The hepatic encephalopathy treatment industry is valued at USD 1.68 billion in 2025. As per FMI's analysis, the industry will grow at a CAGR of 6.84% and reach USD 3.16 billion by 2035.
In 2024, the hepatic encephalopathy or liver disease therapeutic treatment industry saw rising investments in drug development, with top pharmaceutical companies speeding up clinical trials for new formulations. Approvals for newer drugs such as second-generation rifaximin and novel ammonia-lowering agents helped fuel industry growth.
The analysis revealed that North America dominated the landscape, with a rise in early-stage liver disease therapeutic diagnoses fueling increased prescription rates. European countries, on the other hand, experienced improved access to therapeutics due to supportive reimbursement policies.
The industry will become even more dynamic by 2025 as healthcare providers incorporate AI-based diagnostic solutions, enabling early intervention and improving treatment outcomes. AI will facilitate more accurate and timely diagnoses, particularly in liver diseases, leading to better patient management. Furthermore, increasing awareness campaigns and government-supported liver disease management initiatives will play an important role in educating the public, driving early detection, and encouraging healthier lifestyles.
The decade ahead will see increased innovation, with precision medicine strategies and microbiome-directed therapies transforming treatment paradigms. These advancements will enhance personalized care and targeted therapies. By 2035, according to FMI research, the industry will reach USD 3.16 billion, driven by an aging population and rising incidences of cirrhosis complications.
Industry Forecast Table
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 1.68 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 3.16 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.84 % |
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
The hepatic encephalopathy treatment industry is poised for steady growth, fuelled by the increasing incidence of liver diseases and technological innovations in drug delivery. Pharmaceutical companies developing novel therapeutics and healthcare providers implementing early diagnostic devices are likely to benefit, whereas regions with limited access to specialised treatments will face challenges. With the rise in global awareness and the establishment of reimbursement strategies, industry stakeholders investing in precision medicine and microbiome-targeted therapies are expected to experience long-term growth.
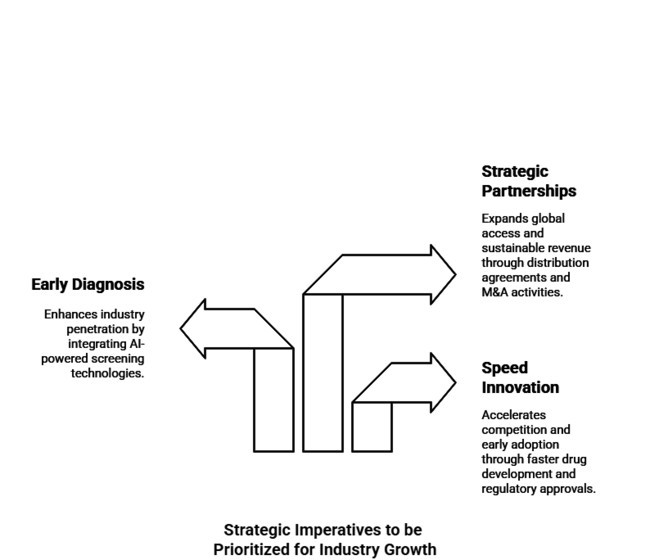
Speeding Innovation Drugs and Regulatory Reviews
R&D Funding Needed for a New Ammonia-Lowering Drug and Next-Gen RifaximinProducts. Quicker clinical trials and regulatory approvals will put them ahead of the competition and spur early adoption
Integrating early diagnosis will boost industry penetration.
AI-powered early detection through AI-based screening technology should involve a collaborative partnership between healthcare professionals and diagnostic firms. Aligning with evolving healthcare policies and reimbursement frameworks will increase patient access and accelerate adoption of treatment options.
Scale Strategic Partnerships for Global Industry Access
Industry players are required to start distribution agreements and M&A activities that will provide them with access to underpenetrated regions. Partnerships with regional health systems and payers will make broader availability and sustainable revenue growth possible.
| Risk | Probability & Impact |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Delays in Drug Approvals | High Probability - High Impact |
| Limited Patient Access in Emerging Markets | Medium Probability - High Impact |
| Rising Competition from Alternative Therapies | High Probability - Medium Impact |
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Accelerate New Drug Approvals | Fast-track late-stage clinical trials and engage with regulatory agencies for expedited approvals |
| Enhance Early Diagnosis Adoption | Partner with AI-driven diagnostic firms to integrate screening tools in healthcare systems |
| Expand Global Reach | Establish distribution partnerships in emerging landscapes and negotiate favorable reimbursement terms |
To stay ahead, companies must prioritize treatment innovation in liver disease therapeutics, accelerate R&D on next-generation drugs and expedite regulatory clearance. Leveraging early diagnostic potential through AI development will enhance industry presence while improving the quality of treatment for patients.
Anticipate forging higher-profile partnerships with payors and providers in emerging landscapes, alongside demand acceleration in these regions, leading to increased revenue and accessibility. This vision marks a shift towards targeted treatment and active moderation, necessitating a new set of directives focused on growth in new geographies, payment advocacy, and truly innovative drug discovery.
Regional Variance:
Extreme Heterogeneity in Innovation Use:
Discovering Commonality on ROI:
Global Price Pressures:
Regional Differences:
Global Alignment:
Regional Investment Priorities:
Manufacturers:
Healthcare Providers:
Key Consensus Areas:
Regional Variances:
Strategic Insight:
| Countries | Regulatory Impact & Mandatory Certifications |
|---|---|
| United States | The FDA's rigorous drug approval process guarantees high safety levels but prolongs timelines for entry into the industry . Medicare and Medicaid's reimbursement policy has a significant impact on treatment uptake. The Breakthrough Therapy Designation accelerates approval of new drugs. |
| United Kingdom | The Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) regulates, with post-Brexit reforms providing the opportunity for faster entry in the industry . NICE (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) is the cost-effectiveness threshold that controls drug pricing and reimbursement. |
| France | All his intensive clinical trials are mandated by the ANSM (French National Agency for Medicament and Health Products Safety). Reimbursement on the basis of therapeutic benefit ratings has some effect on price and patient access; the HAS (High Authority for Health) has a say in this. |
| Germany | Comprehensive efficacy and cost-effectiveness assessment is mandated by the BfArM (Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices) and G-BA (Federal Joint Committee). AMNOG price negotiations inform the strategies for pricing in the early stages of drugs. |
| Italy | Pharmaceutical approvals and prices are regulated by negotiated reimbursement contracts with the AIFA (Italian Medicines Agency). Foreign manufacturers have a local preference for generics and biosimilars. |
| South Korea | The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) regulates drug approvals, whereas HIRA (Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service) oversees reimbursement policy. This role gives an increasing push to regulators to incentivize digital health solutions. |
| Japan | Safety and efficacy are stringently regulated by the PMDA (Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency). The government provides a fast-track approval scheme for orphan drugs for liver disease therapeutic , with the aim of enabling them to enter the industry . |
| China | Current reforms have rationalized drug approval procedures and minimized waiting periods, according to the Chinese National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). Price reductions in VBP policies based on evidence from the data favor generics over innovative, expensive medications. |
| India | The CDSCO (Central Drugs Standard Control Organization ) controls drug approvals, and biosimilars are receiving more attention. Across all industries, the National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) enforces price caps on manufacturers. |
Antibiotics dominate the hepatic encephalopathy treatment industry, with rifaximin being the leading drug because of its efficacy in lowering ammonia-producing gut bacteria. The increasing prescription of rifaximin, especially in the USA and Europe, can be attributed to its low systemic absorption and favorable safety profile. Laxatives, mainly lactulose, are a close second, as they are still the first-line therapy for ammonia detoxification.
Even though L-ornithine L-aspartate (LOLA) is the fastest-growing segment, FMI opines that its increasing adoption in medicine, especially in Asia, is due to its ability to enhance liver cell ammonia metabolism. Although classically overshadowed by laxatives and antibiotics, LOLA is gaining popularity as an adjunct therapy, especially in emerging economies. Greater study of new ammonia-lowering drugs, including possible enzyme-based treatments, will continue to increase treatment options in the coming decade.
Hepatic encephalopathy can only be diagnosed through lab tests. FMI data indicates that the most common screening methods worldwide include measuring ammonia levels and profiling liver enzymes. They are the most readily available economic diagnostic tools, and so they remain the dominant segment within both developed and developing nations. Yet, CT scans are observing the quickest growth since advanced imaging modalities are being used more for comprehensive brain evaluation in severe cases of liver disease.
Hospitals are increasingly utilizing CT and MRI scans to identify mild neurological alterations induced by hyperammonemia in nations with strong healthcare infrastructure, such as Germany and Japan. Liver function tests, although commonly applied, are a second-line diagnostic tool to ammonia testing and neuroimaging. Wider implementation of AI-based diagnosis platforms will likely increase the precision and speed of detecting liver disease, especially in developed countries.
Oral administration continues to be the most prevalent segment, with FMI’s analysis identifying rifaximin, lactulose, and LOLA in tablet or syrup formulation as receiving most of the prescriptions owing to their convenience and patient compliance. Rifaximin's widespread usage in outpatient clinics supports this trend, especially in the USA and Western Europe. Nevertheless, intravenous administration is the fastest-growing segment, primarily due to its necessity in severe cases requiring hospital-based treatment.
The need for IV-administered lactulose infusions and LOLA is growing with the rising prevalence of acute hepatic encephalopathy in intensive care units. Although injectables hold a significant share, they are primarily used in hospitals, particularly for ammonia-reducing medications in emergency settings. Upcoming developments in drug delivery systems, such as sustained-release drugs, would bring about a shift in this segment's dynamics by enhancing therapy's efficacy and decreasing hospitalization rates.
Hospital pharmacies lead the industry, with FMI analysis indicating that most hepatic encephalopathy treatment, especially injectable and IV drugs, is provided in hospital outlets. The predominant role of hospitals as the central treatment facilities for advanced cases guarantees this segment's leadership. Nevertheless, online pharmacies have been the fastest-growing sector, fuelled by growing digital acceptance and increased consumer demand for at-home delivery of prescription drugs.
Countries such as China and India, the growth of e-pharmacies has greatly enhanced patient availability to treatment of chronic liver disease. Retail pharmacies also hold a large industry share, particularly in developed countries where rifaximin and lactulose are commonly prescribed for chronic use. As telemedicine services and electronic prescriptions receive regulatory clearances, the expansion of online pharmacies is likely to accelerate further, transforming the distribution landscape for liver disease therapeutic treatments.
The United States hepatic encephalopathy treatment industry is estimated to be valued at USD 1,586.2 million in 2025. It is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.8% over the forecast years, owing to high R&D expenditure by various companies, favorable reimbursement policies, and the rising prevalence of liver diseases. The FDA’s expedited pathways help the agency approve more drugs, and Medicare and Medicaid make treatment more accessible.
Innovations are growing and include AI-driven diagnostics and microbiome therapies. However, pricing and reimbursement bottlenecks pose significant challenges. Major players emphasize price strategy and partnerships to remain profitable. Funding for digital health solutions is increasing, facilitating early detection. The long-term outlook for the industry remains positive, supported by tech advances and rising healthcare spending.
With the NHS's reimbursement policies, the UK hepatic encephalopathy treatment industry is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% between 2025 and 2035. This is because more people are getting liver diseases because of obesity and better diagnostic tools that use artificial intelligence (AI). Post-Brexit regulatory adjustments enabled MHRA to accelerate approvals, enhancing drug availability. Cost-effectiveness evaluations by NICE determine whether to enter the industry.
Some gut microbiome-targeted treatments are currently being investigated in clinical trials and could represent the next frontier in personalized medicine. Budgetary restraint with the NHS continues to hamper uptake of premium pharmaceuticals. Sustainable drug manufacturing is coming into view. Pharma companies are negotiating reimbursement strategies while ensuring structured, competitive pricing in subsequent processes.
In France, the industry for hepatic encephalopathy treatment is estimated to expand at a CAGR of 5.7% over the course of 2025 to 2035 owing to government-supported healthcare initiatives, robust R&D expenditure, and the growing burden of cirrhosis. HAS assesses the added therapeutic value of new drugs as compared to existing alternatives, which impacts pricing and reimbursement, among others. High demand for ammonia-lowering agents due to jaundice prevalence among alcohol-related liver disease (20%) and metabolic disorders.
There is an expansion in AI-powered diagnostics and microbiome-based therapies. But limits on public health care budgets may be a brake on the uptake of costly treatment. France also focuses on sustainable drug manufacturing, propelling companies to adopt greener production methods. The industry is still promising for pharmaceutical companies that have adopted innovative but affordable solutions.
The German hepatic encephalopathy treatment industry is expected to register a growth rate of 6.2% during 2025 to 2035, driven by rigorous health regulations, extremely high R&D expenditure, and early adoption of technology. The cost-effectiveness assessment by the G-BA dictates reimbursement approvals. Because of metabolic disorders and cirrhosis, people are very interested in new ways to treat liver disease, such as microbiome modulation therapy and AI-assisted diagnosis.
Sustainable pharmaceutical production is increasing, courtesy of government incentives. Stringent price controls pose barriers by requiring proof of long-term cost savings. In regulation, apart from challenges, Germany's highly funded health care and rich pipeline of innovation make it a leading industry for liver disease therapeutic drugs.
From 2025 to 2035, the industry for hepatic encephalopathy treatment in Italy is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5%, supported by an ageing population, growing prevalence of liver diseases, and growing investment in healthcare. The AIFA- Italian Drug Agency - negotiates the price and reimbursement of drugs, hence the accessibility to the industry. The increasing incidence of NAFLD and cirrhosis cases requires cost-efficient treatment alternatives.
Spending limits in the public health system mean that biosimilars and generics are prioritized over the most expensive drugs. Digital healthcare is on the rise, with telemedicine facilitating better patient management. In fact, pharmaceutical companies need to work closely with regulatory agencies to obtain favorable reimbursement conditions. Companies providing novel but cost-effective liver disease therapies will find an industry rewarding.
The South Korean hepatic encephalopathy treatment industry is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% over the period from 2025 to 2035, owing to an increasing number of patients with nonalcoholic liver disease and the modernization of the healthcare system. The MFDS is trying to expedite drug approvals, meaning that people can access new treatments more quickly. In South Korea, robots and artificial intelligence are used in diagnostic processes.
But pricing sensitivity and reimbursement constraints create obstacles for premium drug uptake. Public-private partnerships in medical research are surging, and innovation is accelerating. By offering cost-effective solutions and leveraging South Korea's advanced healthcare infrastructure, we can achieve industry growth.
The Japan hepatic encephalopathy treatment industry is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2025 to 2035, aided by an ageing demographic, increasing liver disease incidences, and rapid development of precision medicine. The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) conducts rigorous drug evaluations, which often results in delayed approvals. Japanese consumers tend to favor conservative treatment methods, which can affect their rapid adoption of high-cost drugs.
However, this means that research into diagnostics, microbiome therapies, and other AI fields is accelerating. The Japanese regulatory system supports cost-effective treatment models, which encourage the use of generic drugs. For drug manufacturers targeting Japan, looking to highlight long-term clinical benefits at an affordable price is critical to gaining industry and regulatory acceptance.
China's hepatic encephalopathy treatment industry is projected to experience a CAGR of 7.1% from 2025 to 2035, largely driven by the rising prevalence of liver disease, healthcare reforms, and improved insurance coverage. The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has accelerated drug approvals to improve accessibility in the industry.
Government strategies aim to improve treatment affordability, and homegrown pharmaceutical companies are investing in ammonia-reducing therapies and AI-enabled diagnostics. Nonetheless, disparities in healthcare access and regulatory divergences persist regionally. To penetrate the industry, companies targeting China need to systematically adjust pricing strategies and use local partnerships.
The hepatic encephalopathy treatment industry in India is projected to register a substantial CAGR of 7.4% between 2025 and 2035, driven by a high prevalence of hepatitis-related liver diseases, rising awareness among people regarding healthcare, and government initiatives. The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) is accelerating the approval process for drugs, giving companies a bigger window to sale their products.
However, affordability is still a significant issue, with cheaper generics being preferred over premium therapies. A spectrum of care, including Ayushman Bharat, is making advanced treatments more accessible. Implementing pricing strategies, distribution networks, and patient education programs in India Companies need to set their footing in the Indian industry by developing pricing strategies to keep a competitive edge, expanding distribution networks, and looking at patient education programs.
The industry for hepatic encephalopathy treatments is fragmented. The landscape is influenced by mergers and collaborations, but it still consists of several regional networks with varying degrees of penetration. The diversity of players, ranging from large pharmaceutical firms with premium-priced branded drugs to generic manufacturers offering more affordable alternatives, suggests that the industry shall remain fragmented during the forecast years.
According to FMI studies, leading firms are focusing on investment in R&D to develop innovative ammonia-reducing therapies, thereby improving the safety and efficacy of the drugs. Branded drugs, such as rifaximin, differentiate themselves through premium pricing, while generic alternatives enhance affordability.
The global liver disease therapeutic treatment industry consists of several regional networks with strong penetration, influenced by mergers and collaborations with research centers and hospitals. The companies are also furthering distribution networks in high-growth regions, such as Asia and Latin America. Approval of new formulations and lifecycle management strategies also shape the competitive landscape.
Industry Share Analysis
Bausch Health Companies, Inc.
Industry Share: ~25-30%
The company is the industry leader for hepatic encephalopathy (HE) treatment, with its lead asset, Xifaxan (rifaximin), commanding the HE treatment industry.
Salix Pharmaceuticals (subsidiary company of Bausch Health)
Industry Share: ~20-25%
The primary driver behind HE treatment through Xifaxan is Salix, which has ensured Bausch Health's dominance in the space.
Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals
Industry Share: ~15 to 20%
Mallinckrodt is a major player known for HE and ammonia-lowering treatment products.
Horizon Therapeutics (which was acquired by Amgen)
Industry Share: ~10-15%
The product was already present among HE-associated metabolic therapies prior to its acquisition by Amgen in October 2023.
Pfizer Inc.
Industry Share: ~5-10%
The research share for HE treatment is smaller than that of specialist players.
Other players (non-branded drug manufacturers)
Industry Share: ~10-15%
The competitive landscape includes companies producing lactulose and other generics.
Increasing liver disease prevalence, enhanced diagnostic technology, and greater awareness of treatment choices are driving the sales of the industry.
Ammonia-lowering therapy advancements, growing healthcare access, and approvals will create a steady growth in the upcoming years.
These companies include Bausch Health, Abbott, Norgine, Mallinckrodt, and Cipla, among others.
L-ornithine L-aspartate is experiencing high uptake as a result of its efficacy in ammonia metabolism.
The industry will reach USD 3.16 billion in 2035.
the industry is segmented into antibiotics, laxatives, L-ornithine and L-aspartate.
it is segmented into blood tests, CT scan, liver functioning tests
it is fragmented among oral, injectable, intravenous and others.
it is segmented among hospital pharmacy, online pharmacy and retail pharmacy.
the industry is studied across North America, Latin America, Europe, South Asia, East Asia, Oceania, Middle East & Africa.
Eyelid Scrub Market Analysis & Forecast by Product, Application and Region 2025 to 2035
Protein Diagnostics Market Share, Size and Forecast 2025 to 2035
Intraoperative Fluorescence Imaging Market Report - Demand, Trends & Industry Forecast 2025 to 2035
Lung Cancer PCR Panel Market Trends, Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Polymyxin Resistance Testing Market Trends – Innovations & Growth 2025 to 2035
Procalcitonin (PCT) Assay Market Analysis by Component, Type, and Region - Forecast for 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.