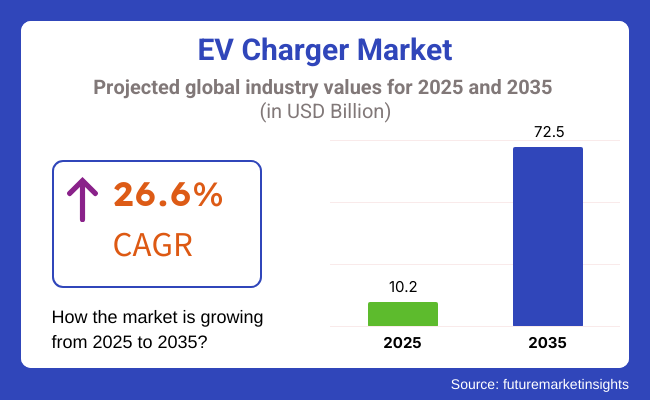
The EV charger market is expected to rise from USD 6.5 billion in 2023 to USD 10.2 billion by 2025. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is projected to be 26.6%, which will result in a significant rise to USD 72.5 billion by 2035. The electric vehicle (EV) charger market is undergoing spectacular growth driven by the increasing adoption of batteries and the continuous infrastructure development of chargers.
As more and more clients choose the electric mobility option, the need for fast, reliable, and open EV charging facilities is climbing. The market comprises various types of technologies, starting from home chargers to the public high-speed DC fast chargers. These are the tools that help the electric vehicle entrust the public with the range issue and the charging discomfort.
In addition, the growth is maximized through increasing governmental incentives and investments in both public and private charging networks. Yet, the industry has its own disadvantages, for instance, the uneven distribution of charging infrastructure which makes it an issue in rural and developing areas. Establishing a wide network requires a huge amount of capital and development of infrastructure, the very two things that are hard to get in resource-constrained areas.
Another pressing problem is that charging technologies and vehicle models are not standardized across the industry, which may lead to compatibility issues. Even though ultra-fast charging is the most needed, uniform charging protocols need to be worked on over time to enable hassle-free client use.
Furthermore, the expansion of the charging networks provides a new area of growth. State and private sectors are committing to the project by laying the foundations of a massive charging network, particularly in regions with poor urbanization. Norway, Germany, and China are the leading nations deploying the thick-charging networks to back the electric car revolution.
The emergence of workplace and home-based charging solutions also advances the expansion of the market, since the client can consider it as a convenient and less costly method to charge their electric cars. Besides that, the integration of renewable energy in the electric vehicle charging stations is acquiring the mass, with the emergence of solar and wind chargers as the conquerors of the sustainable domain.
Companies like Ionity and BP Pulse are, for example, making an investment in the ultra-fast chargers that are powered by renewable energy in the drive for greener transport. While the industry grows and develops, overcoming the problems of infrastructure and compatibility while also adopting the new technologies will be foundational steps to developing the EV charger market.
Network coverage and reliability is rated highly by OEMs and infrastructure providers, but only moderately important by end users and utility companies, as the latter trade-off performance with more general operational considerations. [Smart grid integration is important for OEMs and utility companies both rated it high, illustrating the need for chargers that talk to modern energy networks.
This indicates that cost/value for money is important, with infrastructure providers ranking it high and other stakeholders ranking it as medium. It is also no secret that utility companies highly prioritize sustainability and energy efficiency, while OEMs tout innovation and “future-proofing” a solution as part of their core benefits.
Between 2020 and 2024, the EV charging market expanded rapidly, driven by the rising adoption of electric vehicles, advancements in charging technology, and government incentives for green transportation. Faster and more efficient charging solutions became a priority, with ultra-fast DC chargers (150 kW to 350 kW) reducing charging times to under 20 minutes.
Car manufacturers and charging network operators joined forces to increase charging facilities, with smart home and work-place chargers rationalizing electricity consumption. Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology appeared to enable EVs to store and feedback energy into the grid, though regulatory and compatibility issues held back mass market adoption.
Its charging future between 2025 to 2035 shall comprise ultra-fast and wireless, renewable energy integrated, and artificial intelligence-based energy management to make the charging both efficient and intelligent.
AI will optimize charging based on efficiency and perform it wirelessly off of plug-in areas to maximize users' convenience. Governments, automotive companies, and technology companies would drive these to enable smart, seamless charging of EVs to boost worldwide sales of EVs.
A Comparative Market Shift Analysis (2020 to 2024 vs. 2025 to 2035)
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| Government subsidies for charger deployment | Stricter EV infrastructure mandates, grid integration policies |
| Expansion of fast-charging networks | Megawatt charging, wireless, and dynamic charging solutions |
| Growth in residential, public, and highway charging | Autonomous fleet charging, AI-driven energy management |
| Smart home chargers with energy monitoring | AI-optimized charging schedules, robotic charging arms |
| Solar-powered chargers, grid modernization | Second-life battery storage, decentralized energy trading |
| Limited real-time analytics in charging networks | AI-powered predictive maintenance, blockchain-based energy transactions |
| Supply chain disruptions impacting charger availability | Scalable manufacturing of high-power charging systems |
| EV adoption, fast-charging demand | Wireless charging expansion, seamless interconnectivity across networks |
The EV charger market has a lot of regulation-required uncertainty, as changing standards for things like connectors, money collection, and safety could require retrofits or expensive redesigns. As different regions and automakers have long had competing charging standards, recent moves-such as Tesla's NACS gaining traction-would potentially require non-Tesla networks to overhaul their infrastructure.
Moreover, permitting and zoning issues can create delays and add costs to charger installations. They also face supply chain risks: EV chargers depend on semiconductors, power electronics, and raw materials like copper, which have all suffered shortages and price fluctuations.
Geopolitical factors, like global trade tensions or order backlogs in manufacturing, can also hit supply chains, impacting production timeframes. There’s also volatility in utilization rates in the market - charging infrastructure is capital-intensive and, in fact, if EV adoption grows slower than the projected speeds in some locations, certain stations may lie underutilized and delay the return on investment.
On the other hand, quick consumer growth in EV adoption may drive the network to congestion and unreliability, diminishing the user experience. The operational risks of hardware durability, cyberthreats, and volatility in electricity prices could affect profitability. Much of the expansion is being driven by government incentives, but changes in policy or cuts in funding could stymie deployment.
Companies should prepare for these risks through regulatory compliance, supply chain diversification, and strategic location planning.
Pricing strategies for EV charging differ on hardware sales and charging services. Charger makers often follow a cost-plus formula for hardware, with even higher margins for advanced capabilities such as ultra-fast charging or smart connectivity.
The Level 2 home charger segment, in particular, is seeing an influx of competition, which is complicating market pricing. Pricing models for public charging services vary and can range from per-kWh billing to time-based rates to dynamic pricing based demand or electricity cost.
Subscriptions, like Electrify America’s Pass+, with reduced prices for members locks in recurring revenue. Some places offer free or subsidized charging as a carrot, with retailers or automakers paying for the privilege. Few were willing to share, so penetration pricing became common - networks went low to court the users at first, but profitability worries are pushing gradual price rises.
Operators play with idle fees and cross-subsidization (i.e., highway chargers don’t necessarily have to cost less than urban ones). Pricing is heavily influenced by electricity tariffs and demand charges from the grid, which include peak demand costs that can eat into margins, especially for fast chargers.
Low prices hinge on location density and service reliability-drivers care more about availability and speed than small differences in price. As EV adoption increases, pricing becomes more stabilized, with networks optimizing rates in terms of profitability for them and affordability for users.
| Country | CAGR (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| The USA | 9.0% |
| The UK | 8.6% |
| European Union (EU) | 8.8% |
| Japan | 8.2% |
| South Korea | 8.7% |
The USA market for electric vehicle charging infrastructure is expanding at a fast pace primarily because of the transition to electric mobility. As a result of increasing consumer acceptance of EVs and rising government incentives, there is increasing demand for efficient, high-speed charging networks.
The USA is expected to lead in 2025 with over 500,000 EV charging stations owing to initiatives like the Biden administration's proposal to invest in electric vehicle infrastructure.
Players in the industry such as Tesla, ChargePoint, and Electrify America are transforming charging technology with AI-driven energy management systems and grid integration. The systems ensure that energy is utilized efficiently, minimizing charging time while integrating with renewable energy sources to offer a green supply.
The development of universal charging compatibility and wireless charging technologies is also shaping the future of the EV infrastructure market. FMI estimates that the USA market will grow at 9.0% CAGR during the research period (2025 to 2035).
Growth Drivers in the USA
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Government incentives | Government initiatives such as the Biden administration's plan to invest in charging infrastructure for electric vehicles are driving market growth. |
| Consumer EV adoption | Higher consumer uptake of EVs is creating demand for high-speed and efficient charging stations. |
| Improved charging technology | Manufacturer-led AI-powered energy networks and grid connections by companies like Tesla and Electrify America propel efficiency. |
The UK market is experiencing massive growth as a result of government plans to phase out ICE cars by 2035. This move is increasing the demand for electric cars, as well as public and private charging stations. The UK has launched a series of government incentives, such as discounts on purchasing EVs, which have promoted the use of electric cars.
Major companies like BP Pulse, Gridserve, and Shell Recharge are developing intelligent charging networks through real-time energy consumption optimization and dynamic pricing to make it more convenient and reduce customer cost. The networks are also being connected with renewable energy solutions in a bid to support the country's green mobility targets. FMI has quantified that UK demand will expand at 8.6% CAGR from 2025 to 2035.
Growth Drivers in the UK
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Government policies | The initiative towards phasing out ICE cars by 2035 is propelling EV adoption and charging point demand. |
| Smart charging infrastructure | Players like BP Pulse and Shell Recharge are leading the way with smart, real-time energy-maximizing charging points. |
| Green energy integration | Smart charging networks combined with green energy systems minimize charging expenditure and maximize levels of sustainability. |
The EU electric vehicle charging infrastructure market is growing exponentially, propelled by ambitious EU emissions targets, increasing numbers of electric vehicles on the road, and significant investment in renewable energy integration. Germany, France, and the Netherlands are making large investments in city-center charging points, highway fast-charging corridors, and smart-grid-enabled solutions.
These organizations, such as Ionity, ABB, and Siemens, are pioneering modular, AI-driven charging stations that simplify energy distribution with improved user experience. In tandem, integration of solar and wind power into the EV charging infrastructure is building pace, providing cleaner and sustainable electricity for EVs. FMI projects the EU market to expand at 8.8% CAGR during the forecast period (2025 to 2035).
Growth Drivers in the EU
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| EU emissions law | Tighter anti-pollution measures mandate installing electric vehicles and charging stations in exchange. |
| Investment in green energy | Extreme emissions make governments increase investment in clean energy sources like the wind and sunlight. |
| Smart charge technology | Employment of artificially intelligent charging stations that were designed by businesses such as Ionity and ABB decreases costs of dispersion of electricity and improves the ease of use. |
Japan's EV charging sector is slowly growing as the nation invests in smart mobility, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, and ultra-fast charging. The nation has ambitious carbon-neutral goals with the goal of becoming net-zero by 2050. Therefore, investment in EV infrastructure has been on the rise.
Japanese car manufacturers such as Toyota, Honda, and Nissan are investing heavily in solid-state battery technology that can potentially deliver faster charging and high energy density. Such technologies are supporting next-generation charging systems with high efficiency and less heat generation. The Japanese market is expected to grow at 8.2% CAGR during the forecast period (2025 to 2035), says FMI.
Growth Drivers in Japan
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Carbon-neutrality targets | Japan's 2050 target for carbon neutrality is propelling investment in EV charging infrastructure. |
| Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology | We require high-efficiency, low-heat charging technology to advance V2G systems. |
| Solid-state battery development | Automakers are investing in solid-state batteries like Toyota and Nissan with demanding charging systems needed. |
South Korea's electric vehicle charging market is growing strongly as well, with goading from government subsidies, fast-track local production of EVs, and adoption of AI-charged charging infrastructure. As Hyundai and Kia take the lead in pushing forward next-generation EV development, there is increasing pressure to build wireless and fast-charging networks
Companies such as SK Innovation, LG Energy Solution, and Hyundai Mobis are introducing smart grid solutions and real-time charging monitoring and energy-efficient charging stations. The features enhance the efficiency of charging infrastructure and match the increasing trend of EV demands. The growth of the South Korean market will be 8.7% CAGR by the forecasted period (2025 to 2035), as indicated by FMI.
Growth Drivers for South Korea
| Key Drivers | Details |
|---|---|
| Government incentives | Government policy support and incentives are driving EV and supporting infrastructure development. |
| Industry collaboration | Locally based companies such as SK Innovation and Hyundai Mobis are collaborating to develop smart grid solutions. |
| Wireless charging demand | Expansion of wireless and high-speed charging systems to match the country's volume of EVs. |
You know that PHEV vehicles need to be plugged in and both need AC and IC support, which is why you need AC (Level 1 (120V), Level 2 (240V)) chargers for home charging and public charging. Because PHEVs can run on electricity only for short distances and then revert to gasoline, their owners value convenient charging options to maximize electric operation during the day.
That is good for a growing PHEV market - the Toyota RAV4 Prime and BMW X5 xDrive45e lead the way - and demand for smart home chargers and workplace charging stations. A steady growth in the PHEV charger segment is also notable, given the impact of government incentives & increasing Hybrid option availability by automakers as a bridge to complete electrification.
The dependency of BEVs on electricity at the same time makes their charging infrastructure need widespread and highly efficient. BEVs primarily use Level 2 (home/public) and DC fast chargers (50-350 kW) to reduce charging times and make long-distance travel practical. Long-range BEVs are growing rapidly, from high-range options like the Tesla Model 3, Volkswagen ID.
4 and Hyundai Ioniq 5, has sped up the deployment of high-power charging networks like Tesla Superchargers, Ionity, and Electrify Europe. As Europe sets ambitious goals, aiming for 30 million EVs on roads by 2030, the need to invest in fast-charging hubs and ultra-fast DC charging stations is key to resolving range anxiety and promoting the smooth transition away from fossil-fuel cars.
On-board chargers (OBCs): The foundation of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure, OBCs are built inside EVs to convert AC power into DC power for battery storage from home or public chargers. Their power range is usually between 3.3 kW to 22 kW, which is mandatory for Level 1 and Level 2 charging.
State-of-the-art semiconductor technology utilizing silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) has increased OBC efficiency, minimizing heat wastage and consequently allowing for faster AC charging. For example, it has a 19.2 kW OBC, so the Lucid Air can get 62 miles of range per hour of charging.
Three-phase 11 kW and 22 kW on-board chargers (OBC) are gaining traction in Europe, and it is increasingly likely that EVs will be fully compatible with high-power AC charging infrastructure.
On the other hand, off-board chargers are standalone DC charging hardware that sends direct power for charging an EV battery without requiring in-car conversion. These are DC fast-charge stations (50-350 kW), which dramatically shorter charge times.
Peer companies like Tesla Superchargers, Ionity and Electrify Europe charge with off-board chargers, offering ultra-quick charging that can turn cars like the Porsche Taycan or Hyundai Ioniq 5 from 10% to 80% in under 20mins. With governments calling for wide-ranging fast-charging networks, innovations in liquid-cooled and megawatt charging systems (MCS) will help usher in the future of high-speed EV charging.
The fast-paced growth of EV adoption, fast- technology, as well as smart grid integration makes the EV charging market one of the most competitive markets. The company's focus is on high-power DC fast chargers, wireless charging, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capabilities to enhance charging efficiency and grid stability. The market is thus influenced by energy conglomerates, automobile manufacturers, and tech startups, which are all racing to extend public and private charging networks for better user accessibility and charging speed.
The major players in the market, including Tesla, ABB, ChargePoint, Shell Recharge, and Ionity, are leveraging extensive networks of charging stations, proprietary technologies of fast charging, and strategic partnerships to enhance their presence in a very competitive market. Tesla's Supercharger network has been seen as the industry benchmark, while ABB and ChargePoint look toward building scalable, high-power charging solutions for both commercial and residential applications. Ionity and Shell Recharge, meanwhile, are promoting Pan-European charging expansion that is vital to long-distance EV travel. New entrants have started distinguishing themselves in this very fast-evolving sector with their developments in bidirectional charging, AI-driven energy management, and ultra-fast charging stations. With governments and automakers pushing for the widespread electrification of transport, companies which have already wagered in grid-friendly, high-speed, and green charging solutions will achieve a lasting edge against competition.
Market Share Analysis by Company
| Company Name | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Tesla Inc. | 18-22% |
| ChargePoint Holdings | 15-20% |
| ABB | 12-16% |
| Siemens | 10-14% |
| Blink Charging Co. | 6-10% |
| Other Companies (combined) | 30-40% |
| Company Name | Key Offerings/Activities |
|---|---|
| Tesla Inc. | Develops and operates Supercharger networks with ultra-fast DC charging capabilities. |
| ChargePoint Holdings | Specializes in Level 2 and DC fast-charging stations with extensive public and private networks. |
| ABB | Provides high-power fast chargers with smart energy management and grid integration. |
| Siemens | Innovates in wireless charging and scalable EV infrastructure solutions. |
| Blink Charging Co. | Focuses on flexible as well as affordable residential and commercial EV charging solutions. |
Key Company Insights
Tesla Inc. (18-22%)
Tesla leads the charge in the electric vehicle (EV) charging markets through its Supercharger network, providing high-speed charging for its vehicles. The company consistently expands the network to shorten charging times as well as enhance accessibility to EV owners.
ChargePoint Holdings (15-20%)
ChargePoint has a strong presence in EV charging on public and private levels. It provides flexible and scalable charging options to small and large companies and individuals. Its emphasis on the expansion of the network and the ease of integration has put this company at the leading edge of the market.
ABB (12-16%)
ABB is driving the development of high-power charging technology, supplying fast chargers that can serve many vehicle types while cooperating with smart grids to improve the energy efficiency of the whole power system.
Siemens (10-14%)
Siemens is working on making the first wireless and modular EV charging infrastructure that will provide seamless and scalable solutions for urban and commercial charging needs.
Blink Charging Co. (6-10%)
With user-friendly designs for residential and commercial EV chargers, Blink Charging offers flexible and cost-effective charging solutions for easy adoption.
The EV charger market supports Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs), with BEVs leading due to increasing adoption of zero-emission vehicles.
Charging solutions include on-board chargers, off-board chargers, and others, with off-board chargers gaining traction for faster charging capabilities.
EV chargers cater to residential, commercial, and other electric vehicles, with commercial charging infrastructure expanding due to rising fleet electrification.
The market spans North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia and the Pacific, and the Middle East and Africa (MEA), with Europe and North America leading due to government incentives and charging network expansion.
A revenue of USD 10.2 billion is expected to be generated from manufacturing EV chargers in 2025.
The market is predicted to reach a size of USD 72.5 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 26.6% from 2025 to 2035.
Key manufacturers in the market include ABB Ltd., Robert Bosch GmbH, Siemens AG, Delphi Automotive, Chroma ATE, Aerovironment Inc., Silicon Laboratories, bp pulse, Schaffner Holding AG, and POD Point.
Europe is expected to be a prominent hub for EV charger manufacturers, driven by government incentives and increasing EV adoption.
Level 2 chargers are the most widely used product segment in the EV charger market due to their balance of charging speed and cost-effectiveness.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: Global Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: Global Market Volume (Units) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: North America Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: North America Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: North America Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: North America Market Volume (Units) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: Latin America Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: Latin America Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: Latin America Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: Latin America Market Volume (Units) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: Europe Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: Europe Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: Europe Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: Europe Market Volume (Units) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 33: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 34: Asia Pacific Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 35: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 36: Asia Pacific Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 37: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 38: Asia Pacific Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 39: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 40: Asia Pacific Market Volume (Units) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 41: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 42: MEA Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 43: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 44: MEA Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 45: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 46: MEA Market Volume (Units) Forecast by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Table 47: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 48: MEA Market Volume (Units) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Volume (Units) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: Global Market Attractiveness by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: Global Market Attractiveness by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: Global Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 42: North America Market Volume (Units) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 43: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: North America Market Attractiveness by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 46: North America Market Attractiveness by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: North America Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 62: Latin America Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 63: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: Latin America Market Volume (Units) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 67: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 69: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Latin America Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 72: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 75: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 78: Europe Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 79: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 82: Europe Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 83: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 86: Europe Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 87: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 89: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 90: Europe Market Volume (Units) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 91: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 92: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: Europe Market Attractiveness by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: Europe Market Attractiveness by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 95: Europe Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 102: Asia Pacific Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 103: Asia Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: Asia Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: Asia Pacific Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 107: Asia Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: Asia Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 109: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 110: Asia Pacific Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 111: Asia Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 112: Asia Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: Asia Pacific Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 114: Asia Pacific Market Volume (Units) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 115: Asia Pacific Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: Asia Pacific Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: Asia Pacific Market Attractiveness by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: Asia Pacific Market Attractiveness by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: Asia Pacific Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: Asia Pacific Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 126: MEA Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 127: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 129: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 130: MEA Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 131: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 132: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 134: MEA Market Volume (Units) Analysis by Charging Type, 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 138: MEA Market Volume (Units) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 139: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: MEA Market Attractiveness by Vehicle Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: MEA Market Attractiveness by Charging Type, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: MEA Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 144: MEA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
EV Charger Converter Module Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
BEV On-Board Charger Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
DC BEV On-Board Charger Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
AC BEV On-Board Charger Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
EV Charging Panelboard Market Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Evacuated Miniature Crystal Oscillator (EMXO) Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
EV Charging Tester Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Evaporative Air Cooler Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
EV Charging Cable Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
EVOH Encapsulation Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
eVTOL Charging Facilities Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Event Tourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
EV Telematics Control Systems Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Evidence Collection Tubes Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
EV Battery Recycling and Black Mass Processing Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
EVA Coated Film Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
EV Charging Management Software Platform Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
EV EMC Battery Filter Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
EV Traction Inverter Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
EV Plant Construction Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA