---|---|
| Value Share (2024) | 40-45% |
Waste-to-Energy (WTE) technologies hold the largest share in the smart energy recovery sector due to their ability to solve two major issues: waste management and energy generation. As cities and industries face growing waste problems, WTE technologies provide a solution by converting non-recyclable waste into usable energy like electricity or heat. This not only reduces the burden on landfills but also offers a sustainable way to dispose of waste.
It is also seen as a green energy solution, since WTE reduces methane emissions from landfills and decreases dependence on fossil fuels, thus meeting the sustainability goals of nations to help reduce carbon emissions. In a time when renewable energy sources are in very high demand, WTE becomes very important in providing a sure source of energy in areas where traditional or renewable sources, like solar and wind energy, may not be readily available.
Governments in countries like China, Germany, and the United States are promoting WTE technologies through incentives and policies, further driving their adoption. WTE facilities also generate revenue by selling the energy produced, benefiting municipalities financially while contributing to cleaner energy production.
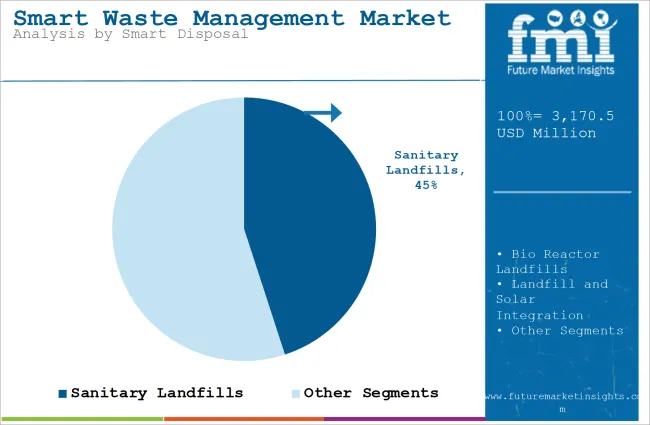
| Segment | Sanitary landfills (Smart Disposal) |
|---|---|
| Value Share (2024) | 40-45% |
Sanitary landfills are the most widely used type of landfill worldwide, dominating the market due to their design and environmental safety. These landfills are lined with materials like clay or plastic to prevent harmful substances from leaking into the environment, ensuring that waste is contained properly. Unlike uncontrolled dumpsites, sanitary landfills use advanced systems like leachate collection and gas management, which help protect nearby soil and water from contamination.
Moreover, strict regulations throughout the world are demanding that garbage must be disposed of in a controlled environment to ensure health hygiene. This fact has enhanced the use of sanitary landfills; specifically, they have become significant in urban areas or developed countries that take environmental concern more seriously.
While both bio-reactor landfills and landfill and solar integration are in their development stage, the bio-reactor landfills are much friendlier to the environment since they speed up the process of waste decomposition; these, however, have not been as widespread yet. Another promising concept of combining landfills with solar power is also in its infancy.
Overall, sanitary landfills continue to lead the market due to their effectiveness, regulation compliance, and environmental protection.
The Impact of Urbanization on Waste Management Solutions
While the cities grow, so does the volume of waste being produced, especially in developing regions. Rapid urbanization simply means more households, businesses, and industries that contribute to volumes of waste. This is followed by large pressure on managing waste efficiently as an urban area.
The smart waste management system addresses the solution to these issues intelligently. Equipped with sensors, smart systems monitor waste in bins, keeping the respective collection services informed of precisely which and when bins need to be emptied. Analytics will also enable the enhancement of routes and schedules to pick up the garbage at the right time and location using less fuel, hence keeping labor costs low.
These smart solutions also contribute positively to improved recycling due to better sorting, minimum contamination, and increased recovery of resources. Broadly, this helps the city handle an increased load of generated waste, promoting efficiency and sustainability with minimum negative environmental impacts.
Technology Driving Smart Waste Management
The improvement in IoT and big data plays a vital role in waste management. IoT sensors embedded in the trash bins provide the current level of the filling status of the bins, which helps waste management teams collect garbage only when required. This reduces unnecessary trips, thereby saving both time and fuel. On the other hand, big data helps cities forecast how much garbage will be generated, enabling them to plan better for collecting and recycling waste.
AI (Artificial Intelligence) and machine learning are also transforming waste management. AI helps sort different types of waste, such as recyclables, hazardous materials, and organic waste, with much greater accuracy than manual sorting. Machine learning models can even predict waste generation patterns, allowing for more effective collection strategies.
Sorting facilities also use automation and robotics to increase the speed and accuracy of the process. This reduces contamination in recyclable materials, increasing the rates of recycling and contributing to a cleaner environment with more efficient waste management systems.
Waste-to-Energy Technologies: Turning Waste into Power
Waste-to-energy (WTE) technologies are gaining attention as a solution to both waste management and energy needs. These technologies convert non-recyclable waste into usable energy, such as electricity or heat. By burning waste materials or using other processes, WTE helps reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, while providing a valuable energy source.
Besides landfill waste reduction, WTE technologies contribute to sustainability goals by offering a source of energy from wastes alternative to traditional fossil fuels, hence helping decrease greenhouse gas emissions and reduce reliance on non-renewable energy sources. This shift supports the transition toward a more sustainable, circular economy in which waste is not simply discarded but repurposed.
WTE solutions can also result in significant cost savings for municipalities and industries. By turning waste into energy, they reduce energy costs and help offset the expenses of waste disposal. This makes waste-to-energy a win-win solution for both the environment and the economy.
Challenges of Infrastructure in Smart Waste Management
In many developing countries, the lack of proper infrastructure is a major challenge for implementing smart waste management systems. These regions often face limited resources, outdated waste management processes, and insufficient technology to handle growing waste volumes effectively.
Waste management smart solutions, such as IoT sensors, data analytics, and automated systems, require a reliable underlying infrastructure in the form of a stable internet connection, collection vehicles, and recycling facilities. If this basic infrastructure is not available, deployment and maintenance will be difficult.
Also, in some areas, there is a shortage of skilled labor and technical knowledge to manage and operate smart systems, making it harder to integrate new technologies into existing waste management operations.
While the potential benefits of smart waste management are clear, overcoming the infrastructure gap is crucial for many regions. Governments and local authorities need to invest in upgrading waste management infrastructure to ensure that smart technologies can be adopted effectively, ultimately leading to cleaner, more sustainable cities.
The global Smart waste management industry recorded a CAGR of 16.0% during the historical period between 2020 and 2024. The growth of the Smart waste management industry was positive as it reached a value of USD 2,733.1 million in 2024 from USD 1,525.2 million in 2020.
The global Smart Waste Management Market has experienced significant growth from 2020 to 2024, driven by increasing urbanization, environmental awareness, and the need for more efficient waste management solutions. This growth is largely attributed to the rising demand for sustainable, energy-efficient technologies across various sectors, including municipalities, industries, and residential areas.
Technological advancements such as IoT-enabled waste bins, real-time data analytics, AI-driven waste sorting, and automated waste collection systems have played a pivotal role in transforming waste management practices. These innovations have allowed for optimized waste collection routes, improved recycling rates, and reduced operational costs, which are essential as cities continue to expand and face mounting waste generation challenges.
Looking ahead to 2025 to 2035, the market is expected to continue expanding, fueled by factors such as increased urbanization, stricter government regulations on waste disposal, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. The adoption of smart waste management technologies will be driven by the demand for eco-friendly, efficient, and cost-effective solutions to address the complexities of waste management in densely populated areas.
Tier 1 companies include industry leaders with annual revenues exceeding USD 500 - 1000 million. These companies are currently capturing a significant share of 40-45% globally. These frontrunners are characterized by high production capacity and a wide product portfolio.
They are distinguished by extensive expertise in manufacturing and a broad geographical reach, underpinned by a robust consumer base. They provide a wide range of products to meet regulatory standards. Prominent companies within Tier 1 include Covanta Energy Republic Services, Veolia North America, BRE SMART Wasteand others.
Tier 2 companies encompass mid-sized participants with revenues ranging from USD 100 - 500 million, holding a presence in specific regions and exerting significant influence in local economies. These smart waste managements are distinguished by their robust presence overseas and in-depth industry expertise.
They possess strong technology capabilities and adhere strictly to regulatory requirements. However, while they may not always possess the latest cutting-edge technologies or maintain an extensive global reach. Noteworthy entities in Tier 2 include Harvest Power, Recycle Smart Solutions, and SENSONEO.
Tier 3 encompasses most of the small-scale enterprises operating within the regional sphere and catering to specialized needs with revenues below USD 50 - 100 million. These businesses are notably focused on meeting local demand and are hence categorized within the Tier 3 segment.
They are small-scale participants with limited geographical presence. In this context, Tier 3 is acknowledged as an informal sector, indicating a segment distinguished by a lack of extensive organization and formal structure in comparison to the structured one. Tier 3 Aspen Waste, IBM Corporation, Enevo Oy and others.
The section below covers assessments of smart waste management sales across key countries. Countries from East Asia, and Latin America, are anticipated to exhibit promising double-digit growth over the forecast period. All the below-listed countries are collectively set to reflect a CAGR of around 16% through the forecast period.
| Countries | Value CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| China | 17.1% |
| India | 16.3% |
| USA | 12.3% |
| Germany | 10.3% |
| UK | 10.6% |
The United States is a global leader in the development and production of advanced waste management technologies. The country is at the forefront of integrating IoT-enabled systems, AI-powered waste sorting, and automated waste collection solutions to improve waste management efficiency. Key companies like Waste Management, Inc. and Republic Services play a significant role in advancing these technologies, making waste management more efficient and sustainable.
Technological changes in the USA have brought a lot of innovatory ideas whereby smart waste containers use sensors that monitor the amount of waste in them, thus optimizing routes for collection. Sorting into recyclables, hazardous materials, and organic waste can be done by AI-driven systems to improve sorting rates and reduce contamination.
Further, the waste-to-energy solution provides for the possibility of conversion of trash into valuable energetic resources, such as electricity and heat, which goes toward common sustainability goals of the country. Overall, the USA continues to lead the charge in waste management innovations, contributing to cleaner, more efficient cities and communities.
China is one of the largest consumers of smart waste management technologies, driven by several key factors. Rapid urbanization and high population density have led to significant waste management challenges in cities across the country. As China continues to grow, managing waste efficiently has become a top priority for both local governments and industries.
The Chinese government plays a leading role in the promotion of smart city projects, with strict policies to reduce waste. For example, China implemented the Waste Sorting Law that requires residents to separate recyclable items, organic waste, and other material types. Due to such regulations, urban cities are prompted to introduce high-tech technologies, such as IoT-enabled sensors fitted in bins that track the level of waste in real time and optimize collection schedules.
Also, China is investing heavily in waste-to-energy solutions, which convert non-recyclable waste into energy, helping the country meet its sustainability and energy goals. The adoption of these technologies is crucial for China to manage its growing waste challenges and reduce environmental impact.
India is becoming a major consumer of smart waste management technologies due to its rapidly growing urban population and the increasing challenges of waste management. As more people move to cities, the amount of waste generated is rising fast, making it harder to manage with traditional methods.
The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Mission), launched by the Indian government, has been a driving force behind the push for better waste management infrastructure. This initiative encourages cleaner cities and better waste management practices, prompting cities to adopt advanced technologies.
India is embracing a bevy of intelligent solutions to the rising challenge of waste-smart bins embedded with sensors that indicate the level of waste; IoT solutions monitor real-time waste and its movement across systems for efficient disposal, and investments in waste-to-energy plants that turn household waste into usable energy, decreasing landfills and providing sources for renewable power. These value-added technologies are very important for India to promote recycling and better management of urban wastes.
The section provides comprehensive assessments and insights that highlight current opportunities and emerging trends for companies in developed and developing countries. It analyzes advancements in manufacturing and identifies the latest trends poised to drive new applications in the industry.
A few key players in the smart waste management industry are actively enhancing capabilities and resources to cater to the growing demand for the compound across diverse applications. Leading companies also leverage partnership and joint venture strategies to co-develop innovative products and bolster their resource base.
Significant players are further introducing new products to address the increasing need for cutting-edge solutions in various end-use sectors. Geographic expansion is another important strategy that is being embraced by reputed companies. Start-ups are likely to emerge in the sector through 2035, thereby making it more competitive.
Industry Updates
In terms of Smart collection, the industry is divided into RFID Technology, Ultrasonic Sensor, GPS, Others
In terms of Smart processing, the industry is divided into segmented Advance MRFs, Mechanical Biological Treatment, RDF Facilities
In terms of Smart Energy Recovery, the industry is divided into Waste to Energy, Incineration, Incineration Variants, Advance Thermal Recycle, Biological Treatment, Direct Use, Electrical Generation, Vehicular use, Advance Thermal Treatment, Gasification, Pyrolysis, Plasma Arc Gasification, Waste to Fuel.
In terms of Smart Disposal, the industry is divided into segmented Sanitary Landfills, Bio reactor Landfills, Landfill and Solar Integration
Key countries of North America, Latin America, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, East Asia, South Asia, Middle East and Africa (MEA), have been covered in the report.
The global market was valued at USD 2,733.1 million in 2024.
The global market is set to reach USD 3,170.5 million in 2025.
Global demand is anticipated to rise at 16.0% CAGR.
The industry is projected to reach USD 13,986.4 million by 2035.
Covanta Energy, Republic Services, Veolia North America, BRE SMART Waste, Harvest Power, Recycle Smart Solutions, SENSONEO, Aspen Waste, IBM Corporation, Enevo Oy
Table 1: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Region, 2017-2032
Table 2: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Technology, 2017-2032
Table 3: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Table 4: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Table 5: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Application, 2017-2032
Table 6: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Country, 2017-2032
Table 7: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Technology, 2017-2032
Table 8: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Table 9: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Table 10: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Application, 2017-2032
Table 11: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Country, 2017-2032
Table 12: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Technology, 2017-2032
Table 13: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Table 14: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Table 15: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Application, 2017-2032
Table 16: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Country, 2017-2032
Table 17: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Technology, 2017-2032
Table 18: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Table 19: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Table 20: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Application, 2017-2032
Table 21: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Country, 2017-2032
Table 22: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Technology, 2017-2032
Table 23: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Table 24: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Table 25: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Application, 2017-2032
Table 26: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Country, 2017-2032
Table 27: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Technology, 2017-2032
Table 28: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Table 29: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Table 30: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Application, 2017-2032
Table 31: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Country, 2017-2032
Table 32: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Technology, 2017-2032
Table 33: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Table 34: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Table 35: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Forecast by Application, 2017-2032
Figure 1: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 2: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 3: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 4: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 5: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Region, 2022-2032
Figure 6: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Region, 2017-2032
Figure 7: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2022-2032
Figure 8: Global Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2022-2032
Figure 9: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Technology, 2017-2032
Figure 10: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 11: Global Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 12: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Figure 13: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 14: Global Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 15: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Figure 16: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 17: Global Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 18: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Application, 2017-2032
Figure 19: Global Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 20: Global Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 21: Global Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 22: Global Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 23: Global Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 24: Global Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 25: Global Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Region, 2022-2032
Figure 26: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 27: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 28: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 29: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 30: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 31: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Country, 2017-2032
Figure 32: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 33: North America Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 34: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Technology, 2017-2032
Figure 35: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 36: North America Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 37: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Figure 38: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 39: North America Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 40: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Figure 41: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 42: North America Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 43: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Application, 2017-2032
Figure 44: North America Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 45: North America Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 46: North America Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 47: North America Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 48: North America Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 49: North America Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 50: North America Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 51: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 52: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 53: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 54: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 55: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 56: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Country, 2017-2032
Figure 57: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 58: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 59: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Technology, 2017-2032
Figure 60: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 61: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 62: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Figure 63: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 64: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 65: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Figure 66: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 67: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 68: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Application, 2017-2032
Figure 69: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 70: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 71: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 72: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 73: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 74: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 75: Latin America Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 76: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 77: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 78: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 79: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 80: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 81: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Country, 2017-2032
Figure 82: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 83: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 84: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Technology, 2017-2032
Figure 85: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 86: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 87: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Figure 88: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 89: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 90: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Figure 91: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 92: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 93: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Application, 2017-2032
Figure 94: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 95: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 96: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 97: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 98: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 99: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 100: Europe Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 101: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 102: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 103: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 104: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 105: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 106: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Country, 2017-2032
Figure 107: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 108: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 109: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Technology, 2017-2032
Figure 110: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 111: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 112: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Figure 113: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 114: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 115: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Figure 116: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 117: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 118: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Application, 2017-2032
Figure 119: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 120: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 121: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 122: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 123: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 124: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 125: East Asia Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 126: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 127: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 128: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 129: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 130: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 131: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Country, 2017-2032
Figure 132: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 133: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 134: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Technology, 2017-2032
Figure 135: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 136: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 137: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Figure 138: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 139: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 140: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Figure 141: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 142: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 143: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Application, 2017-2032
Figure 144: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 145: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 146: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 147: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 148: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 149: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 150: South Asia & Pacific Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 151: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 152: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 153: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 154: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 155: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 156: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Country, 2017-2032
Figure 157: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 158: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2022-2032
Figure 159: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Technology, 2017-2032
Figure 160: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 161: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 162: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Communication Channel, 2017-2032
Figure 163: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 164: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 165: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Type of Waste, 2017-2032
Figure 166: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 167: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 168: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value (US$ Mn) Analysis by Application, 2017-2032
Figure 169: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 170: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 171: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Technology, 2022-2032
Figure 172: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Communication Channel, 2022-2032
Figure 173: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Type of Waste, 2022-2032
Figure 174: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Application, 2022-2032
Figure 175: MEA Smart Waste Management Market Attractiveness by Country, 2022-2032






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Smart Digital Valve Positioner Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Card IC Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart-Tag Inlay Inserters Market Analysis - Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Wheelchair Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart TV Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart/AI Toy Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Locks Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Sprinkler Controller Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Indoor Gardening System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Building Delivery Robot Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Watch Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Label Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Mat Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Built-In Kitchen Appliance Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Cold Therapy Machine Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Personal Assistance Devices Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Speaker Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Vehicle Architecture Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart City Platforms Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Smart Doorbell Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA