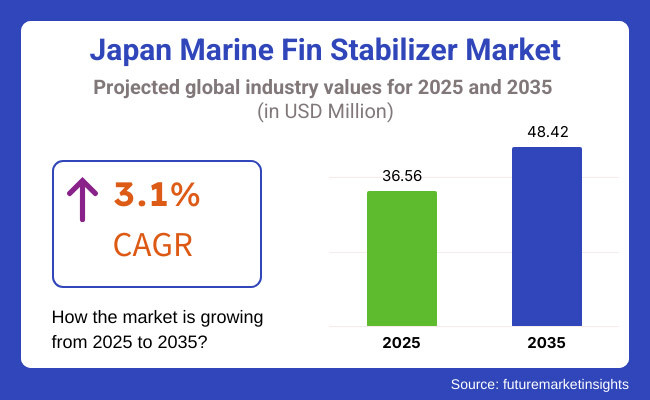
The Japanese marine fin stabilizer market is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 3.1% during the forecast period of 2035. The Japanese market will be valued at USD 36.56 million in 2025. It is forecasted to grow by USD 48.42 million by 2035.
Japan's marine fin stabilizer market saw steady growth in 2024. The industry growth is fueled by the growing demand for fuel-efficient and environment-friendly maritime technologies. Growing interest in fuel savings and reducing carbon emissions in shipping economies is likely to trigger higher investment in advanced stabilization systems.
Japanese shipowners and ship operators particularly made significant investments to fit their fleets with new generation stabilizers in response to tighter environmental regulations and offer onboard comfort on commercial and travel ships.
Moreover, innovation in technology in marine stabilizers, such as the use of smart sensors and predictive maintenance, also propelled the industry. The sector was also aided by growing demand for luxury cruise ships, which require the best stabilizing systems for more comfortable and smoother travel.
During 2025, the industry should continue to expand. The requirements for sustainability across marine operations should drive more utilisation of environmentally friendly and energy-efficient stabiliser solutions. While the trends within global shipping remain to evolve, the Japanese marketplace should expect ever greater competition from the leaders of the industry, driving innovation towards more affordable, reliable technology.
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
Future Market Insights has undertaken a series of surveys with major stakeholders operating in the marine fin stabilizers market. In line with the surveys, we gathered precious information on industry trends, growth drivers and future projections. The survey was carried out across a diversified array of stakeholders including shipowners, manufacturers, suppliers and maritime technology experts. The aim of the industry was to understand evolving needs of the industry and adopt new technologies and the impact of regulatory changes on the industry.
The findings indicated stakeholders were increasingly concerned with sustainability and fuel efficiency in operations. Most of the respondents highlighted compliance with environmental regulations and driving demand for stabilization solutions involving low energy and carbon emissions. The surveys have also confirmed a trend towards more high-tech, digitalized and stabilized systems.
The stakeholders were very interested in intelligent sensor-integrated technologies with predictive maintenance features that improve system reliability and reduce operation downtime.
One of the biggest trends observed from the survey was the growing demand for luxury cruise ships and upscale vessels. The respondents revealed that the cruising public more and more desires smoother and more comfortable cruises, which has resulted in more investment in high-performance fin stabilizers.
| Country | Regulations Impacting the Marine Fin Stabilizer Market |
|---|---|
| Japan | Japan’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) enforces regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions from ships. The Environmental Protection Laws and the "Energy Conservation Law" push for energy-efficient technologies like stabilizers. Japan’s adoption of stricter emission standards under the International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations also encourages the adoption of advanced stabilizers. |
| United States | The USA follows IMO regulations, particularly the Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI) and the Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII). The Jones Act also mandates the use of domestic vessels and associated technologies, promoting the demand for USA-made stabilizer solutions. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations enforce energy efficiency and pollution control, further driving the adoption of stabilizers. |
| European Union | The EU has a robust regulatory framework with the EU MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification) regulation to monitor CO2 emissions from ships. The EU's Green Deal and specific maritime environmental directives encourage the adoption of energy-efficient technologies, including stabilizers, to comply with carbon reduction goals and minimize fuel consumption. |
| China | China's enforcement of stricter environmental regulations, like the "Emission Control Area" (ECA) laws, has pushed for greater adoption of fuel-efficient technologies. These regulations, combined with the Chinese Maritime Safety Administration (CMSA) policies, promote the use of energy-saving devices such as fin stabilizers to meet sustainability and emission targets. |
| South Korea | South Korea enforces the IMO’s sulfur cap regulations and focuses on reducing maritime pollution through national laws. The country encourages the use of advanced stabilization systems to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions in its shipping industry, thereby driving the demand for high-performance stabilizers. |
| India | India adheres to IMO regulations for emission reductions, with increasing emphasis on compliance with international environmental standards. The government’s initiatives, like the National Maritime Development Programme, also promote the adoption of cleaner and more energy-efficient technologies, including stabilizers for reducing fuel consumption and improving operational efficiency. |
Japanese firms like Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) and Nabtesco are integrating AI and machine learning into fin stabilizers, enabling real-time performance optimization. These advanced systems proactively predict wave patterns and adjust fin angles, significantly cutting energy consumption by up to 20%. This technology improves fuel efficiency and actively supports Japan's decarbonization efforts in maritime shipping.
Japan's Green Innovation Fund strongly supports maritime electrification, motivating companies like Kawasaki Heavy Industries to introduce hybrid stabilizers compatible with electric propulsion systems. These innovations specifically target hybrid ferries and LNG carriers, aligning directly with the IMO’s emission targets for 2030 and 2050 and Japan’s goal to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
Stabilizer manufacturers such as Kongsberg actively collaborate with Japanese autonomous shipping initiatives, including the Nippon Foundation’s MEGURI2040 Project. These partnerships customize stabilizers specifically for unmanned vessels, ensuring stability during remote operations and positioning Japan as a global leader in autonomous maritime technologies.
Post-pandemic recovery has spurred demand for luxury cruise ships, benefiting Japanese shipyards like MHI’s Nagasaki Shipyard, which has secured numerous orders. Advanced stabilizers significantly enhance passenger comfort, driving demand for high-end systems from companies such as SKF Marine and Nabtesco. Consequently, the stabilizer market in the cruise segment is projected to expand by approximately 8-10% annually.
Nabtesco and MHI are increasing production at facilities in Japan to reduce exposure to global supply chain disruptions. This localization strategy decreases dependency on imported parts, for example, actuators, sensors, etc., cutting lead time and improving the overall supply chain resilience in case of any geopolitical ambiguities. The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) is encouraging the retrofitting of older ships with the latest stabilizers to maintain compliance with stringent emissions standards set to be implemented in 2024.
That regulatory push establishes a retrofit market of more than USD 50 million, and opportunities for industry leaders like Kongsberg and Quantum Marine Stabilizers. Despite this, demand for stabilizers onboard vessels of under 60m - such as coastal ferries, fishing boats and yachts - remains robustly strong. In turn, Kawasaki and Nabtesco have developed compact and lightweight cost-effective stabilizer systems that effectively widen the scope of the market beyond large commercial vessels. As more stabilizers are connected to vessel networks, Japanese companies focus on strong cybersecurity.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries in concert with Fujitsu are continuously improving cyber-protection protocols to defend stabilizer systems against cyber-attackers - a foundation critical to safe operations within smart shipping ecosystems. In Europe, SKF and Kongsberg are deepening partnerships with Japanese shipbuilders-Imabari Shipbuilding in particular-to develop the next generation of stabilizers.
An example of this international collaboration is SKF's 'Blue Fin' stabilizer, designed specifically for Japanese-built LNG carriers. After-sales services are becoming more significant for the manufacturers as IoT sensors are deployed for predictive maintenance to monitor the condition of a stabilizer.
With subscription-based packages for maintenance, offered by industry leaders MHI and Kongsberg, such offerings can generate predictable, recurring revenue streams while providing a significant boost to customer retention. On one end, some industry events happening in 2024 such as Sea Japan 2024 Expo in Tokyo in April − a massive platform for stabilizer technologies − and the IMO MEPC 81 in March where new maritime regulations can have considerable impact on stabilizer demand.
Kanto is the economic hub of Japan, including Tokyo and its surrounding areas. It is a key region for the marine fin stabilizer industry. The area is one of Japan's busiest ports, including Tokyo and Yokohama, which are located in the region, leading to demand for advanced maritime technologies.
Shipowners and operators in the Kanto area value fuel efficiency and compliance with environmental regulations and continue to deploy energy-saving stabilizers. Additionally, the region is home to a substantial number of major shipbuilders, maritime suppliers, and technology innovators, all of which contribute to industry expansion. This also helps boost demand for complex stabilizer systems that enhance passenger comfort to operators of luxury yachts and cruise ships, with Kanto being home to many such operators.
Another key region for the marine fin stabilizer industry is Chubu, located in central Japan. The area includes Nagoya, one of Japan’s major industrial cities that has a robust maritime industry.
The region also has a wide manufacturing base supporting shipbuilding and the marine equipment industry, contributing to increasing demand for stabilizer solutions. The strategic geographic position of Chubu along the Pacific coast emphasizes its importance in domestic and international maritime trade, creating additional demand for efficient stabilization systems.
Shipowners throughout the region, and especially those in the commercial shipping industry, are looking to advanced stabilisers to comply with sustainability targets and regulatory demands.
The Kinki region is the metropolitan area of Japan that includes Osaka, Kobe and Kyoto. The area is pivotal to the nation’s marine fin stabilizer sector. It has two important ports, Osaka and Kobe, which are active in the fields of shipping and maritime trade in the country. Kinki is one of Japan’s economic hubs that has an increasing demand for sophisticated stabilization systems on commercial and recreational vessels. With strong manufacturing capabilities, and especially with shipbuilding, the region can provide high-quality stabilizer systems. Additionally, as regional investments in sustainable technology continue to increase, the implementation of energy-efficient marine solutions, such as fin stabilizers, for reduced fuel consumption and emissions is becoming more prevalent in Kinki.
Kyushu & Okinawa are the major regions of southern Japan with proximity to major shipping routes and active Japanese ports such as Fukuoka and Kitakyushu. The area is lucrative for both commercial shipping and the naval domain.
Here, the need for stabilizer systems to ensure the stability and fuel efficiency of vessels is poised to be on the rise. Kyushu has been the base for several shipbuilders and maritime technology companies, which has initiated the growth of the marine stabilization industry. Demand for a range of fin stabilizers, specifically for cargo ships and naval vessels, continues to rise as shipping companies concentrate on sustainability and regulatory compliance in the region.
Located in northern Japan, Tohoku supplies essential shipping for both domestic and international industry s. While Tohoku is not as industrially powerful as Kanto or Chubu, the region’s ports, including Sendai and Kitakami, facilitate ample maritime activity, particularly in fishing, cargo and logistics.
Japan's industrial transformation towards greener technologies and greater emissions controls, Tohoku's shipping companies and operators are also adopting more and more marine stabilizers to enhance their energy efficiency and lessen their environmental impact. Although the region doesn't have as many luxuries or fast boats as other areas, there's increasing interest in fuel-efficient technologies, which is boosting the demand for the latest stabilisation solutions.
The ‘rest of the Japan’ segment covers areas outside key economic and seaports. These are the rural coastal areas and minor ports where sea activities are prominent to local communities. The region is less industrialised than other regions of the country. However, the demand for marine fin stabilizers is still surging rapidly. This demand is driven by smaller ships. Local cargo shipping and greater environmental awareness. The rest of Japan is an emerging industry with substantial potential for growth in the upcoming years.
Retractable fin stabilizers are anticipated to lead the industry in the upcoming decade by 2035. Their demand is fueled by the fact that they can be retracted during non-working periods, which saves fuel and reduces drag. They are one of the most prominent in the high-end craft such as cruise ships, yachts and superyachts. Where there is an emphasis on comfort and adherence to the environment. They are expected to account for a share of nearly 65% in 2025.
Non-retractable fin stabilizers will have steady demand, particularly in commercial ships such as bulk carriers and fishing ships, appreciated for their simplicity, reliability, and cost savings. In contrast, anchor or rest stabilizers will have a steady demand in smaller ships, particularly fishing ships, as they minimize roll and maximize stability at anchorage, particularly with rising port congestion.
Passenger ships will keep demand for marine stabilizers high as comfort and safety are of prime importance. As passenger expectations for smooth travel increase, especially on long journeys, stabilizers will be in greater demand, particularly in cruise liners and ferries. Demand for luxury cruises and green ferry operations will drive the uptake of stabilizers that minimize roll and pitch and assist in fuel efficiency and environmental regulation.
Passenger and car ferries will also experience a consistent demand for stabilizers as the world ferry industry grows. Ferries, which tend to operate in congested and turbulent conditions, require stabilizers to ensure smoother travel for passengers and cars, especially in heavy seas. The increasing emphasis on fuel efficiency and environmental issues will compel ferry operators to invest in stabilizing systems. The passenger segment is expected to account for a share of nearly 76% in 2025.
Cruise vessels will remain an important segment even as demand for luxury and comfort continues to rise. Passengers prefer offloading their journey on a smooth and stable ride; thus, influencers of demand will be the strong and high-tech stabilizers that also minimize emissions and maximize fuel efficiency at the same time.
The yachts and superyachts sector will exhibit robust growth as wealthy individuals demand smoother cruising. With increased interest in world cruising, green and fuel-efficient stabilizers will be requisite.
This leads to an increasing demand for advanced stabilizers in naval and coast guard ships for operational stability, safety, fuel efficiency, and sustainability in fishing and merchant ships.
The first fit industry for marine stabilizers will continue to be a key driver of the industry between 2025 and 2035. The demand of the sector is driven by the building of new ships, particularly luxury cruise ships, yachts and passenger ships. Shipbuilders will focus on incorporating advanced stabilisation systems to meet the needs of the fuel economy, aligned with comfortable sailings and compliance with environmental regulations.
The retrofit segment will also enjoy strong growth, particularly in commercial shipping and fishing. This segment is expected to witness significant growth as retrofit solutions offer a cost-effective way to enhance stability and sustainability.
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| The industry experienced steady growth, driven by a focus on improving vessel performance and passenger comfort. | The industry is expected to witness significant growth, driven by rising environmental regulations and demand for energy-efficient technologies. |
| The COVID-19 pandemic had a temporary impact on the cruise and tourism sectors, leading to a slowdown in demand for stabilizers in luxury vessels. | Post-pandemic recovery in the cruise industry and growing demand for passenger vessels, ferries, and yachts will drive a robust recovery. |
| Retrofit solutions became a priority as many older vessels required upgrades to meet stricter emission and performance regulations. | Retrofit solutions will continue to grow as older fleets are modernized to meet stricter environmental regulations and fuel efficiency goals. |
| The focus on luxury vessels like superyachts and cruise ships increased, with a strong demand for high-performance stabilizers to ensure smooth voyages in rough seas. | Growth in the superyacht and luxury cruise industries will continue, with advanced stabilizers that enhance comfort and operational efficiency. |
| A rise in fuel prices and a push for sustainability led shipowners to increasingly seek stabilizers that reduce fuel consumption and emissions. | As sustainability becomes even more critical, stabilization technology will be central in minimizing emissions and improving operational efficiency for all vessel types. |
| There is a strong demand for stabilizers in fishing vessels and merchant ships, with a focus on reducing roll and improving stability. | Demand for stabilizers in commercial vessels like fishing boats and merchant ships will continue to grow as fuel efficiency and environmental regulations evolve. |
| Leading players like Rolls-Royce and Humphree dominated the industry, providing a wide range of stabilization solutions. | Market consolidation and partnerships will continue, with innovation from leading players focusing on smart stabilization solutions and integration with other vessel technologies. |
The marine fin stabilizer industry is a part of the overall maritime and shipbuilding industry encompassing marine and ship-related industry s covering vessel performance, safety, and others. There are several macroeconomic factors impacting the industry, including global trade, shipping demand, environmental regulations, and technological advancements.
Market demand from both commercial and luxury vessels is being driven by an increased focus on fuel efficiency, sustainability and passenger comfort. The phase-out is occurring amid rising maritime activity globally, especially in the cruise and passenger sectors, as the global economy recovers from the pandemic. In addition, strict environmental regulations and fluctuating fuel prices are compelling operators to use stabilizers to reduce carbon emissions and enhance operational efficiency.
The marine fin stabilizer industry offers various growth opportunities, especially in technology. Businesses can invest in creating fuel-efficient and environment-friendly stabilizers, like retractable and smart technologies that enhance performance. These will also align with stringent environmental regulations and surging demand for enhanced vessel performance.
Additionally, Strategic alliances, mergers, and acquisitions will boost industry reach and R&D strength. Alliances with shipbuilders for first-fit stabilizer installations and takeovers of eco-oriented technology companies can fuel innovation. The retrofit market also holds significant growth prospects, with aging ships requiring retrofits to meet newer regulations. Providing cost-efficient retrofit solutions, as well as maintenance services, will be paramount.
They improve vessel stability by reducing roll and enhancing comfort.
They reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency when not in use.
Passenger ships, yachts, ferries, fishing vessels, and merchant ships.
First-fit stabilizers are installed in new vessels, while retrofit ones are added to older vessels.
They enhance passenger comfort by reducing motion, especially in rough seas.
Automotive Load Floor Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Automotive Glass Film Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Automotive Sensors Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Bicycle Components Aftermarket Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Automotive TCU Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Automotive Wires Market Growth – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.