The Australia and New Zealand low and medium voltage drive Market experienced a steady growth with increasing investment in industrial automation and energy efficiency solutions. The mining industry, one of the major end-users, accelerated the implementation of advanced drive systems to optimize energy usage and reduce operational expenses. Similarly, the infrastructure sectors experienced a massive demand for medium-voltage drives, mostly propelled by the integration of renewable energy and water treatment facilities.
Government-sponsored sustainability programs, which were formulating extra budgets for industrial electrification initiatives, also buoyed sustained interest. Supply chain disruptions, however, persisted, especially due to semiconductor shortages, leading to delays in drive system shipments. Still, industry participants localized supply chains and diversified sourcing strategies in response.
Beyond 2025, industry growth will be driven by continued investment in industrial automation, smart grid modernization, and stricter energy efficiency regulations. The rise of drive technology trends, including AI-based predictive maintenance and variable-speed optimization (VSO), continues to also propel the drive industry and its growth.
The industry's long-term growth will be supported by the rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the increasing demand for efficient power distribution. The low- and medium-voltage drive industry is projected to reach USD 0.81 billion in 2025. It will expand at a CAGR of 3.8% during the estimation period and touch USD 1.17 billion by 2035.
Market Forecast Table
| Metric | Value (in Billions) |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2025E) | USD 0.81 billion |
| Market Value (2035F) | USD 1.17 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 3.8% |
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
Regulation Compliance
Regional Differences
Regional Trends
On the contrary, 73% of American stakeholders agreed that automation is well worth its cost, and 35% of Japanese stakeholders still preferred individual alarm units due to lower initial costs.
Worldwide Consensus
Regional Variations
Shared Challenges
Regional Insights
Manufacturers
Distributors
End-Users (Industrial Users)
Global Alignment
Regional Differences
Key Global Agreements
Major Regional Differences
Strategic Insight
| Region | Policy Impact & Regulatory Requirements |
|---|---|
| Australia (National) | The National Energy Productivity Plan (NEPP) and Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) generate energy efficiency upgrades for industrial motor systems. The data training will continue until October 203. The Clean Energy Finance Corporation (CEFC) provides financing for businesses and projects investing in energy-efficient technologies. |
| New South Wales (NSW) | Net Zero Industry and Innovation Program: Fund the electrification of industry. Rebates for high-efficiency drive systems are available through the NSW Energy Savings Scheme (ESS). |
| Victoria (VIC) | Vic's Victorian Energy Upgrades (VEU) scheme mandates efficiencies from businesses. VRET encourages the adoption of energy-efficient drives and motors. |
| Queensland (QLD) | Grid Modernization/Industrial Electrification-The QLD Energy and Jobs Plan supports grid modernization. Drive systems must be safely installed following the Electricity Safety Act, which applies to the industrial sectors. |
| Western Australia (WA) | The Western Australian Clean Energy Future Fund aims to drive energy efficiency into mining and industrial applications. The project is subject to the Electricity (Licensing) Regulations. |
| South Australia (SA) | South Australia has a Net Zero Target by 2050, which encourages businesses to implement high-efficiency drives. REPS provides incentives for energy-efficient solutions for industry. |
| Tasmania | Sustainable adoption of drives aligned with Tasmania's Renewable Energy Target (200% by 2040) Compliance with the Electricity Industry Safety and Management Regulations is required. |
| Northern Territory (NT) | Reliability and efficiency of NT industrial power systems are guaranteed by the NT Electricity Reform Act. Electrifying people in outlying regions is funded by government grants. |
| New Zealand | Industrial motor efficiency standards are regulated by the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority (EECA). The New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme (NZ ETS) rewards businesses for implementing energy-efficient technologies. |
The medium-high voltage range (3 kV to 6 kV) is dominating the industry, chiefly because of widespread application in industries such as mining, power generation, and bulk manufacturing. Western Australia and Queensland's mining industry is a principal driver, with a growing demand for medium-voltage drives that enhance operational efficiency and energy savings.
The mid-voltage range of 1 kV to 3 kV is growing rapidly as medium-sized factories transition to more energy-efficient motor control systems. Conversely, the low-voltage range of 230V to 690V is expanding significantly due to its widespread use in commercial buildings, food processing facilities, and HVAC installations.
The 690V to 1 kV segment is gaining popularity in industrial manufacturing facilities that need precise control for high-power equipment. With increasing government support for energy efficiency, demand across all voltage segments is expected to grow steadily.
In the medium voltage segment, the 1 MW to 3 MW segment is the largest in terms of volume because of its importance in industries like power generation and mining, where medium-sized industrial motors are very common. The >7 MW segment is finding growing use in heavy industries like oil & gas and petrochemicals, especially in offshore operations and big refining complexes.
At the low-voltage side, 750 to 7500 W is the most popular in a range of applications across various industries such as building automation, HVAC, and food processing. The up-to-750 W segment is also developing rapidly, with heightened demand for energy-efficient motor control applications for smaller commercial and residential uses. Automation and digitalization are driving the emergence of the 7500 to 75000 W category in the manufacturing industry, increasing the demand for high-powered low-voltage drives.
The most dominant among medium-voltage drives are variable frequency drives (VFDs) as a result of the fact that they are capable of offering precise control over speed as well as better energy efficiency when applied to industrial use. Industries such as power generation and mining in Australia are notable users of VFDs.
Direct torque control (DTC) drives are also witnessing significant demand, especially in high-performance applications that involve accurate torque regulation. In the low-voltage segment, VFDs continue to dominate, particularly in commercial complexes, HVAC, and food processing industries.
Servo drives are increasing at a very fast rate due to the increased use of robotics and automation in the manufacturing and packaging sectors. Vector control drives are also increasing in popularity, especially in the industrial sector in New Zealand, as manufacturers look for enhanced motor performance and energy efficiency. Across both voltage classes, sensorless control drives are emerging as a promising technology due to their cost-effectiveness and reduced reliance on external sensors.
AC drives have the largest industry share in both medium and low voltage segments, thanks to their application efficiency in variable-speed applications. Increasing industrial automation adoption, especially in power-hungry sectors like mining, oil & gas, and manufacturing, has stimulated demand for AC drives. HVAC, building automation, and electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure heavily utilize AC drives in the low-voltage segment.
DC drives, although with a lesser industry share, remain viable in niche applications such as railway traction, ship propulsion, and heavy industry equipment. The move toward more efficient motor control solutions is propelling innovation in both AC and DC drive technologies, with greater emphasis on digital connectivity and predictive maintenance.
The direct end-user channel dominates the industry because major industries prefer buying from manufacturers directly to get customized solutions, best prices, and hassle-free integration. This approach is mainly applicable to medium-voltage drives for mining, power generation, and heavy manufacturing, where customized solutions are critical. But the distribution/partner channel is also seeing rapid growth, mainly for low-voltage drives in commercial and residential sectors.
Most small and medium-sized enterprises like to purchase through distributors for improved after-sales service and the presence of various brands. Direct system integrators are becoming increasingly popular as companies seek holistic automation solutions that include high-level drive technologies. Digital platforms and e-commerce are also contributing to the transformation of sales channels, enabling companies to source drive systems more flexibly.
Within the medium-voltage industry, the mining and metals industry is the largest end-user, fueled by Australia's internationally prominent mining sector. Mining organizations are making significant investments in energy-efficient drive technology to maximize operational expenses and meet sustainability requirements. The power generation sector is also a major segment, especially as Australia and New Zealand shift toward renewable energy sources that demand sophisticated motor control solutions.
The oil and gas industry is also an important sector, with refineries and offshore platforms incorporating high-performance medium-voltage drives. The building and construction sector is also seeing considerable demand for low-voltage drives, especially for smart buildings and HVAC.
The food and beverage industry is a rapidly developing segment, with manufacturers investing in energy-efficient packaging and processing equipment. The transport industry is another area of rapid growth, with the increasing use of electric cars and rail electrification schemes that demand accurate motor control solutions.
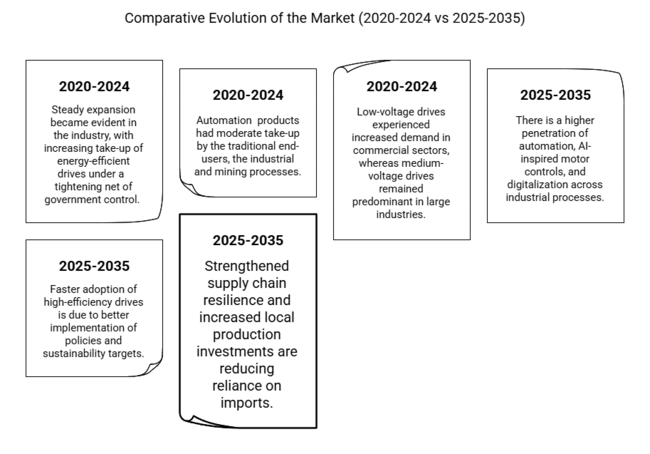
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Steady expansion became evident in the industry, with increasing take-up of energy-efficient drives under a tightening net of government control. | Faster adoption of high-efficiency drives is due to better implementation of policies and sustainability targets. |
| The shortage of semiconductors in particular disrupted supply chains, leading to production and purchase delays. | Strengthened supply chain resilience and increased local production investments are reducing reliance on imports. |
| Automation products had moderate take-up by the traditional end-users, the industrial and mining processes. | There is a higher penetration of automation, AI-inspired motor controls, and digitalization across industrial processes. |
| Business incentives and government rebates encouraged the adoption of energy-efficient technologies. | Bolder policies and investments in decarbonization and electrification. |
| Low-voltage drives experienced increased demand in commercial sectors, whereas medium-voltage drives remained predominant in large industries. | Medium-voltage drives are growing in renewable energy generation and infrastructure installations, while low-voltage drives are penetrating into smart buildings and electric vehicle infrastructure. |
| The industry was fragmented, and multiple players competed across price and technology development. | Consolidation is expected, as leading players are expanding their portfolios through innovation and acquisition. |
The low and medium voltage drives (VSDs) for Australia and New Zealand are a segment within the industrial automation and energy efficiency equipment industry and are closely related to the power electronics, manufacturing, and renewable energy sectors. It gets affected by macroeconomic drivers, including infrastructure development, industrial automation, energy transition policies, and global supply chain dynamics.
At a macroeconomic level, the industry responds to government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions, rising energy costs, and improving energy efficiency in industrial operations. Australia's ambitious net-zero target set for 2050 and its new renewable energy strategy are driving investment in mining, manufacturing, and energy industries.
They remain the major drivers of growth, and automation is a key enabler of optimizing the use of power. Economic cycles, such as commodity price volatility, fuel industrial investments, while supply chain optimization and domestic manufacturing initiatives stabilize the industry. With the drive of industrial digitalization, the demand for smart and AI-enabled motor drives will rise, and the industry will become one of the regional champion industries that will bring the future sustainable energy economy to the region.
The Australia and New Zealand low and medium voltage drive industry faces competition from industry leaders regarding price strategies, technology innovation, strategic alliances, and industry expansions. Many focus on low-cost, low-energy solutions to help companies meet stringent regulations while still providing competitive pricing.
Innovations in AI-based motor controls, IoT-based drives, and predictive maintenance offerings drive this trend. Manufacturers are actively collaborating with OEMs, automation companies, and energy solution providers to increase their industry share.
Local production, acquisitions, and upgrades to a wider service network are used to improve supply chain resilience and are all considered strategies for expansion. Through digital platforms and distribution networks, businesses further expand their customer reach and engagement.
ABB Ltd.
Industry share: ~25-30%
ABB is among the top three players in the ANZ low and medium voltage drive industry, where it leverages its extensive global footprint and offerings of innovative drive technologies. ABB is focusing on industries such as mining, water treatment, and manufacturing with an emphasis on energy efficiency and digitalization.
Siemens AG
Industry Share: ~20-25%
With its excellent drive solution, Siemens holds a significant industry share in the ANZ industry and has the potential to integrate into IoT-based systems. The company also specializes in automation and sustainability, both of which align with ANZ's pursuits in green energy and intelligent manufacturing.
Schneider Electric
Industry Share: ~15-20%
Schneider Electric is still a heavyweight with a wide range of low and medium voltage drives. Focusing on modular and scalable solutions has allowed the firm to reinforce its position in areas such as infrastructure and renewable energy.
Danfoss Group
Industry Share: ~10-15%
Danfoss has a notable presence in the ANZ industry, particularly in HVAC and refrigeration applications. Its energy-efficient drives and decarbonization initiative resonate favorably with local sustainability ambitions.
Rockwell Automation
Industry Share: ~5-10%
In 2024, the company's focus on digital transformation and predictive maintenance has gained significant popularity.
WEG Industries
Industry Share: ~5-10%
WEG continues to expand its presence in ANZ, offering affordable and reliable drive solutions. Business development: Growth aided by a focus on emerging industries and renewable energy applications.
The ANZ low & medium voltage drive industry witnessed significant advancements in 2024, with new technology and strategic decisions driving the evolution. ABB Ltd. has designed a new-generation ACS880 industrial drive with improved energy efficiency and connectivity for Internet of Things applications. ABB's introduction further strengthened their leadership position, particularly in the mining and water treatment sectors, where energy savings are critical.
Siemens AG: Sinamics G220 Series of Drives Siemens AG has introduced its Sinamics G220 Series of drives specifically for HVAC and pump drives. This new series is compatible with Siemens’ MindSphere platform for predictive maintenance and optimization of operations. The choice is consistent with ANZ's growing demand for smart building technologies and energy-efficient infrastructure.
The company also expanded its Altivar Process drive range with an emphasis on modularity and scaling for the needs of industrial drives and partnered with local energy providers to encourage the uptake of renewable energy solutions, adding to its existing hold in ANZ.
In 2024, Danfoss Group made strides with the launch of its VACON NXP Liquid Cooled drives, which are majorly targeted towards heavy industries like mining and marine. Danfoss designed the drives to withstand harsh environments, ensuring dependability and energy efficiency.
Rockwell Automation's news focused on the need for digital transformation, introducing the PowerFlex 6000T medium voltage drives with built-in analytics capabilities. The company's focus on predictive maintenance and remote monitoring resonated with ANZ manufacturers seeking to enhance their efficiency and agility.
WEG Industries has forged further into the ANZ industry with an expanded distribution network as local distributors work to boost penetration. It also introduced its W22 Magnet drive with high efficiency and a small footprint, catering to the region's rising demand for green solutions.
Growth opportunities: The convergence of AI and IoT-based predictive maintenance solutions in mining, power generation, and other manufacturing sectors offers potential growth for businesses in the Australia and New Zealand low & medium voltage drive industry.
As industries continue to seek real-time operational intelligence, businesses that leverage cloud-based remote monitoring combined with digital twin technology will be at a competitive advantage. Transport and renewable energy are another major opportunity, with smart drive solutions ensuring maximum productivity across EV charging points/grid-based sock systems.
Companies can collaborate with government-sponsored sustainability initiatives to accelerate adoption and secure preferred contracts. Recommendations: To exploit these opportunities, stakeholders shall prioritize local assembly and component manufacturing to prevent supply disruption and enable speedier delivery cycles.
Industries that wish to upgrade existing motor control systems without substantial changes to infrastructure will be eager for modular and retrofit-compatible drive solutions as well. Predictive analytics and AI-driven maintenance solutions will also provide new revenue sources to OEMs, with long-term customer retention ensured. Engaging with energy utilities and regulatory agencies to get ahead of efficiency future requirements will also provide an early-mover advantage for capturing large-scale industrial and infrastructure projects.
Energy efficiency legislation and a transition to renewable sources of energy are the leading drivers of industrial automation.
The heavy users are mining, manufacturing, power generation, and infrastructure development.
It can be AI-based predictive maintenance, IoT connectivity, or energy-efficient designs that can help improve performance and reliability.
Supply chain disruptions, high upfront costs, and changing regulatory requirements are challenges.
Diakont is not alone, and these are indeed crucial subsidies and tax relief to promote energy-efficient industrial technologies.
It is segmented into medium voltage drives (low-medium voltage (1 kV to 3 kV), medium-high voltage (3 kV to 6 kV) & high voltage (6 kV and above)) and low voltage drives (up to 230V, 230V to 690V & 690V to 1 KV)
It is fragmented into medium voltage drives(<1MW, 1 MW to 3 MW, 3 MW to 7 MW & > 7 MW) and low voltage drives (Up to 750 W, 750 to 7500 W & 7500 to 75000W)
The industry is segmented into medium voltage drives (variable frequency drives (VFDs), servo drives, direct torque control (DTC) drives, vector control drives and sensorless control drives) and low voltage drives (variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), Servo Drives, Direct Torque Control (DTC) drives, vector control drives & sensorless control drives)
It is divided into medium voltage drives (AC & DC) and low voltage drives (AC & DC)
It is fragmented into direct end-user, direct machine builder, direct systems integrator and distribution/partner
It is segmented into medium voltage drives (oil and gas, mining and metals, power generation, chemicals and petrochemicals, water and wastewater, marine and offshore and others) and low voltage drives (building and construction, manufacturing, food and beverage, transportation, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, commercial facilities & others)
The industry is segmented among Australia (New South Wales (NSW), Victoria (VIC), Queensland (QLD), Western Australia, South Australia, Tasmania & Northern Territory), New Zealand
Electric Winch Market Report - Demand, Growth & Industry Outlook 2025 to 2035
Commercial RAC PD Compressor Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Commercial Induction Cooktops Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Echo Sounders Market Insights - Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025 to 2035
Electric Hedge Trimmer Market Insights Demand, Size & Industry Trends 2025 to 2035
Air Quality Monitoring Equipment Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.