Renewable methanol market is expected to grow in the upcoming years between 2025 and 2035. Power-to-Liquids research is working to bring renewable methanol from derived biomass, industrial waste, and carbon dioxide into the energy marketplace as a sustainable alternative to fossil-based methanol to address the high demand for low-emission transportation fuels, greener chemicals feedstock’s, and practical fuel storage solutions.
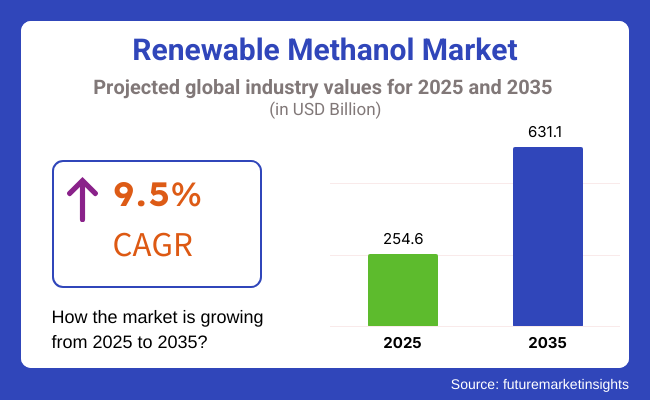
Global Renewable Methanol Market revenue is expected to reach USD 254.6 Billion by 2025. It is projected to be worth USD 631.1 Billion by 2035, growing at a healthy CAGR of 9.5% during the forecast period. Driven into a spiral with the focus on renewable energy targets, investments in new methanol plants using captured CO2 and/or bio-based feedstocks are booming especially in Europe, North America and Asia-Pacific.
Various sectors like automotive, marine, and chemicals are incorporating renewable methanol in their energy and production networks to meet decarbonisation targets and adhere to stringent environmental standards. Subsidies, tax credits, and other research funding are being asynchronously coloured by various government and industry stakeholders, in order to drive forward the adoption of renewable methanol technologies.
The major factors that drive the growth of the market are the shift from fossil-based to renewable energy sources, rising demand for green mobility solutions, and constant technological improvements in methanol synthesis and carbon capture. Also, a growing consumer consciousness of environmental sustainability and circular economy solutions that reduce waste and lower the greenhouse gas emissions also propels the market.
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
The renewable methanol market in North America is anticipated to account for a notable share owing to the existing renewable energy infrastructure, the active policy support for green fuels, and a developed industrial base. The regional uptake of renewable methanol is being driven chiefly by the USA and Canada, working through government incentives and the presence of major players developing large methanol production projects.
California Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) and similar regional programs are accelerating the integration of low-carbon renewable fuels across transportation. In addition, the USA Department of Energy has continued to fund research on carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) technologies, which provide a major boost to renewable methanol production as well.
Renewable methanol is being adopted across various industries, including automotive, marine transportation and chemicals, as a drop-in replacement for conventional fuels and feedstock’s, addressing their sustainability goals. Consequently, the North America renewable methanol market is expected to grow considerably during the forecast period.
Europe is leading the initiative for this renewable methanol since terrestrial air transportation has tough environmental regulations and ambitious decarbonist plans, countries are collaborating, with their respective governments financing the green energy. Germany, Sweden, the Netherlands, and Denmark are front and centre with investments in facilities, pilot projects, and research partnerships to store carbon through renewable methanol and reduce the carbon intensity of fuels and industrial processes.
Europe is rapidly seeing out public-private partnerships towards developing new advanced bio-methanol plants and applying carbon capture technologies for methanol production. Strong policy support, continued innovation, and rising consumer demand for sustainable products, will bolster Europe’s renewable methanol market and bring considerable growth in the forecast period
Asia Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest growing market for renewable methanol, owing to the rapid economic growth of countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea in addition to the rising emphasis on sustainability and energy security in this region. Asia-Pacific is positioning itself as a major hub for methanol production and consumption, with investment of scale in the establishment of green energy projects, bio-based production facilities, an adoption of circular economy principles.
In China, the world's largest methanol producer and consumer, projects for converting coal-derived methanol to renewable methanol are encouraged by national policies, accompanied by a rapidly growing demand for clean energy. In India, the government’s National Policy on Biofuels and its advocacy of methanol blending for transportation fuels are building a strong market for renewable methanol. Japan and South Korea are similarly moving toward low-carbon energy sources, running pilot projects and partnering with international players to include renewable methanol in their plans for green energy.
Due to the increasing population density, urbanization, and industrialization, Asia-Pacific nations are preferring renewable methanol more to lessen reliance on imported fossil fuels, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and to enhance long-term energy sustainability. This, in turn, may result in the Asia-Pacific renewable methanol market expanding steadily throughout the forecast period.
Challenge
High Production Costs and Infrastructure Limitations
The hurdles barring the renewable methanol industry are substantial, linked greatly to immense fabrication expenses and lack of comprehensive storage and transportation infrastructure. Generating renewable methanol necessitates colossal capital commitments for carbon sequestration, electrolysis, and biomass transformation engineering. Elevating these avenues to compete financially with conventional methanol output presents a tremendously formidable endeavor.
The minuscule infrastructure accessible for transporting and stocking renewable methanol severely constricts its market portion. Companies must center on pioneering techniques to reduce manufacturing costs and forging important partnerships to expand distribution networks. Governments and industries need to collaborate on policies incentivizing framework growth and investments in renewable methanol.
Public awareness and consciousness raising concerning the advantages of renewable methanol will also be important in motivating broader acceptance and investments in these advancements. Furthermore, progressing different raw materials and lower-cost fabrication processes will be fundamental to maintaining long-term market stability and expansion.
Opportunity
Expanding Demand for Sustainable Fuels and Chemical Feed stocks
The Renewable Methanol Market faces unprecedented challenge in the form of growing global demand to cut back on carbon emissions and transition towards clean fuels. Increasingly, companies have turned to renewable methanol as the cleaner alternative to fuel transportation, produce industrial chemicals, and power our world. Strict new emissions standards from governments have heightened demand for low-carbon methanol in applications such as marine fuel, fuel blending, and manufacturing various chemicals.
Technological breakthroughs in green hydrogen generation and carbon capture have made mass production of renewable methanol increasingly viable. Those firms making smart financial commitments to cost-effective production methods while also forging beneficial relationships with policymakers to craft supportive regulations will gain a clear edge in this emerging marketplace.
Growth in international carbon trading arrangements and government subsidies for investments in green power will provide further support to industry expansion. In addition, collaborations between energy companies and technology companies will result in production efficiency innovations, making renewable methanol more suitable for commercial use on a large scale.
From 2020 to 2024, the Renewable Methanol Market grew due to growing awareness of carbon-neutral fuels and advancements in green methanol technology. Sectors embraced renewable methanol due to its potential to lower greenhouse gas emissions as well as its compatibility with current methanol infrastructure. The automotive and shipping sectors investigated its use as a clean fuel substitute, while policy support for low-carbon energy solutions increased the funding of renewable methanol projects.
But production expenses were high and technology was limited, so large-scale application was not feasible. Firms concentrated on optimizing carbon capture efficiency and scaling up pilot projects to prove commercial applicability. Use of waste-to-methanol technologies and bio-methanol manufacturing also became more popular, providing alternative routes for bulk methanol synthesis. As research went on, efficiency of catalysts and process optimization improved, and energy consumption and operating costs for manufacturers decreased.
Looking forward to 2025 to 2035, the industry will see more rapid growth in response to technology advancements in efficiency of production, government policies for incentives, and the growing part of renewable methanol in driving decarbonization in industries. Blending the use of solar and wind sources of renewable energy with methanol production will provide higher sustainability levels and lower expenses. AI technology in optimizing process and automation will further enhance efficiency in methanol synthesis and logistics.
The global use of green methanol in transportation and chemical industries will help meet world emission reduction targets. With industries shifting to net-zero operations, renewable methanol will play an essential role in sustainable energy systems, promoting a circular economy and reducing fossil fuel reliance. Its widespread adoption as marine and road transport fuel would considerably lower carbon emissions from these sectors supporting international aims to transition to a greener future.
In addition, more public-private collaborations will see additional financing going into R&D, with a guarantee of continued improvement in scalable and cost-effective renewable methanol technology. Decentralized methanol manufacturing units will also improve local energy security and foster economic development in developing countries.
Market Shifts: A Comparative Analysis (2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035)
| Market Shift | 2020 to 2024 Trends |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Landscape | Supportive policies for low-carbon fuels and pilot projects |
| Technological Advancements | Early-stage carbon capture and biomass conversion technologies |
| Industry Adoption | Exploration of renewable methanol in shipping and fuel blending |
| Supply Chain and Infrastructure | Limited distribution and high transportation costs |
| Market Competition | Growth of early adopters and pilot projects |
| Market Growth Drivers | Rising demand for carbon-neutral fuels and regulatory pressure |
| Market Shift | 2025 to 2035 Projections |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Landscape | Expansion of carbon pricing, emission reduction mandates, and global incentives for renewable methanol adoption. |
| Technological Advancements | AI-driven optimization, large-scale green hydrogen integration, and improved electrolysis efficiency. |
| Industry Adoption | Widespread implementation in marine transport, aviation, and large-scale chemical manufacturing. |
| Supply Chain and Infrastructure | Expansion of global supply networks, dedicated storage solutions, and increased production capacity. |
| Market Competition | Entry of major energy and chemical companies investing in large-scale renewable methanol production. |
| Market Growth Drivers | Increased investment in circular economy models, industrial decarbonisation, and global energy transition. |
The renewable methanol market is being driven by government incentives for clean fuels, increasing demand for low-carbon transportation, and more investments in hydrogen-based methanol production in the United States. The USA DOE and EPA are working with the CCU technologies and bio-based methanol system to bring the urea and reduction solution to market.
It is driven predominantly by the automotive and marine sectors, with renewable methanol emerging as a fuel option for internal combustion engines and fuel cells. Methanol-blended gasoline and its application in biofuels are also under development for carbon reduction.
Increasing hydrogen economy in the USA also propels additional investments in renewable methanol as a hydrogen carrier. The USA renewable methanol market is anticipated to flourish throughout the growth period, owing to increasing carbon-neutral chemical manufacturing demand and green fuel generation.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| USA | 10.1% |
The UK renewable methanol market is fuelled by strong support from the government for decarbonisation, greater investments in green hydrogen, and an increasing demand for sustainable fuels in shipping and aviation, among other factors. The UK is now a part of 2050’s net-zero emissions target, encouraging industries to use renewable methanol as a more sustainable alternative to fossil-based chemicals and fuels.
Methanol is becoming increasingly interesting as a low-carbon marine fuel, particularly in the maritime sector in ports and ferry operations. Renewable methanol is also being explored for the development of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) - supporting the UK’s intention to ensure more environmentally friendly air travel
Other initiatives in the UK government, regarding carbon capture and storage (CCS) and renewable energy production, are also driving demand for bio-methanol and electro-methanol. Supported by its industrialisation and regulatory support, the UK renewable methanol market could witness consistent growth.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| UK | 9.2% |
The European Union renewable methanol market is soaring due to stringent environmental policies, high adoption of green fuels in transportation, along with growing investments in circular carbon technologies. European Union (EU) s Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) and Green Deal initiatives are also fuelling a shift towards low-carbon fuels in industrial and mobility sectors.
Germany, France and the Netherlands leading with adoption of bio-based and hydrogen-derived methanol in automotive, chemical and maritime applications. The shipping industry is a top driver, as methanol is emerging as an alternative fuel option for compliance with International Maritime Organization (IMO) emission regulations.
In addition, European oil and gas companies are also investing in power-to-methanol (PtM) projects in which captured CO₂ is converted into methanol using renewable energy. Increased focus on EU fossil fuel dependencies and hydrogen infrastructure will further accelerate market growth.
Underpinned by solid policy support and a growing number of industrial applications, the EU renewable methanol market is set for sustained growth.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| European Union (EU) | 9.6% |
Japanese renewable methanol market is expanding rapidly due to government efforts in the clean energy sector, increasing interest in hydrogen-based methanol production, and growing demand for low-carbon fuel sources. Japan is at the forefront of carbon-neutral energy technologies with companies exploring methanol synthesis from green hydrogen and waste CO₂.
Key consumers include the automotive and chemical sectors, which use methanol in fuel blending, synthetic chemical production and hydrogen fuel applications. The support of the Japanese government for green ammonia and methanol-based power generation also creates new opportunities.
Furthermore, Japan’s shipping industry is also looking at methanol as a bunker fuel to meet IMO’s 2050 decarbonisation objectives. The Japanese renewable Methanol market will grow steady with strong research and development of carbon capture and alternative fuels.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Japan | 9.4% |
The South Korea renewable methanol market is projected to grow over the next few years owing to rising investments in hydrogen energy, escalating adoption of green fuels for industrial applications and government policies promoting carbon neutrality. Industries are utilizing renewable methanol as a fuel alternative for power generation and transportation to promote the Korean New Deal and Carbon Neutrality Roadmap.
Shipping is a big growth pivot, with methanol a focus of interest as a marine fuel to cut emissions for South Korea’s large shipbuilding and maritime logistics industry. Petrochemical firms are also incorporating renewable methanol into the production of sustainable chemicals.
As investments in carbon capture, green hydrogen and waste-to-methanol projects ramp up, the South Korean renewable methanol market will keep growing steadily.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| South Korea | 9.5% |
The biomass and waste industries account for significant share of renewable methanol market as more transition to low-carbon alternatives lessen environmental impact and optimize sustainability across transportation, chemicals, manufacturing. These primary sources play critical roles in cleaner fuel, less fossil dependence, optimizing waste conversion-essential for green transition, circular economy, decarbonization.
Emerging as widely-used renewable methanol source, biomass offers abundant availability and carbon-neutral properties and compatibility with existing methanol technologies. Unlike fossil methanol, biomass methanol synthesis gasifies and catalytically converts organic matter ensuring lower footprints and impacts.
Stringent emission rules, clean energy incentives, rising green fuel adoption fuel bio-based methanol adoption as energy producers prioritize sustainable feedstocks replacing conventional. Studies show biomass methanol cuts emissions up to 95% versus fossil, ensuring better compliance and sustainability long-term.
The expansion of second-generation biomass-residues, wastes, energy crops-for methanol strengthened demand, ensuring greater adoption in waste projects and bio-refineries. Integrating advanced gasification, hydrolysis, fermentation hybridized biomass conversion boosted adoption through better efficiency, less energy used, reduced costs. Developing carbon-negative biomass methanol optimizes growth through sequestration, capture, recycling-greater adoption in neutral fuels and sustainable manufacturing. Adopting biomass methanol in aviation, shipping reinforced expansion through blended biofuels, jet conversion, emissions fuels compliance with IMO, ICAO standards.
Despite sustainability, neutrality, availability advantages, biomass methanol faces challenges as constraints, high capital costs and scalability limitations. Emerging AI sourcing, bio-catalytic synthesis, blockchain transparency improve efficiency, economics, commercializing potential continuing growth.
Industrial waste-based methanol development has significantly grown in traction, notably in carbon capture and reuse (CCR), transforming waste into fuel, and substance reusing, as producers progressively leverage CO2-wealthy emissions and procedure byproducts to synthesize uncharted forms of renewable methanol.
In contrast with conventional methanol making, waste-based methanol is created through carbon recycling infrastructures that seize and recycle industrial fumes, synthesis gas, and CO2 outflows into methanol, confirming a closed-loop carbon cycle and enhanced resource efficiency.
The expanding requirement for CCR-centered methanol fabrication in metal, concrete, and substance industries, highlighting straight CO2 hydrogenation and catalytic methanol synthesis from fumes, has pushed adoption of waste-derived methanol, as corporations seek to decrease carbon footprints and accomplish net-zero emissions targets. Evaluations exhibit that trash-based methanol can moderate approximately 1.4 tons of CO2 for each ton of methanol synthesized, legitimizing meaningful discharge reductions and advanced carbon offset capability.
The magnification of waste-to-methanol undertakings, focusing on refuse gasification, synthesis gas refinement, and plasma-aided methanol formation, has boosted requirement, guaranteeing more extensive reception in carbon reusing, fuel blending, and maintainable petrochemical creation.
Additionally, smaller tests have proven the viability of novel plasma reactors for direct waste conversion to methanol, a promising path toward enhanced scalability and more extensive geographical appropriateness to supplement or supplant customary landfilling. Although preserving challenges stay, including expense and network support, the possible environment and monetary advantages of carbon negative methanol recommend continued advancement and industrial authorization on local and worldwide scales will be fundamental for a cleaner energy future.
The integration of AI-powered process optimization in waste methanol manufacturing, highlighting real-time emission observation, adaptive catalytic administration, and automated feedstock modifications, has additionally boosted adoption, guaranteeing improved conversion proficiency, lessened operational risks, and enhanced process scalability.
The evolution of net-zero industrial methanol plants, highlighting entirely incorporated carbon capture, hydrogen electrolyzers, and closed-loop methanol conversion cycles, has optimized market growth, guaranteeing greater adoption in next-generation energy and chemical production structures.The emergence of waste-based methanol fuels has strengthened due to power-to-methanol technologies harnessing renewable hydrogen and electrochemical carbon dioxide conversion.
This has supported a broadening market by enabling greater fuel diversity, improved energy storage solutions, and enhanced compatibility with developing energy systems. While reducing emissions, closing resource loops and achieving carbon neutrality, producing waste-based methanol also faces hurdles such as high costs associated with novel technologies, limited carbon capture infrastructure and barriers inhibiting carbon recycling adoption.
However, cutting-edge innovations in artificial intelligence optimized carbon reuse, next-generation catalytic approaches synthesizing methanol and green hydrogen powering carbon dioxide transformation are amplifying scalability, economic viability and policy alignment. If continued, such improvements will further stimulate marketplace expansion for renewably-derived methanol from discarded resources.
Renewable methanol has attracted considerable attention from a variety of industries as synthetic producers and energy firms increasingly adopt low-carbon methanol to enhance performance, minimize carbon emissions, and improve fuel blending approaches.
One of the greatest end-use applications for sustainable methanol, for example, has been its use as a building block in the production of formaldehyde, where chemical producers increasingly integrate bioprocess methanol produced from renewable resources into formaldehyde production, both to reduce dependability on fossil fuels and improve environmental sustainability. However, green methanol based formaldehyde is relatively less carbon intensive and confirms compliance with green chemistry principles and sustainability metrics.
The variability in applications of methanol for formaldehyde has increased as complexity arises in combinations such as glues, resins, and building materials. This prioritizes bio-derived adhesives alongside more eco-conscious coatings and sustainable lumber goods.
Consequently, the low-carbon formaldehyde has encouraged in the industries to pursue alternatives towards global carbon reduction goal. Although methanol-based formaldehyde is considered to be sustainable and carbon-neutral, it still has certain problems that need to be considered: uncertainty of feedstock prices, incompatibility during processing, and limited availability of green methanol supply network. Methanol's potential in anti-carbon and replacement of petroleum-based formaldehyde products is obvious.
But to maximize its climate-friendly potential, it will be crucial to navigate barriers of fluctuating costs, difficult compatibility and limited renewable infrastructure. Emerging developments in AI-guided synthetic synthesis, closed-loop processes converting methanol into formaldehyde and biological approaches enhancing feedstocks are optimizing output, expansibility and marketplace competitiveness, guaranteeing continued progress for formaldehyde programs utilizing lasting methanol production.
Blending gasoline with lasting methanol has gained strong marketplace acceptance, particularly in low-emission transportation fuels, other fuel standards and ethanol-methanol hybrid fuel mixtures as energy providers increasingly employ bio-derived methanol to boost octane ratings, decrease tiny particulate emissions and improve combustion efficiency.
Unlike regular gasoline additives, eco-friendly methanol-based fuel blends offer unparalleled knock resistance, guaranteeing improved engine function and decreased ecological effects. Despite advantages concerning emissions reduction, efficiency gains and regulatory adherence, eco-friendly methanol in gasoline mixing still encounters obstacles including infrastructure compatibility queries, stability worries and marketplace receptiveness restraints.
However, emerging breakthroughs in AI-guided fuel optimization, crossbred methanol-hydrogen fuel technologies and advanced methanol storage solutions are enhancing scalability, security and commercial practicality, making sure ongoing sector development for gasoline applications leveraging sustainable methanol genesis.
Concurrently, recent analysis has revealed that optimally-blended methanol combinations can provide double-digit cuts in greenhouse emissions and triple-digit boosts in driving range, particularly when paired with hybrid or electric powertrains, representing fantastic unrealized prospects for the auto industry, suppliers and surrounding communities alike if standardization and scaling challenges can be adequately addressed.
The renewable methanol market opportunity is significant with demand for low carbon fuel alternatives, sustainable chemical feedstocks and carbon capture utilization (CCU) technologies. Bio-methanol production, green hydrogen-based methanol synthesis, and AI-assisted carbon recycling are among a range of technologies companies are pursuing with the aim of improving efficiencies, sustainability, and cost. Such players range from global energy companies, specialty chemical manufacturers, and sustainable fuel producers driving innovation in biomass-to-methanol and electro-methanol and CO₂-to-methanol conversion technologies to other verticals.
Market Share Analysis by Company
| Company Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Methanex Corporation | 12-17% |
| OCI N.V. | 10-14% |
| Carbon Recycling International (CRI) | 9-13% |
| Enerkem Inc. | 7-11% |
| BioMCN (OCI N.V.) | 5-9% |
| Other Companies (combined) | 40-50% |
| Company Name | Key Offerings/Activities |
|---|---|
| Methanex Corporation | Develops bio-methanol and sustainable methanol production using biomass and waste CO₂ streams. |
| OCI N.V. | Specializes in renewable methanol for chemical and fuel applications, integrating green hydrogen and biomass gasification. |
| Carbon Recycling International (CRI) | Manufactures electro-methanol using CO₂ and hydrogen, focusing on zero-carbon methanol production. |
| Enerkem Inc. | Provides waste-to-methanol technology, converting municipal solid waste (MSW) into low-carbon methanol. |
| BioMCN (OCI N.V.) | Offers bio-methanol solutions for industrial and fuel applications, emphasizing carbon-negative production technologies. |
Key Company Insights
Methanex Corporation (12-17%)
Methanex the leader in the renewable methanol sector, providing sustainable methanol solutions through biomass and carbon capture technologies, optimizing the production of low-emission methanol.
OCI N.V. (10-14%)
OCI is a global leader in the production of bio-methanol, combining green hydrogen as a platform to enable sustainable chemicals and fuels
Carbon Recycling International (CRI) (9-13%)
CRI is a leader in electro-methanol production, using CO₂-to-methanol conversion to create zero-carbon fuels and chemicals.
Enerkem Inc. (7-11%)
Enerkem is cost-effective in CO₂ reduction for waste to methanol technologies for sustainable fuels.
BioMCN (OCI N.V.) (5-9%)
BioMCN produces renewable methanol from biomass and waste-based feedstocks to provide the industry and transport with low-carbon methanol solutions.
Other Key Players (40-50% Combined)
Next-generation bio-methanol, synthetic methanol, and carbon-neutral methanol is already produced by a number of energy and chemical companies. These include:
The overall market size for Renewable Methanol Market USD 254.6 Billion In 2025.
The Renewable Methanol Market expected to reach USD 631.1 Billion in 2035.
The demand for the renewable methanol market will grow due to increasing adoption of sustainable fuels, rising environmental regulations on carbon emissions, growing interest in green hydrogen and bio-based chemicals, and expanding applications in transportation, chemicals, and power generation sectors.
The top 5 countries which drives the development of Renewable Methanol Market are USA, UK, Europe Union, Japan and South Korea.
Biomass and Industrial Waste Drive Market to command significant share over the assessment period.
Diamond Wire Market Size & Outlook 2025 to 2035
Thioesters Market Growth & Trends 2025 to 2035
The Self-Healing Materials Market is segmented by product, technology, and application from 2025 to 2035.
Polyurethane Foam Market Size & Trends 2025 to 2035
Polyurethane Adhesives Market Trends 2025 to 2035
Heat Resistant Glass Market Size & Trends 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.