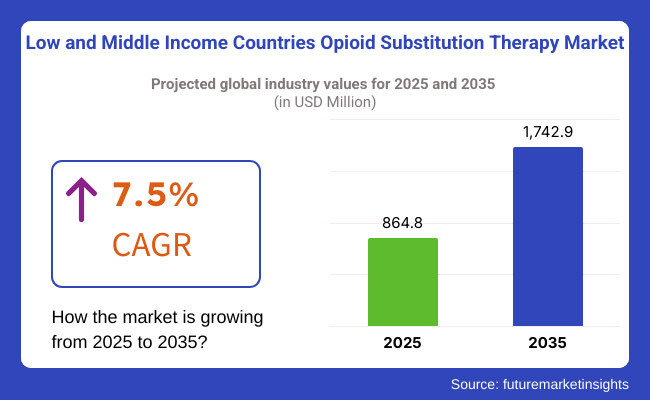
The low and middle income countries opioid substitution therapy market is slated to exhibit USD 864.8 million in 2025. The industry is poised to showcase 7.5% CAGR from 2025 to 2035 and reach USD 1,742.9 million by 2035.
This upsurge can be ascribed to a combination of factors like the increased governmental and NGO backing and the surge of opioid dependency cases. The distribution of medication-assisted treatment (MAT) which is processed with the help of opioid agonists such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naloxone is a crucial step toward saving lives
A case in point is the increase of OST programs in countries like India and Nigeria which are faced with the problem of opioid and other health issues that are driven by the support of international organizations.
One of the critical challenges that LMICs face is the legal and regulatory barriers regarding opioid-based treatment. Furthermore, these countries' healthcare systems primarily lack the professional workers who have experience in chemical dependency which reduces the effectiveness of the OST facilities.
The understanding that opioid addiction stands out as a crucial public health problem has thus been the need for LMICs to modify their public policies and allocate more resources to the sector. The nations using community empowerment approaches along with the digital health innovations are the ones that have registered positive results in treatment adherence and health outcomes.
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
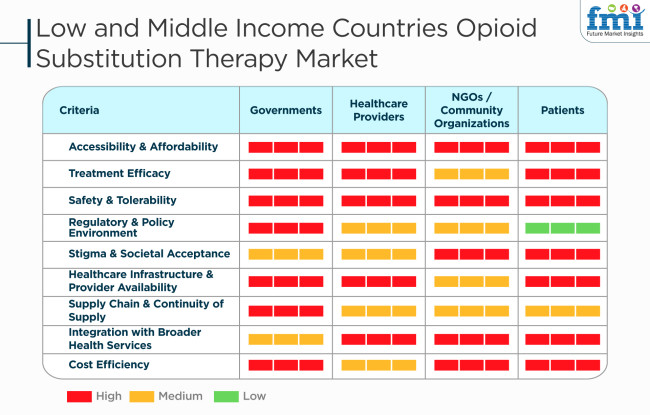
Low and middle-income countries need to deal with many barriers in the opioid substitution therapy market that have a great impact on governments, healthcare providers, NGOs, and patients. Accessibility and affordability are the main challenges that remain, limiting the reach of essential drugs. The efficacy and safety of the treatment are the points that are necessary, but adverse policy issues like regulatory and policy constraints on the use of the drug make it unattainable for people. Societal labeling is still a quality issue, beyond which people are inhibited from seeking the therapy they so rightly need. Poor healthcare structure and a lack of medical practitioners also function as impediments to the effectiveness of treatment.
The bottleneck in the supply chain leads to the inability to get a regular supply of medicines, thus disrupting the treatment process. The insufficient integration with the general health services infrastructure erodes the efficiency of the entire program. Governments and healthcare institutions, who constantly worry about cost efficiency, are in pursuit of solutions that will not only provide necessary drugs to the patients but also achieve effective and sustainable opioid substitution therapy in the long run.
During the years 2020 to 2024, low and middle-income nations (LMICs) have progressively identified opioid substitution therapy (OST) as a key intervention for addressing opioid dependence. This time was marked by a coordinated attempt to mainstream OST into prevailing health systems in a bid to decrease the negative consequences of opioid abuse and facilitate harm reduction. Evidence-based interventions are treated along with the availability of methadone and buprenorphine in promoting the treatment of opioid use disorder in these domains. Joint efforts by the government, NGOs, and international agencies have been instrumental in making OST service access more available, socially as well as medically.
During 2025 to 2035, OST demand in LMICs is further going to increase. Additional growth is anticipated due to rising awareness about opioid use disorder and the efficacy of substitution therapies. Formulation and delivery technologies for drugs will advance to improve adherence and access. The challenges remain, however, in the form of regulatory obstacles, stigma around treatment for addiction, and inequalities in healthcare infrastructure. These challenges will need to be addressed through long-term policy support, investment in healthcare systems, and community mobilization to make OST services effective and accessible to a broad range of diverse LMIC settings.
Comparative Market Shift Analysis (2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035)
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| WHO and UNODC advocated for harm reduction activities, but national policies in most LMICs were still restrictive. Insufficient government funding for OST expansion. | Policy reforms mandate decriminalization and harm reduction. Governments implement national OST programs with global funding support. |
| Limited use of digital health technologies for OST tracking. A few mobile health (mHealth) programs for addiction treatment. | Artificial intelligence-based mobile platforms facilitate remote OST management and adherence monitoring. Blockchain ensures prescription tracking and delivery. |
| Growing need based on increasing opioid dependence but stigma and access issues restricted uptake. | Higher acceptance of OST as a result of sensitization efforts. Growth in community-based and pharmacy-dispensed OST programs. |
| WHO and NGO-driven projects expanded access in certain LMICs. Increase in illicit use of opioids necessitated harm reduction efforts. | Expansion of OST led by governments, telemedicine implementation, and addiction treatment predictive analytics through AI. |
| Overreliance on overseas suppliers. Reduced investment in local methadone and buprenorphine production. | Domestic OST drug production increase. Supply chain optimization using AI reduces shortages and enhances affordability. |
| Import dependence on wealthy countries. Supply chain interruptions in the COVID-19 period impacted availability. | Decentralized production hubs increase affordability and access. AI-driven distribution networks enhance last-mile delivery in rural areas. |
One of the biggest dangers in the opioid substitution therapy (OST) market in LMICs is the regulatory and legal problems. Many states have very tough drug policies that restrict the distribution and use of opioid substitutes like methadone and buprenorphine. Paperwork, licensing, and shifting political will can blockade or hamper the movement of therapy programs.
Absence of adequate health facilities is another major stumbling block. Many LMICs do not have well equipped clinics, skilled medical professionals, and a supply chain for OST distribution. This leads to irregular treatment which in turn results in a higher dropout rate and, consequently, a greater risk of relapse among patients.
Affordability and funding constraints are the major threats. OST programs need much of the funding to carry on, these funds are frequently sourced from government budgets or foreign donors. A drop in the economy, a cut in funding, or a shift in public health priorities could decrease the financial support for these programs, thus making them unsustainable in the future.
Social stigma and cultural opposition to opioid substitution therapy are still the main barriers to the adoption of these programs. In several LMICs, drug dependence is seen as a sin rather than a disorder; hence, the policymakers, the healthcare providers, and the patients before accepting it to be with OST. The communication of false information must be tackled, and the public's knowledge of the project needs to be increased.
Pricing strategies for the OST sector in LMICs must merge issues of affordability and sustainability to the point that all can access drugs in the long run. Given that a lot of the patients are economically underprivileged; the use of cost-effective means is important in achieving acceptance and adherence to treatment programs on a large scale.
Subsidization of medications through the government is a widely used strategy, where OST medications are offered for free, or at a meager cost, through the public health care system. The governments make agreements about bulk prices with the pharmaceutical manufacturers or rely on the international aid programs for the treatments to be cheaper for patients.
Cost-plus pricing is the tool used by private heath care facilities and pharmaceutical companies to ensure that they are profitable; meanwhile, patients are not affected much by the price of the medicine. In LMICs that have low purchasing power, this method should not be used without adjustments to the price if it is believed that it will limit patient access.
Tiered pricing is an excellent pricing model that is based on the income level and/or funding source of the patients. OST medications can be given to low-income patients at a discounted price while other healthcare providers or NGOs that can afford to pay more can maintain the standard price which in turn ensures a balanced revenue model.
Public-private partnerships (PPP) can also be effective in securing a well-running and affordable pricing strategy. Collaborative projects among governments, international organizations, and pharmaceutical companies should lead to the negotiation of bulk purchases, which will in turn, ensure both the affordability and the availability of these drugs in the LMICs.
Methadone is the most commonly used opioid agonist in opioid substitution therapy (OST), due to its long half-life, clinically proven effectiveness in alleviating craving and providing withdrawal blocking. Its low cost renders it especially feasible in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where funding for opioid use disorder treatment programs is frequently limited. It is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) and United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), which strongly promote the use of methadone maintenance treatment (MMT).
The primary indication of Opioid Substitution Therapy (OST) is Opioid Withdrawal and Opioid Use Disorder (OUD). OST is a treatment strategy under medical supervision where illicit opioids (e.g., heroin or fentanyl) are substituted with long-acting, less euphoric opioid agonists such as methadone or buprenorphine. This stabilizes patients, suppresses cravings, and prevents withdrawal, enabling individuals to reassert control over their lives while minimizing the risks of opioid misuse, including overdose and infectious diseases.
The largest distribution channel for Opioid Substitution Therapy (OST) is government-funded centers, NGOs, and tenders. OST is a public health program to decrease the harm caused by opioid dependence, including overdose deaths, HIV infection, and crime. Numerous governments across the globe, including those in low and middle income countries, operate OST programs through public health clinics, hospitals, and NGOs that offer methadone, buprenorphine, or naloxone at low or no cost to the patients.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| Brazil | 6.8% |
| China | 7.5% |
| India | 7.9% |
The market for opioid substitution therapy in Brazil is growing on the increasing trend of opioid abuse, total government efforts to curb drug abuse, and more exposure to harm reduction policies. Prescription opioid abuse in Brazil has also grown, further driving the demand for buprenorphine and methadone as replacement medication.
Government-sponsored healthcare programs, supported by global organizations, are driving OST adoption. Furthermore, increased telemedicine service coverage and mobile clinics are supplementing treatment supply in rural and underserved communities.
FMI is of the opinion that the Brazil market is slated to grow at 6.8% CAGR during the study period.
Growth Drivers in Brazil
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Opioid Abuse Boosted | Increased prescription opioid abuse driving OST demand |
| Government Harm Reduction Programs | OST implementation to prevent opioid-related deaths |
| Growth in Telehealth | Expanded access to OST via telemedicine and mobile health clinics |
| Subsidy by Government & Generic Drug Availability | Lower cost of methadone & buprenorphine treatment |
| Global Alliances | International health organizations' support for enhancing OST programs |
China's opioid substitution therapy market increases due to policy-driven harm reduction, increased growth of methadone maintenance treatment (MMT) clinics, and increased education on the treatment of opioid use disorders. China possesses one of the largest OST infrastructures in the globe, with massive government investment guaranteeing its sustainability.
The addition of digital health technologies, like AI-based remote consultation, is facilitating patient tracking and compliance. China's pharma sector is also facilitating cost-effective domestic production of opioid substitution drugs, increasing market access.
FMI believes that the China market will achieve 7.5% CAGR during the forecast period.
Growth Drivers in China
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Big OST Network | National roll-out of MMT clinics increasing treatment coverage |
| Strong Government Support | Policies supportive of opioid addiction treatment driving OST adoption |
| Integration of Digital Health | AI-driven tracking and telemedicine streamlining patient compliance |
| Emerging Pharmaceutical Industry | Domestic production reducing opioid replacement drug prices |
| R&D Spending Growing | OST improvements leading to cost-effective and efficient treatment |
India's opioid substitution therapy market is growing with rising opioid abuse rates, growing government attention, and improving healthcare infrastructure. India has a huge opioid dependence epidemic sweeping across northern states, controlled by heroin and synthetic opioid abuse.
The Indian government, as well as global health organizations, are increasingly supporting OST programs through subsidized buprenorphine and methadone treatment. Moreover, non-profit and community health organization set-ups are contributing to OST supply among high-risk groups.
FMI is of the opinion that the India market is slated to grow at 7.9% CAGR during the study period.
Growth Drivers in India
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Increased Opioid Dependence | Man-made opioid and heroin dependence on the increase fueling the need for OST |
| Government OST Programs | Government-run public health programs increasing accessibility to OST |
| Subsidized Medications | Methadone and buprenorphine both made affordable via government subsidy |
| Nonprofit & Community Outreach | Expanded access to OST to under-served groups |
| Rural Healthcare Expansion | Mobile clinics and telemedicine centers expanding access to OST |
Some of the key players include Indivior, Hikma Pharmaceuticals, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, and local generic drug manufacturers. They want to expand their reach using affordable pricing strategies, regulatory collaborations, and supply chain developments. At the same time, developing market contenders seek to establish themselves within this evolving regulatory landscape by coming up with novel formulations of drugs and patient-centric treatment models. International health organizations financing, harm reduction, and alternative medication-assisted treatment also shape the competitive environment.
Market Share Analysis by Company
| Company Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Indivior PLC | 22-26% |
| Hikma Pharmaceuticals | 18-22% |
| Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals | 10-14% |
| Camurus AB | 8-12% |
| Viatris (Mylan) | 5-9% |
| Other Companies (combined) | 25-35% |
| Company Name | Key Offerings/Activities |
|---|---|
| Indivior PLC | Develops buprenorphine-based opioid substitution treatments, including Suboxone and Sublocade, targeting opioid dependence. |
| Hikma Pharmaceuticals | Manufactures methadone and buprenorphine generics, ensuring affordability and availability in LMICs. |
| Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals | Produces opioid agonist therapies and extended-release formulations for opioid dependence treatment. |
| Camurus AB | Specializes in long-acting buprenorphine treatments, such as Buvidal, osffering extended relief for patients. |
| Viatris (Mylan) | Provides cost-effective generic alternatives for opioid substitution therapy, increasing access in developing markets. |
Indivior PLC (22-26%)
A global leader in opioid dependence treatment, Indivior offers innovative buprenorphine-based therapies, supporting harm reduction efforts worldwide.
Hikma Pharmaceuticals (18-22%)
A key provider of methadone and buprenorphine, Hikma focuses on affordability and accessibility for opioid substitution therapy in LMICs.
Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals (10-14%)
Specializing in opioid addiction management, Mallinckrodt produces both agonist and antagonist therapies to support treatment programs.
Camurus AB (8-12%)
With its long-acting Buvidal formulation, Camurus enhances patient adherence and treatment outcomes in opioid dependence therapy.
Viatris (Mylan) (5-9%)
A major supplier of generic opioid substitution medications, Viatris expands access to cost-effective therapies in underserved regions.
Other Key Players (25-35% Combined)
The market is expected to be USD 864.8 million in 2025.
The market is predicted to reach a size of USD 1,742.9 million by 2035.
The key companies in the market include Pfizer Inc., Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Alkermes Inc., Hikma Pharmaceuticals, Emergent BioSolutions Inc., Indivior Inc., Mundipharma GmbH, Purdue Pharma LP, Orexo US Inc., Boehringer Ingelheim, Jamp Pharma Corporation, Vistapharm Inc., Atlantic Biologicals Corp., BLISTECO S.A.S., BioDelivery Sciences International Inc., Braeburn Inc., Camurus AB, Knight Therapeutics Inc., Titan Pharmaceuticals Inc., Braeburn Pharmaceuticals, L. Molteni & C. Dei Fratelli Alitti Società Di Esercizio S.P.A., Sterinova Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., USWM LLC, Wellona Pharma, Taj Pharmaceuticals Limited, Livealth Biopharma Pvt Ltd, Somerset Therapeutics Limited, Walter Healthcare Private Limited, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, Rusan Pharma Ltd, Viatris Inc., RINQUE PHARMA, Par Pharmaceutical, The Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Intas Pharmaceuticals, and STERIS PHARMA.
India, slated to witness 7.9% CAGR during the study period, will witness fastest growth.
The most widely used product segment is methadone-based therapy.
By drug class, the segmentation is as opioid antagonists and opioid agonists and partial agonists.
By indication, the segmentation is as pain management, opioid withdrawal/opioid use disorder (OUD), alcohol de-addiction, and depression.
By distribution channel, the segmentation is as government-supported centers/NGOs/tenders, institutional sales, and retail sales.
By region, the segmentation is as Latin America, China, South Asia and Pacific, Europe, Central Asia, Africa.
Pet DNA Testing Market Analysis by Animal Type, Sample Type, Test Type, End User and Region: Forecast for 2025 to 2035
Dental Practice Management Software Market Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Dental Consumables Market Insights by Product, End-Users, and Region through 2035
Hypoventilation Management Market – Growth & Treatment Innovations 2025 to 2035
Hyperpigmentation Treatment Market – Trends & Future Outlook 2025 to 2035
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Management Market - Growth & Drug Advances 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.