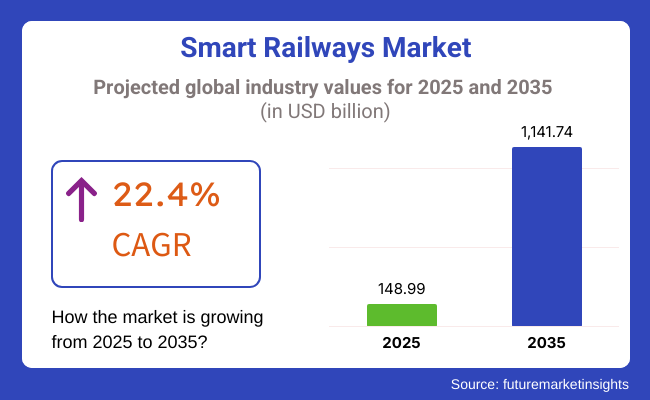
The smart railways market is estimated as USD 148.99 billion in 2025 and USD 1,141.74 billion in the year 2035. This rapid expansion is driven by continuing advancements in railway infrastructure, increasing government investment in transport upgradation, and expanding demand for low-cost and effective rail solutions. A greater CAGR suggests a robust industry expansion with a dramatic increase in the use of digital technologies within the railway sector.
Smart railway systems are the newest digital technologies like IoT, AI, cloud computing, and big data analytics being utilized to optimize the whole range of activities involved in railway operations, including safety and customer experience. The systems also enable predictive maintenance, real-time tracking, autonomous signalling, and energy-efficient rail networks.
All over the world, governments and private investors are investing in modernizing railway infrastructures, including automation and data-based solutions to increase transport efficiency and sustainability. In addition, increasing focus on green and smart urban mobility is driving the growth of the industry.
Increased safety, efficiency, and sustainability in transport is perhaps the most evident catalyst for the smart railways industry. Predictive analytics based on AI minimize downtime, and sensor-based IoT enable devices to detect and strategically schedule asset maintenance. In addition, digital ticketing and automatic fare collection systems are increasing passenger convenience and lowering the cost of operations. Increasing demand for smart city initiatives is also driving industry growth, along with expansion of high-speed rail networks and urban surrogate systems.
Even as it forges ahead to develop smart railways at a fast pace, the smart railway market is beset by issues. A major obstacle is the huge initial investment required to bring smart railway solutions such as AI-driven automation, data analytics platforms, and digital signaling systems. Digitalization presents new security risks in terms of data security and cyber-attacks. Existing railway networks' legacy systems also pose integration problems that require gigantic investment in order to modernize them and make them compatible.
Smart railways industry is led by technological innovation and partnership between governments and technology companies. Sophisticated technologies like 5G connectivity for fast data transmission, blockchain for safe data transfer and AI-based automation are poised to revolutionize rail operations. Investment High-speed rail, energy-efficient transport, and hybrid-electric train technology are powering new growth opportunities.
Besides this, the implementation of smart railways has a high rate due to sustained support of public-private partnership for speeding up the development of infrastructure. With the growth of urbanization and sustainability targets driving global transport policies, the industry of smart railways will expand exponentially during the next ten years.
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
The industry is changing through the process of integrating automation, AI, IoT-based monitoring, and real-time data analytics, enhancing the safety and efficiency of rail operations.
Urban transit and high-speed transit systems emphasize automated train control, optimum propulsion systems, and real-time passenger information systems to facilitate travel.
Freight railways emphasize predictive maintenance, tracking of cargo, and automated scheduling to streamline logistics and minimize delay. Railway infrastructure management is also moving toward more IoT sensors, AI-based track monitoring, and digital signaling systems to enhance operational safety and minimize maintenance expenses.
Passenger services are combining contactless ticketing, smart station solutions, and AI-powered customer service to enhance the travel experience. Moreover, cybersecurity functions are becoming mandatory with digitalization growing throughout railway networks.
The trend towards sustainable rail transport is also driving investment in electrification, hydrogen trains, and energy-efficient rolling stock.
| Company | Contract Value (USD Million) |
|---|---|
| Siemens Mobility | Approximately USD 85 - USD 95 |
| Alstom | Approximately USD 75 - USD 85 |
| Hitachi Rail | Approximately USD 65 - USD 75 |
| Thales | Approximately USD 55 - USD 65 |
| Kawasaki Heavy Industries | Approximately USD 70 - USD 80 |
During 2024 and the first half of 2025, the industry kept advancing, driven by the need for greater operational efficiency, safety and customer experience through digitalization. Landmark contracts have also been awarded to large industry players Siemens Mobility, Alstom, Hitachi Rail, Thales and Kawasaki Heavy Industries, which reflect the focus on blending smart technologies with rail operations, defining the way forward for safer, more efficient and cleaner modes of transport.
Between 2020 and 2024, the industry grew strongly with urbanization, technologies, and sustainability as drivers. Governments and transport authorities drove railway digitalization to enhance efficiency, safety, and travel experience. Artificial intelligence (AI)-based predictive maintenance, autonomous train control, and intelligent signaling systems minimized delays and optimized train planning.
Germany, Japan, and the UK were among the nations at the forefront of high-speed rail automation. The COVID-19 crisis accelerated demand for contactless ticketing, AI crowd management, and digital payment systems. Sustainability was a driving force, with investment in electrification, solar-powered networks, and hydrogen-powered trains to minimize carbon emissions. Obstacles like high costs of infrastructure, cybersecurity attacks, and interoperability were mitigated through standardization and regulatory frameworks so that smart railway technologies could be used on a larger scale.
Between 2025 and 2035, automation, artificial intelligence, and sustainable solutions will propel the smart railway innovation.
AI programs will regulate train velocity, maintenance schedules, and timetables automated. Hyperloop trains and Maglev trains will dominate high-speed movement with low-friction efficiency and reduced energy draw. Blockchain ticketing will offer enhanced security and hassle-free cross-border travel with smart passes that are universally valid. Autonomous, AI-driven trains will enhance operating precision and network capacity through 5G-based real-time communication. Sustainability will be enhanced through solar-powered stations, hydrogen fuel cells, and wind-assisted power.
Smart stations will feature facial recognition for biometric ticketing, AI-managed crowd handling, and real-time tracking of baggage, strengthening connectivity with city mobility networks. Cybersecurity will be strengthened with AI-powered threat detection, quantum encryption, and blockchain security standards, safeguarding data and infrastructure resilience.
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Contactless ticketing, smart payment systems, and others. | AI-driven passenger experiences, blockchain-based ticketing, and others. |
| Electric and solar-powered signaling, real-time monitoring, and others. | AI-optimized train scheduling, autonomous rail operations, and others. |
| Solar-powered rail stations, hydrogen trains, and others. | Fully green railway ecosystems, zero-carbon rail networks, and others. |
| IoT-based maintenance, predictive analytics, and others. | 5G-supported train communication, AI-driven operations, and others. |
| Cloud data storage, cyber protection measures, and others. | Quantum encryption, blockchain-protected passenger data, and others. |
| Expansion of high-speed rail, Maglev pilot schemes | Global spread of Hyperloop and Maglev railways |
The industry is flourishing, with robots, IoT, and AI technologies significantly improving efficiency, safety, and passenger comfort. Automation is yet not a universal herald. For instance, rail transport and some components of the railway are still in use despite reducing their percentage in the global technology industry.
Railways infrastructure and operations are suffering from supply chain disruptions like semiconductor shortages and dependence on specialized equipment. The geopolitical tensions, trade limitations, and raw material price fluctuations are among the other factors that add to industry uncertainties.
On the other hand, the previous issues of the suppliers' inability to meet the deadlines, increased costs of materials, and the need to have local production, turned out to be real crises. As a result, it is crucial for the company to perform the tasks efficiently. Therefore, these are the main five actions we have implemented to protect our operations and minimize service disruptions.
The rapid growth of artificial intelligence, big data, and predictive maintenance develops the possibility of invalidation. Enterprises should mainly build kit solutions that are interchangeable and include ongoing R&D in order to remain competitive and adjust to changing norms and client expectations.
Cybersecurity is also one of the major issues as smart railways working with a lot of interconnected networks and cloud-based control systems. Cybernetic attack, data leakage, and unauthorized admission that could lead to operations disruptions as well as indirect passenger safety endangerment are concerned. Executing AI-based security protocols, organizing robust encryption as well as conducting regular software updates are the essentials to protecting our infrastructure and data integrity.
In 2025, rail sensors will secure 55% of the industry, followed by video surveillance cameras, which will account for 45% of the smart railways share (Smart Railways Market, by Device & Component).
Rail Sensors enable predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and railway safety. Companies like Siemens, Alstom, and Hitachi Rail are integrating IoT-enabled sensors that help detect and track anomalies, monitor train speed, and improve operational efficiency using advanced vibration, temperature, and acoustic sensors to avert derailments or optimize maintenance schedules. For example, Deutsche Bahn uses AI-enabled sensor networking to predict track failures to minimize downtime.
Video Surveillance Cameras are being adopted as the concerns over passenger safety and security rise. AI is not only allowing for the fast synthesis of multi-faceted information but also facilitate identification, automating threat assessment through the AI-powered facial recognition and the behavior analytics improve threat detection and response times.
Companies like Fire, Hikvision, Axis Communications provide High definition cameras, thermal imaging and data processing on real time basis to provide surveillance on railway stations and in trains. Largely, Governments around the world are investing in smart security infrastructure with the projects such as RailTel Video Surveillance System and Shift2Rail initiative proved the focus of digital transformation.
Rail sensors and video surveillance cameras will drive the modernization of railway networks worldwide as investments in rail automation, passenger safety, and predictive maintenance grow. In the coming years, the growing development of high-speed rail and metro will spur the demand for a smart monitoring and security solution.
The industry by Service would hit growth figures in 2025, with Professional Services holding nearly 58% of the industry share and Cloud Services covering 42% share.
Professional Services include integration methods, consulting, and maintenance services to guarantee the smooth implementation of smart railway solutions. Siemens, Alstom, and Wabtec, for example, focus on railway infrastructure modernization, asset management optimization, and integration of AI-driven predictive maintenance systems.
Governments and rail operators invest big in digital transformation and automation, which tends to drive demand for their professional services. One hides in plain sight: the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS) requires expert consulting and integration of standardized signaling and traffic control.
One such advancement is in Cloud Services, which allow the railways to implement real-time data analytics, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance. IBM, Hitachi Rail, and Huawei's cloud-based systems provide increasingly efficient and secure forms of automated ticketing, passenger flow analysis, and cybersecurity.
Cloud Computing in Rail Cloud computing is gaining popularity in rail networks due to the emergence of IoT-attached rail frameworks and AI-based operational insights. Cloud platforms are being used to centralize control for traffic/asset management and to create predictive solutions for asset management (such as India's SMART Railway initiative), which collectively lower operational expenditure and improve service reliability.
With the expansion of smart railway infrastructure, professional and cloud services will be crucial to the future of smart rail transport by improving operational efficiency, safety, and passenger experience globally.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| USA | 8.5% |
| UK | 8.1% |
| France | 8.3% |
| Germany | 8.7% |
| hItaly | 8.2% |
| South Korea | 8.9% |
| Japan | 8.3% |
| China | 9.1% |
| Australia | 7.9% |
| New Zealand | 7.6% |
The USA smart railways industry is transforming at a very fast pace with enormous investments in railway automation, predictive maintenance through AI, and top-of-the-line signaling. Constructing high-speed rail and integrating smart railways are the federal plans to make it more efficient and sustainable. Siemens Mobility, Alstom, and Wabtec are leading the charge with AI-driven traffic control and cloud predictive analytics to reduce journey delays and enhance passengers' experiences.
Adopting AI-based scheduling and condition monitoring by IoT is reshaping rail operations. Autonomous trains, real-time traffic management, and AI-based asset management are the most crucial areas of work for the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) to make railway operations safer and more reliable. Greater emphasis on carbon-neutral railway networks also aligns with the global sustainability platform and is long-term industry growth.
UK smart railway is booming amidst government-sponsored schemes of modernization and digitalized signaling. The Department for Transport (DfT) is in charge of AI-based traffic management, real-time passenger information systems, and cloud-based ticketing. Decarbonization initiatives are bringing electric trains as well as hydrogen trains more onboard earlier, cutting fuel dependence on fossils.
Industry pioneers like Hitachi Rail, Network Rail, and Thales Group are pushing 5G-capable railway communications, AI traffic congestion management, and intelligent rolling stock planning into the mainstream. Contactless payment, automated timetables, and condition-based maintenance are boosting efficiency and passenger satisfaction. Integrated smart stations with greater connectivity and security are improving the rail network.
Smart rail development in France is spearheading massive investment in high-speed rail and artificial intelligence-based rail infrastructure. AI-based predictive maintenance and asset monitoring are the government's priorities to achieve operational performance and passenger safety. French railways are also making their infrastructure digital with smart sensors, autonomous control systems, and AI-based maintenance technology.
Companies like Alstom, Thales, and SNCF are also investing heavily in AI-based signaling, automatic control of trains, and cloud mobility platforms. The system is more efficient, and there are fewer delays with energy-saving trains and real-time monitoring. The country's goal of carbon neutrality for rail transport perfectly aligns with EU-level sustainability objectives, driving long-term industry growth.
Germany has high growth in the industry, driven by digitalization and AI-driven safety features initiatives. Route optimization based on AI, real-time observation, and next-generation cyber security are of interest to the government. Germany's emphasis on sustainable mobility is driving energy-efficient trains and networked rail.
Technology innovators in the rail industry, like Siemens Mobility, Deutsche Bahn, and Stadler Rail, are concentrating on predictive maintenance, autonomous train control, and cloud-based railway management. AI-enabled scheduling, smart ticketing, and IoT-enabled railway monitoring are enhancing efficiency. Studies on autonomous train operation and integration with 5G-enabled platforms are leading Germany's smart rail network.
Italy is developing smart rail technology, and investment in automation with the help of AI, high-speed rail, and electronic ticketing is on the rise. The government is especially keen on modernizing railway infrastructure with AI-based traffic management and predictive analytics to reduce accidents and increase efficiency. Its carbon emission battle is forcing the transition towards electrification and hydrogen fuel for rail transport.
Innovators like Trenitalia, Hitachi Rail Italy, and Ansaldo STS are leading the way with autonomous train operation, cloud management of the railway, and real-time traffic congestion monitoring. IoT-based maintenance and demand forecasting with AI are maximizing operations. Increasing investments in smart stations and frictionless mobility by Italy are transforming passenger experience.
The smart railway market in South Korea is growing at a high growth rate, fueled by high-speed rail modernization, AI-based automation, and 5G-based rail communication. The government is encouraging AI-based traffic control, cloud-based asset tracking, and real-time train location tracking to enhance efficiency and safety.
Leading firms like Hyundai Rotem, Samsung SDS, and SK Telecom are investing in smart railway infrastructure, predictive maintenance using AI, and automated ticketing. South Korea's focus on digitalization and the development of smart stations is also fueling industry growth. AI-driven train operation and real-time analytics are making railway efficiency easier.
Japan is at the forefront of the smart railway revolution with cutting-edge automation, AI-based train control, and high-speed rail technology. The government is creating AI-based predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and smart signaling to ensure improved safety and efficiency. Autonomous trains and 5G-based rail communication are transforming the industry.
Industry players like JR East, Hitachi Rail, and Kawasaki Heavy Industries are spearheading AI-powered scheduling, cloud ticketing, and autonomous train operations. The intersection of next-gen railway mobility platforms and cyber security is fueling the industry growth. Japan's leadership in high-speed rail technology gives it the lead position in worldwide smart railway innovation.
The Chinese smart railway market is growing fast with AI-based automation investment by the government, high-speed rail network extension, and real-time monitoring. China is focusing on AI-based asset management, predictive maintenance, and inter-operable rail.
These leaders are investing in cloud computing railway operations, 5G-based communication, and smart signaling. Congestion control, automatic fare collection, and real-time monitoring with artificial intelligence-based solutions are enhancing efficiency. China's carbon-neutral transportation push and digital railway transformation program are fueling industry growth.
Australia is upgrading its rail network with AI-driven automation, intelligent ticketing, and predictive maintenance. High-speed rail, cloud operation of rail, and real-time passenger information systems are being prioritized by the government.
Downer Group, Alstom, and Siemens Mobility are leading innovations in AI-driven railway safety, automated timetabling, and IoT-based condition monitoring. Green mobility investment and smart railway connectivity in Australia are transforming the transport sector.
New Zealand's smart railways industry is expanding steadily, with investments in AI-based maintenance, automated ticketing, and real-time train monitoring. The government is focusing on digital transformation and green rail transport.
KiwiRail, Transdev, and Thales are driving the use of AI-based predictive analytics, cloud-based asset management, and smart signaling. 5G communication and IoT-based monitoring are making railways efficient and safe.
The industry is witnessing a series of rapid transformations by the governments and transportation authorities due to the digitalization that they prefer to adopt for the prorating efficiency, safety, and convenience of passengers. The rise of IoT, AI-powered predictive maintenance, and real-time analytics is changing the face of railway systems by reducing delays and improving network reliability.
The industry is dominated by more established railway technology suppliers, telecom giants, and infrastructure disrupters Siemens Mobility, Alstom, Hitachi Rail, and Bombardier Transportation, for example. These companies incorporate automation, cloud-based monitoring, and energy-efficient rail solutions into their performance. Newcomers are trying to find a niche contributing to cutting-edge areas, including advanced systems cybersecurity, advanced high-speed rail connectivity for transporting vehicles, and AI-based management of traffic.
Some of the key drivers for the growth of the industry include technological advancements in autonomous train operations, the introduction of smart ticketing and passenger information systems, and regulatory initiatives for sustainable rail infrastructure. To help preserve their competitive position, companies are increasing spending on predictive analytics, electrification, and digital signaling.
Cost pressures, supply chain resilience, and changing consumer expectations around seamless, technology-enabled transportation are also driving change in the industry. Companies globally should focus on technology differentiation, compliance with safety regulations, and providing integrated smart mobility solutions to drive adoption and expansion into new markets to facilitate sustained growth.
Market Share Analysis by Company
| Company Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Siemens Mobility | 25-30% |
| Alstom | 20-25% |
| Hitachi Rail | 15-20% |
| Bombardier Transportation | 10-14% |
| Thales Group | 6-10% |
| Other Companies (combined) | 20-30% |
| Company Name | Key Offerings/Activities |
|---|---|
| Siemens Mobility | Focuses on digital rail automation, AI-powered signaling, and real-time monitoring of trains |
| Alstom | Focuses on smart train control, energy-efficient rail systems, and high-speed connectivity. |
| Hitachi Rail | Leading advancements in predictive maintenance, automated train operations, and intelligent transport solutions. |
| Bombardier Transportation | Develops next-generation rolling stock, smart ticketing, and rail network optimization. |
| Thales Group | Provides AI-driven cybersecurity, digital signaling, and integrated rail traffic management. |
Strategic Outlook of Key Companies
Siemens Mobility (25-30%)
Siemens is the pioneer in the smart railways market by providing smart automation solutions, AI-based traffic management, and predictive maintenance technologies.
Alstom (20-25%)
About Alstom is at the forefront of sustainable rail solutions, combining digital signaling and high-speed train automation to make rail accessible and greener.
Hitachi Rail (15-20%)
Hitachi's predictive rail maintenance, AI-assisted train control, and intelligent transport solutions are leading the way to ensuring reliable and safe railway operations.
Bombardier Transport (10-14 %)
Bombardier focuses on next-gen rolling stock, digital ticketing, and advanced energy-efficient rail solutions, enhancing passenger convenience and operational efficiency.
Thales Group (6-10%)
Thales fortifies rail safety with unrivaled cybersecurity solutions, AI-optimized traffic management, and digital signaling, keeping railroads running smoothly and securely.
Other Key Players (20-30% Combined)
The industry is expected to generate USD 148.99 billion in revenue by 2025.
The industry is projected to reach USD 1,141.74 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 22.4%.
Key players include Siemens Mobility, Alstom, Hitachi Rail, Bombardier Transportation, Thales Group, General Electric (GE), Cisco Systems, Huawei Technologies, ABB Group, and Indra Sistemas.
Europe and Asia-Pacific, driven by rapid urbanization, government initiatives for railway modernization, and the adoption of AI and big data in rail management.
Railway traffic management systems dominate due to their role in enhancing operational efficiency, safety, and real-time monitoring of rail networks.
By device and component, the industry includes rail sensors, video surveillance cameras, smart cards, networking & connectivity devices (such as routers, Wi-Fi, and switches), and other components like multimedia displays, with networking & connectivity devices leading due to the growing demand for seamless railway communication systems.
By service, the industry is categorized into professional services, cloud services, and integration services, with cloud services dominating due to the increasing need for scalable data storage and real-time railway analytics.
By system, the industry includes Passenger Information Systems (PIS), Railway Traffic Management Systems (RTMS), Advanced Security Management Systems (ASMS), Smart Ticketing Systems (STS), rail operations management systems, rail communication & networking systems, and others, with Passenger Information Systems (PIS) leading due to the rising demand for real-time travel updates.
By region, the industry spans North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia & Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa (MEA), with Europe leading due to strong investments in smart railway infrastructure and digital transformation initiatives.
Catenary Infrastructure Inspection Market Insights - Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Category Management Software Market Analysis - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
DC Power Systems Market Trends - Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Residential VoIP Services Market Insights – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Switching Mode Power Supply Market - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Safety Mirrors Market - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.