The Gene Therapy in CNS Disorder Market is projected to reach USD 13.86 billion by 2025. As per FMI's analysis, the gene therapy in CNS disorder will grow at a CAGR of 30% and reach USD 191.04 billion by 2035. The worldwide gene therapy market for CNS disorders is growing at a fast pace, spurred by progress in genetic studies, rising incidence of neurological disorders, and growing investments in biotech advancements.
With rising clinical trials and regulatory approvals, gene therapy is becoming a key treatment approach for conditions such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's, ALS, and Huntington's disease.
In 2024, the gene therapy industry for CNS disorders experienced major advancements in research, regulatory, and commercialization fronts. Several late-stage clinical trials for Parkinson's disease and ALS advanced, with multiple therapies receiving FDA Fast Track and Breakthrough Therapy designations. Biogen and Roche were among the companies that grew their pipelines, while CRISPR-based gene editing startups picked up momentum.
By 2035, the industry is spurred by ongoing innovations in gene-editing technologies like CRISPR and viral vector-based delivery systems. Growing partnerships among pharmaceutical leaders, research institutions, and biotech companies are expected to further accelerate market expansion. Moreover, the increasing need for personalized medicine and precision therapies will maximize treatment effectiveness, enhancing patient outcomes.
Market Metrics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 13.86 Billion |
| Industry Size (2035F) | USD 191.04 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 30% |
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
The landscape is accelerating fast in growth, fueled by the advances of genetic editing, mounting regulatory encouragement, and growing investment in precision medicine.
Chief beneficiaries are biotech companies leading the way in gene-based therapies, major pharmaceutical companies expanding their neurology pipelines, and patients with previously incurable neurological conditions. High development expenses, price pressures, and regulatory obstacles, though, can represent threats for smaller players and healthcare systems grappling with costs.
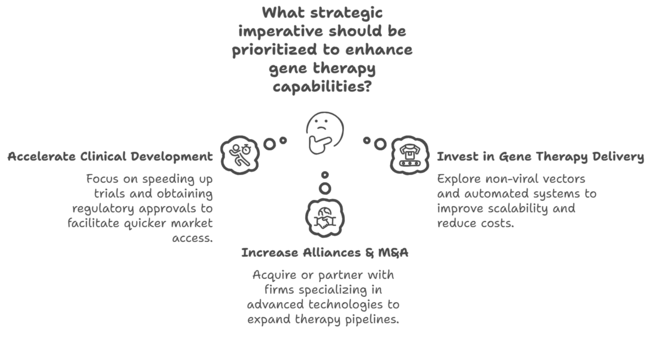
Speed Up Clinical Development & Regulatory Approvals
Executives need to make it a priority to accelerate clinical trials and obtain regulatory designations (e.g., Fast Track, Breakthrough Therapy) to facilitate quicker sector access. Spending in adaptive trial design and real-world evidence gathering will increase approval rates.
Invest in Scalable & Cost-Effective Gene Therapy Delivery
To keep pace with market demand and advancing technology, businesses must explore non-viral delivery vectors and automated manufacturing systems to improve scalability and reduce therapy costs. CDMOs (Contract Development & Manufacturing Organizations) partnerships will be essential in their ability to expand production capacity.
Increase Strategic Alliances & M&A Activities
Companies must acquire or partner with biotech firms specializing in CRISPR, AAV, and lipid nanoparticle technologies to expand their gene therapy pipelines. Collaboration with healthcare payers and the government will also be important to help manage price issues and enhance patient access.
| Risk | Probability & Impact |
|---|---|
| Regulatory & Approval Delays - Lengthy clinical trials and evolving FDA/EMA guidelines could slow segment entry. | High Probability, High Impact |
| High Treatment Costs & Reimbursement Challenges - Payers may resist covering expensive gene therapies, limiting patient access. | Medium Probability, High Impact |
| Manufacturing & Supply Chain Constraints - Limited capacity for viral vector production and complex delivery mechanisms could hinder scalability. | High Probability, High Impact |
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Accelerate Late-Stage Clinical Trials | Expedite patient recruitment and optimize trial design to secure faster regulatory approvals. |
| Enhance Cost-Effectiveness & Reimbursement Strategies | Engage with payers and policymakers to establish value-based pricing and reimbursement models. |
| Scale Up Manufacturing & Supply Chain Resilience | Invest in advanced bioprocessing technologies and expand CDMO partnerships to meet growing demand. |
To remain competitive in the evolving CNS gene therapy landscape, the industry must sustain clinical advancements, enhance manufacturing scalability, and secure payer adoption. Key immediate focuses must be accelerating late-phase studies, investing in scalable and cost-effective delivery technologies, and establishing strategic alliances with biotech innovators and CDMOs.
This segment presents a significant untapped opportunity; however, success depends on effectively navigating regulatory hurdles and securing reimbursement. Executives must align R&D investments with advancements in gene editing while developing commercial infrastructure to sustain long-term industry leadership.
Regional Differences:
High Variance:
Convergent and Divergent Perspectives on ROI:
Consensus:
Variance:
Shared Challenges:
Regional Differences:
Manufacturers:
Healthcare Providers & Distributors:
Alignment:
Divergence:
USA:
Western Europe:
Japan/South Korea:
| Country/Region | Regulatory Impact & Key Developments |
|---|---|
| United States | 71% of stakeholders cited FDA Fast Track & Breakthrough Therapy designations as accelerating approvals. State-level policies (e.g., Right to Try laws) expanded early patient access. CMS reimbursement challenges remain a barrier for pricing models. |
| Western Europe | 82% viewed the EU Pharmaceutical Strategy 2023 to 2027 as a growth driver for premium gene therapies. EMA’s new adaptive licensing pathways helped streamline approval for rare CNS disorders. Strict sustainability compliance increased manufacturing costs. |
| Japan | Only 36% felt regulatory shifts had a major impact. PMDA approval timelines remained slow, leading to delayed sector entry. Government subsidies for local biotech R&D increased but still lagged behind Western counterparts. |
| South Korea | 41% of firms cited fast-track approval programs under the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) as helpful but not widely adopted. Interest in public-private partnerships to support domestic manufacturing and lower import dependency. |
The majority of gene therapy for CNS disorders will be executed in the USA landscape, with a projected CAGR of 32% over the period from 2025 to 2035. The leadership position of the country is based on significant R&D investments, a dynamic regulatory framework and accelerating acceptance of gene therapies in neurology.
In addition to the NIH’s BRAIN Initiative, the heavy funding from NINDS has also pushed forward innovations around gene therapy. Pricing and reimbursement still present a hurdle, and high costs can translate to a lack of access.
But value-based payment models are catching on, and insurers are testing outcome-based reimbursement. The USA biotech ecosystem including owners like Novartis, Biogen and Sarepta fosters constant progress in AAV and CRISPR-based treatment methodologies.
The UK is likely to see a CAGR of 28% between 2025 and 2035 thanks to buoyant government funding, a mature biotech sector and streamlined regulatory pathways. Gene therapy-based CNS products have benefited from the MHRA’s Innovative Licensing and Access Pathway (ILAP) which has streamlined approvals, making the UK an attractive place for pharmaceutical and biotech companies to run trials.
In England, the National Health Service (NHS) facilitates the incorporation of gene therapies by providing cost-sharing mechanisms and early patient access via the Early Access to Medicines Scheme (EAMS).
Other drivers include the UK’s push for genomic medicine and institutions such as the Wellcome Sanger Institute and Oxford University. Pricing negotiations with NICE (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) remain a crucial hurdle, particularly since cost-effectiveness thresholds could potentially slow down approvals.
French gene therapy for CNS disease is expected to expand at a 27% compound annual growth rate during 2025 to 2035 due to governance-led funding in health care, booming notable biotechnology and dynamic academic research partnerships. Accelerated pathways from France have improved access to novel therapies. Lysogene and other French Biotechs contribute significantly to the CNS-related gene therapy research efforts.
One of France's strong-suits in discovering and bringing novel treatments for diseases are the many public-private partnerships between the National Institute of Health and Medical Research (INSERM). Pharmaceutical/biotechnology companies that have developed across the country, working on how to scale up and, bring to segment, gene therapy. Nevertheless, pricing regulations within the French healthcare system can be strict, which might result in delayed commercial offerings.
Germany's CNS gene therapy landscape is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 29% during the 2025 to 2035 period, profiting from advanced biomanufacturing capabilities, robust regulatory support, and leadership in the area of neurology research. All these therapies are subject to approval at the Paul Ehrlich Institute (PEI)-the agency responsible for approving gene therapies-whose use is growing in clinics and specialized treatment centers.
With one of the biggest healthcare budgets in Europe, Germany represents a lucrative sector for premium-priced gene therapies. It also maintains a lead in sustainability-driven biomanufacturing, with various green bioproduction projects developing. Negotiations over reimbursement with the statutory health insurance (GKV) can hamper market access. Long-term sector sustainability is ensured by Germany's status as the place for clinical trials and industrial bioproduction.
The CNS gene therapy sector in Italy is predicted to grow closely with a CAGR of 26% due to rising clinical trials and approvals, along with widespread adoption in hospitals. Adaptive licensing initiatives in gene therapy are being implemented by the Italian Medicines Agency (AIFA) in order to expedite approvals.
However, pricing and reimbursement is nuanced, needing negotiation under Italy’s National Health Service (SSN). Biotech companies such as MolMed and research partnerships with European firms persist in driving innovation. However, economic constraints and disparities in healthcare access across regions could slow widespread adoption.
South Korea is expected to grow at 31% CAGR supported by government incentives, strong R&D investments, and increasing biotech ecosystem. The MFDS (Ministry of Food and Drug Safety) has streamlined review pathways for gene therapies in line with the government’s Bioeconomy 2030 initiative.
South Korea has been spending to develop a gene therapy production technology at home to curb disruption to imports. South Korea is expanding academic hospitals and increasing Samsung Biologics' manufacturing capacity to address the high cost of therapy and limited insurance coverage.
The CNS landscape for gene therapy in Japan is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 26% for the period spanning from 2025 to 2035, driven by the ageing population, high burden of neurodegenerative disease, biotechnology government initiatives. Regulatory conservatism and cost-sensitive healthcare policies create major obstacles to segment expansion. Japan’s Central Social Insurance Medical Council (Chuikyo) also has strict reimbursement policies.
Japan is taking gradual steps toward improving accessibility and making changes to its current policies, particularly in the area of regenerative medicine, which has been supported by the Revised Pharmaceutical Affairs Law through conditional approval.
Leading pharma companies like Astellas Pharma, Takeda, SNC - invest substantially in developing gene therapy product candidates for CNS disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The Japanese government has a history of boosting biotech, including relatively more funding toward CRISPR and viral vector-based gene therapies.
The market for gene therapy in CNS disorders in China is projected to grow at a CAGR of 32% between 2025 and 2035, making it one of the fastest-growing sectors for gene therapy for CNS disorders. The fast-paced growth is supported by biotech funding backed by the government, increased investment in healthcare infrastructure, and policy reforms that are encouraging innovative gene therapies.
Chinese biotech companies including Beijing GeneScience, CanSino Biologics, and Sinopharm are rapidly entering the CNS gene therapy sector, deploying a cost-conscious approach to drug development. Foreign firms have increasingly entered joint ventures with Chinese companies to oversee regulations and earn access to segment. However, concerns about intellectual property (IP) protection still linger for multinationals seeking to gain a foothold in China’s landscape.
The Australia and New Zealand (ANZ) gene therapy landscape for CNS disorders is forecasted to increase at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28 % from 2025 to 2035, oweing to world-class research institutions, strong infrastructure for clinical trials, and progressive policy for regulation. MediSafe in New Zealand and the therapeutic goods administration (TGA) in Australia, have embraced global best practices for the integration of gene therapy into their healthcare systems.
The region's rapid adoption of CNS gene therapies is due in part to the TGA's history of faster regulatory approvals for breakthrough gene therapies, while other segments have moved more slowly in their approvals of new treatments. The high cost of treatment and the limited market size remain obstacles.
The Indian gene therapy landscape for Central Nervous System (CNS) disorders is expected to grow with a CAGR of 25% during 2025 to 2035. India's gene therapy sector is projected to grow at 25% CAGR, though challenges such as high costs and regulatory delays may slow adoption. Although India has a massive patient population diagnosed with CNS disorders, comprehension of high cost attached to gene therapies remained a barrier for accessibility.
Over the years, the Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) has been continuously updating its regulatory framework for granting approvals for cell and gene therapy, yet stringent clinical trial requirements and a low approval rate for industrialization have hindered the commercialization effort. But India’s biotech industry is growing, and companies such as Bharat Biotech, Biocon and Zydus Cadila are venturing into research and manufacturing for gene therapy.
Gene therapy is considered a prospective treatment for a number of neurodegenerative disorders. Gene therapies in the case of Alzheimer's disease concentrate on the genetic modification of decreasing amyloid plaques and tau tangles that are the central causes of dementia. Huntington's disease gene therapy targets inhibiting the mutant huntingtin gene, which is accountable for the neuronal degeneration.
Gene therapy in Parkinson's disease helps restore dopamine synthesis through the administration of therapeutic genes straight into the brain. Batten disease, a genetic disorder, is treated by gene replacement therapy, in which functional genes are added to replace defective ones.
Gene therapy is divided into Ex Vivo and In Vivo types. Ex Vivo therapy consists of extracting cells from a patient, genetically altering them in the lab, and returning them to the body. This process provides more control over the genetic alterations.
In Vivo gene therapy, however, entails the direct introduction of genetic material into the patient's body through viral vectors or other delivery systems. This is more prevalent for neurodegenerative disorders because it provides targeted treatment of the affected brain cells.
The major end recipients of gene therapy are specialty clinics and hospitals. Hospitals act as the primary hubs for gene therapy treatment, offering access to the latest research and clinical trials. They are appropriately geared to perform complex gene therapy treatment.
Specialty clinics deal with a particular neurological condition and offer specialized care in a more intimate environment. The clinics usually partner with research facilities to provide sophisticated gene therapy treatment for neurodegenerative diseases.
Leading players in the gene therapy industry are fighting on the basis of pricing strategies, innovation, strategic collaborations, and international expansion. Companies are taking pricing strategies like value-based pricing and installment payment schemes due to the exorbitant price of gene therapy so that the treatment remains affordable.
Innovation is a major competitive driver, with companies spending heavily on research and development (R&D) to advance gene delivery systems, optimize viral vectors, and create safer, more potent therapies.
Growth tactics in this area are centered on increasing clinical trials, obtaining regulatory approvals, and international industry penetration. Firms are busy building their pipelines by pursuing numerous neurological diseases and orphan diseases. Most companies are also making in-licensing deals with small biotech firms to add on their expertise and build their position in the marketplace.
Novartis - ~25-30%
Biogen - ~20-25%
Spark Therapeutics (Roche) - ~15-20%
UniQure - ~10-15%
Voyager Therapeutics - ~5-10%
Emerging Biotech Players (Sarepta, Neurocrine, CRISPR-based firms) - ~10-15%
Mergers & Acquisitions
Regulatory Milestones
Product Launches & Clinical Advancements
Strategic Partnerships
Emerging Tech & Investments
Progress in genetic research, rising incidence of neurological disorders, and growing investments in biotechnology are key growth drivers.
Gene therapy in CNS disorder is being investigated for Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, and Batten disease, among others.
High drug prices, regulatory barriers, lengthy approvals, and long-term safety concerns are a few of the major issues.
Novartis, Biogen, Pfizer, and Bluebird Bio are some of the prominent companies that are working on novel gene therapies.
Based on the approach, gene therapy in CNS disorder can be carried out through ex vivo methods (editing cells outside the body) or in vivo methods (injecting genetic material into the patient).
Intraoperative Fluorescence Imaging Market Report - Demand, Trends & Industry Forecast 2025 to 2035
Lung Cancer PCR Panel Market Trends, Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Polymyxin Resistance Testing Market Analysis by Product, Testing Methods, End User, and Region - Forecast for 2025 to 2035
Cardiovascular Diagnostics Market Report- Trends & Innovations 2025 to 2035
Venous Ulcer Treatment Market Overview - Growth, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Bone Regeneration Market Analysis - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.