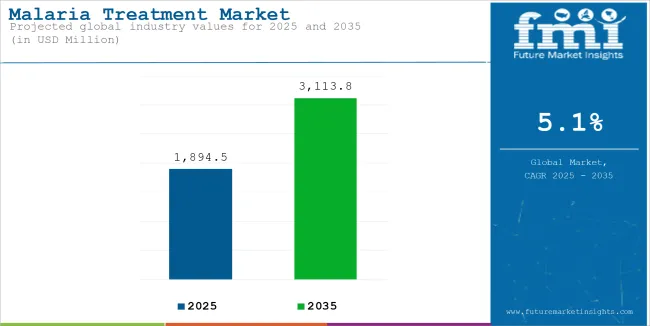
The global sales of malaria treatment is estimated to be worth USD 1,894.5 million in 2025 and anticipated to reach a value of USD 3,113.8 million by 2035. Sales are projected to rise at a CAGR of 5.1% over the forecast period between 2025 and 2035. The revenue generated by malaria treatment in 2024 was USD 1,830.6 million.
Malaria is a, life-threatening parasitic disease caused by Plasmodium parasites by the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes in humans. In terms of tropical and subtropical regions, most cases occur. Sub-Saharan Africa bears the maximum burden of such cases.
This disease presents severe symptoms, among which include fever, chills, and headache, causing severe conditions sometimes leading to organs failing or deaths. Prevention techniques, diagnostic products, and curative medicines comprise antimalarial drugs and vaccines. The growing number of malaria cases in endemic regions fuels the growth of the market.
WHO reported more than 247 million malaria cases in 2022, indicating a strong demand for effective treatments and preventive measures.
Global Malaria Treatment Industry Assessment
| Attributes | Key Insights |
|---|---|
| Historical Size, 2024 | USD 1,830.6 million |
| Estimated Size, 2025 | USD 1,894.5 million |
| Projected Size, 2035 | USD 3,113.8 million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.1% |
Coordination of global strategies, technical support, and monitoring of progress in malaria prevention, control, and elimination through efforts such as the WHO Global Malaria Program help ensure access to effective treatments, strengthen healthcare systems, and address challenges such as drug resistance.
Furthermore, a multitude of funds from organizations such as the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria sees a boost in affordable, high-quality drugs available in low and middle-income countries.
The Global Fund has allocated billions of dollars towards malaria programs in different countries, making a multitude of life-saving drugs and RDTs widely distributed, and ITNs available for the improvement of the malaria situation.
Besides, philanthropic organizations such as the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation have invested significantly in malaria research and development. Their efforts target innovative treatment, including single-dose cures and vaccines, and also improve drug availability in under-served areas.
Government involvement is equally important because national malaria programs have implemented a subsidized treatment policy, free drug distribution campaigns in endemic areas for essential drugs, and preventive measures in endemic areas. Public-private sector coordination further strengthens these efforts.
Together, this concentrated effort not only accelerates the development and spread of malaria treatment but also directs these solutions toward vulnerable populations. This drives steady growth in the market.
The global malaria treatment market's compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the first half of 2024 and 2025 is compared in the table below. This analysis provides important insights into the performance of the industry by highlighting significant shifts and trends in revenue generation.
The first half (H1) is the period from January to June, and the second half (H2) is July to December. In the first half (H1) of the decade from 2024 to 2034, the business is predicted to surge at a CAGR of 6.2%, followed by a slightly lower growth rate of 5.8% in the second half (H2) of the same decade.
| Particular | Value CAGR |
|---|---|
| H1 | 6.2% (2024 to 2034) |
| H2 | 5.8% (2024 to 2034) |
| H1 | 5.1% (2025 to 2035) |
| H2 | 4.7% (2025 to 2035) |
Moving into the subsequent period, from H1 2025 to H2 2035, the CAGR is projected to decrease slightly to 5.1% in the first half and remain relatively moderate at 4.7% in the second half. In the first half (H1) the industry witnessed a decrease of 110 BPS while in the second half (H2), the industry witnessed a decrease of 110 BPS.
Rising global incidence and prevalence of malaria drives growth of malaria treatment
Malaria remains a great challenge to health worldwide, especially in tropical and subtropical regions where there is an increase in the development of Anopheles mosquitoes as the primary vectors for Plasmodium parasites.
The WHO reports that, in 2022, over 247 million cases of malaria were reported in the world with the highest disease burden being shared between Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. Children under five and pregnant women are the most vulnerable groups, accounting for the majority of deaths.
This persistent prevalence has underscored the need for proper treatments against the disease. With the increased health and economic burdens of malaria, there has been a focus on developing effective antimalarial drugs. Countries with the highest rates of incidence suffer from recurrent infections, drug resistance, and restricted access to health facilities, making innovative and reliable treatments even more important.
In addition, the heavy burden of malaria attracts immense attention from governments, international organizations, and private sectors, hence investments in R&D and massive issuance of antimalarial drugs.
For such a long time that malaria remains endemic in several parts of this world, the wide spread the disease is will be a crucial locomotive for the long-term growth that the global market for malaria treatment will experience.
Advancements in antimalarial drug development fuels growth of malaria treatment
The advancements in developing antimalarial drugs are considered one of the major factors that drive the growth of the malaria treatment market. In regions, particularly Southeast Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, the sudden emergence of resistance to antimalarial drugs has compelled research and development for the identification of novel therapies.
Several pharmaceutical companies and research institutions are now investing in the development of next-generation drugs that will offer enhanced ACTs and single-dose treatments that ensure better compliance and effectiveness.
Furthermore, there are innovative formulations, including pediatric-friendly dispersible tablets and extended-release drugs that have also raised market demand to give better care to vulnerable populations, including pregnant women and children. Further, clinical trials for new antimalarials, such as tafenoquine and triple ACTs, continue to seek to offer even better prevention and treatment.
Global funding and partnerships, like those provided by the Medicines for Malaria Venture and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, accelerate the discovery and distribution process.
These efforts improve treatment outcomes and also increase the market by addressing the unmet needs of malaria-endemic regions. Collectively, these innovations drive growth in the malaria treatment market by offering safer, more effective, and accessible therapeutic options.
Increasing public-private partnerships offers an opportunity for market growth
Public-private partnership is also considered a crucial opportunity, creating a bond among pharmaceutical companies, governments, and NGOs to address the global malaria burden. In Public-private partnership, different stakeholders harness each other's strengths such as innovation and production capacity by private partners, policy-making, and financing mechanisms by the governments.
Examples include initiatives such as the Medicines for Malaria Venture, which demonstrate how PPPs have driven access to affordable, high-quality antimalarial drugs. These collaborations pool resources and expertise to accelerate R&D and ensure that advanced treatments, including ACTs and novel drugs such as tafenoquine, reach the most vulnerable populations in endemic regions.
While the governments and organizations like the Global Fund and WHO are very important in subsidizing the cost of the drugs, private companies ensure large-scale manufacturing and distribution. NGOs facilitate outreach and education, thereby increasing awareness and access at the community level.
The advantage of such a partnership increases market penetration through cost reduction and accessibility of the products, therefore guaranteeing that healthcare systems are sustainable, capable, and responsive to the needs of control and elimination. In this rapidly developing malaria treatment market, stakeholders are offered a great opportunity to achieve common goals with expanding PPPs.
Emergence of drug resistance hinder the market growth
Artemisinin, the cornerstone of ACTs, is the drug that is increasingly being subjected to resistance. Its growing resistance threatens the efficacy of ACTs, which are perceived currently as the most effective treatments against malaria. Resistance goes directly against the achievement of better treatment outcomes, increases the chances of treatment failures, and further complicates disease management efforts across the world.
Improper use of antimalarial drugs often increases drug resistance, such as incomplete courses of treatment or reliance on monotherapies rather than combination therapies. Poor quality and counterfeit drugs are prevalent in a number of malaria-endemic countries and facilitate the development of the resistant strain.
It requires constant struggle in developing new drugs, which is time- and money-consuming. This dependency on R&D burdens healthcare systems and pharmaceutical companies, hence prolonging the arrival of next-generation treatments.
Since resistance continues to spread, particularly to high-burden regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa, it threatens to reverse the gains made in malaria control and elimination, thus being a significant restraint to the growth and effectiveness of the global malaria treatment market.
The global malaria treatment industry recorded a CAGR of 4.1% during the historical period between 2020 and 2024. The growth of malaria treatment industry was positive as it reached a value of USD 3,113.8 million in 2035 from USD 1,894.5 million in 2025.
The treatment market of malaria was almost based on the use of monotherapies, including chloroquine and quinine. These drugs initially worked well; however, misuse and their excessive use promoted the development of resistant Plasmodium strains, especially P. falciparum. Poor diagnostic methods and poor infrastructure in health systems of endemic countries were other constraining factors of management of malaria.
In the present scenario, the market has progressed significantly, with ACTs becoming the gold standard for treatment. Innovations such as tafenoquine for P. vivax and pipeline drugs targeting resistant strains highlight progress in drug development.
Enhanced diagnostics, government initiatives, and global funding from organizations like the Global Fund have improved treatment accessibility, although challenges such as resistance and healthcare disparities remain pressing concerns.
Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) have greatly revolutionized malaria treatment, especially in regions with resistant Plasmodium falciparum strains. ACTs are artemisinin derivatives combined with partner drugs to enhance efficacy and reduce the risk of resistance development. These treatments target various stages of the parasite lifecycle, hence rapid relief of symptoms and high cure rates.
ACTs are increasingly being recommended as first-line treatments in malaria-endemic regions because of their proven efficacy against drug-resistant strains. Integrations into national malaria programs, along with funding by organizations such as the Global Fund, have facilitated greater access and better treatment results.
This has resulted in high-scale adoption and solidifies ACTs as critical drugs in managing malaria, sustaining the growth trend of the global malaria treatment market.
Tier 1 companies are the industry leaders with 58.3% of the global industry. These companies stand out for having a large product portfolio and a high production capacity.
These industry leaders also stand out for having a wide geographic reach, a strong customer base, and substantial experience in manufacturing and having enough financial resources, which enables them to enhance their research and development efforts and expand into new industries.
The companies within tier 1 have a good reputation and high brand value. These companies frequently get involved in strategies such as acquisition and product launches. Prominent companies within tier 1 include Novartis AG, Sanofi, Ajanta Pharma, and Pfizer Inc.
Tier 2 companies are relatively smaller as compared with tier 1 players. The tier 2 companies hold a market share of 35.7% worldwide. These firms may not have cutting-edge technology or a broad global reach, but they do ensure regulatory compliance and have good technology.
The players are more competitive when it comes to pricing and target niche markets. Key Companies under this category include F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Merck & Co., Inc. and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK).
Compared to Tiers 1 and 2, Tier 3 companies offer malaria treatment, but with smaller revenue spouts and less influence. These companies mostly operate in one or two countries and have limited customer base.
The companies such as Cipla Limited, Ipca Laboratories and Others, and others falls under tier 3 category. They specialize in specific products and cater to niche markets, adding diversity to the industry.
The market analysis for malaria treatment in various nations is covered in the section below. An analysis of important nations in Latin America, Asia and Middle East & Africa of the world has been mentioned below.
It is projected that the Nigeria will maintain its leading position in Middle East & Africa through 2035, holding a value share of 62.6%. By 2035, India is expected to experience a CAGR of 4.8% in the Asia region.
| Countries | Value CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Nigeria | 7.0% |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | 6.8% |
| Uganda | 6.0% |
| Mozambique | 5.4% |
| Brazil | 4.3% |
| India | 4.8% |
Nigeria’s market is poised to exhibit a CAGR of 7.0% between 2025 and 2035. The Nigeria holds highest market share in the market.
Nigeria accounts for 27% of all malaria cases and 23% of all malaria-related deaths, and its burden is massive, making it a strategic market for the treatment of malaria. The tropical climate of the country ensures year-round breeding of mosquitoes, resulting in high levels of transmission throughout the country. High prevalence in vulnerable populations like children under five years and pregnant women creates constant demand for effective therapies such as ACTs.
Treatment access and affordability have improved through government initiatives, such as the National Malaria Elimination Programme (NMEP), supported by international partners like the Global Fund.
Rapid urbanization and population growth expose communities further to malaria, hence treatments are increased further. There has been enhanced awareness campaigns and diagnostics enhancing early detection and treatment rates.
Added to that, supportive policies, such as the provision of subsidies and promotion of local drug manufacturing, ensure wider availability of antimalarials. Collectively, all these factors have underlined the increasing incidence of malaria as the major growth factor for Nigeria's malaria treatment market.
Uganda is anticipated to show a CAGR of 6.0% between 2025 and 2035.
In Uganda, there are government and NGO initiatives, which are very fundamental in addressing the country's heavy malaria burden at 5% of the world's malaria cases. The access to treatment has been improved with the programs, such as the Ministry of Health's National Malaria Control Program, and the international efforts of the WHO's Global Malaria Program.
These initiatives are targeted at improving the distribution of effective therapies, such as Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies (ACTs), especially in rural and underserved regions.
NGOs, such as Malaria Consortium and PATH, are actively involved with local stakeholders to distribute free or subsidized antimalarial drugs and community health education. The interventions are supported by campaigns for the increased use of diagnostic tools and preventive measures such as insecticide-treated nets and indoor residual spraying.
Further, public private partnerships between the government and the international organizations ensure steady funding and operationalization of control measures. The approach creates an enabling environment for the expansion of Uganda's malaria treatment market in addition to reducing the disease burden.
India is anticipated to show a CAGR of 4.8% between 2025 and 2035.
Increased funding for research in India drives the growth of the malaria treatment market. Efforts to eradicate malaria have increased significantly through collaborative efforts between organizations such as the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Indian government, and local research institutions. Investments aim at developing novel treatments, enhancing diagnostics, and strengthening surveillance systems.
India has committed under the NFME to eliminate malaria by 2030, resulting in significant fund inflows internationally and domestically to support this program.
Such money enables the conduction of rigorous research on drugs that are more resistant to this disease, meaning that more robust treatments, for example, Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies (ACTs), can emerge. Research funding allows pilot projects and clinical trials on new antimalarial drugs and vaccines to be set up, like the RTS,S/AS01 malaria vaccine.
There is a greater number of these advanced treatments available due to increased availability, making this even more conducive to market growth. Increased funding accelerates innovation and expands access to effective solutions-all factors that can significantly shape the Indian malaria treatment landscape.
The section contains information about the leading segments in the industry. Based on drug type, the artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) segment is expected to account for 45.6% of the global share in 2023.
| By Drug Type | Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies (ACTs) |
|---|---|
| Value Share (2025) | 45.6% |
The Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies (ACTs) segment is projected to be a dominating segment in terms of revenue, accounting for almost 45.6% of the market share in 2025.
ACT will continue to lead the malaria treatment market due to unparalleled efficacy and an address to drug-resistant malaria strains. The ACTs combine a fast-acting compound artemisinin that rapidly reduces parasite load, with a longer-acting partner drug that completely removes the remaining parasites to prevent recurrence.
Being the first line of treatment, it has especially been highly recommended by the World Health Organization against Plasmodium falciparum malaria, known to be the most lethal form of the disease.
Since its vast governmental and international support further seeks its assurance for wide availability in malaria endemic regions of the world. Further, innovative formulations of ACT, such as fixed-dose combination and child-friendly dispersible tablets, facilitated ease of access to treatment and hence improved patient compliance. These factors make ACTs the leading segment in malaria treatment.
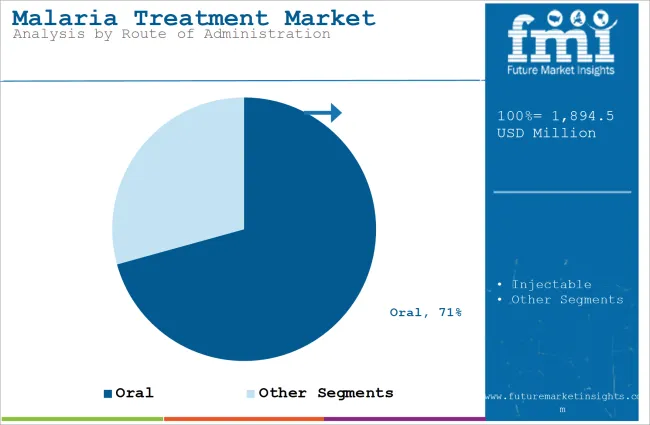
| By Route of Administration | Oral |
|---|---|
| Value Share (2025) | 70.7% |
The oral segment will dominate the industry in terms of revenue, accounting for almost 70.7% of the market share in 2025.
The oral segment is foreseen to dominate the malaria treatment market due to its convenience, affordability, and wide acceptance among patients. Oral formulations, in forms such as tablets and capsules, are easy to administer and, therefore, remain the preferred choice for outpatient care and large-scale distribution in resource-limited settings.
Oral preparations of artemisinin-based combination therapies, being among those most preferred, are very often availed in oral forms. Likewise, the governments and NGOs ensure accessibility even to the remotest, unserved areas through community health programs that also advocate the administration of oral antimalarials.
In addition, oral drugs will negate the requirement for special health infrastructure necessary for injectable therapies and will be cheaper, while decreasing the logistical challenges accompanying such. All these put the oral segment in the leading position in malaria treatment.
The malaria treatment industry faces a high competition, as there are large number of manufacturer. These manufacturers are focused on constantly innovating and improving their product portfolio.
Prominent producers of anti-malarial drugs are concentrating on growing internationally in order to increase their revenue and increase the size of their sales footprint in developing nations through the acquisition of regional small players. Manufacturers utilize various key strategies such as agreements, product launches, research sponsorship, and strategic collaborations to boost product sales and establish their market presence.
Recent Industry Developments in Malaria Treatment Market
In terms of drug type, the industry is divided into artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs), quinine and derivatives, antifolates, atovaquone-based drugs and others.
In terms of route of administration, the industry is segregated into oral and injectable.
In terms of type, the industry is segregated into branded and generic.
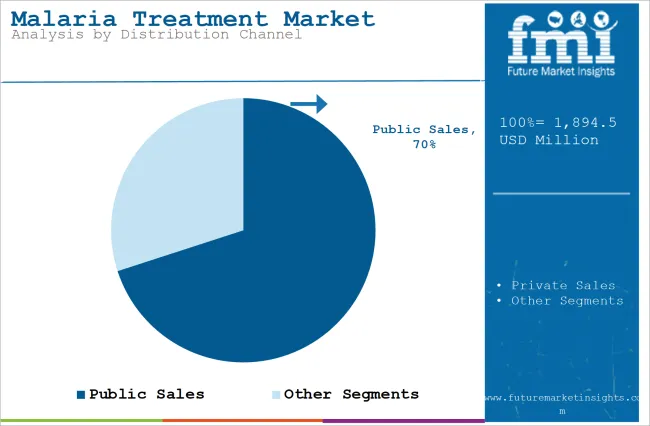
In terms of distribution channel, the industry is segregated into public sales and private sales.
Key countries of Latin America, Asia, and Middle East and Africa (MEA) have been covered in the report.
The global malaria treatment industry is projected to witness CAGR of 5.1% between 2025 and 2035.
The global malaria treatment industry stood at USD 1,830.6 million in 2024.
The global malaria treatment industry is anticipated to reach USD 3,113.8 million by 2035 end.
India is expected to show a CAGR of 4.8% in the assessment period.
The key players operating in the global malaria treatment industry Novartis AG, Sanofi, Ajanta Pharma, Pfizer Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Merck & Co., Inc., GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Cipla Limited, Ipca Laboratories and Others.






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Malaria Ag Rapid Testing Market - Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Anti-Malarial drugs Market
Treatment-Resistant Hypertension Management Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment-Resistant Depression Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Treatment Pumps Market Insights Growth & Demand Forecast 2025 to 2035
Pretreatment Coatings Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Air Treatment Ozone Generator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
CNS Treatment and Therapy Market Insights - Trends & Growth Forecast 2025 to 2035
Seed Treatment Materials Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Acne Treatment Solutions Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Scar Treatment Market Overview - Growth & Demand Forecast 2025 to 2035
Soil Treatment Chemicals Market
Water Treatment System Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Chemical Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Algae Treatment Chemical Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Ozone Generator Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Water Treatment Equipment Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Burns Treatment Market Overview – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
CRBSI Treatment Market Insights - Growth, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA