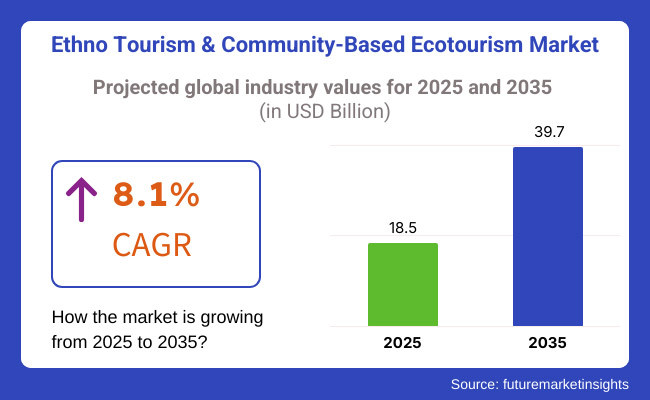
The global ethno tourism and community-based ecotourism market is projected to reach USD 18.5 billion by 2025 and expand significantly to USD 39.7 billion by 2035. The industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.1% during 2025 to 2035, fueled by rising demand for authentic cultural experiences, sustainable travel options, and local community empowerment.
Companies specializing in ethno and ecotourism are expanding their offerings by integrating immersive experiences with conservation-focused initiatives and technology-driven cultural preservation programs. Industry leaders such as G Adventures, Intrepid Travel, and National Geographic Expeditions promote locally-led tourism experiences that emphasize indigenous knowledge, environmental protection, and economic benefits for rural communities.
Cultural travelers, conservationists, and eco-conscious tourists increasingly seek off-the-beaten-path destinations where they can engage directly with local traditions and support community-driven tourism enterprises. The need for sustainable tourism models has led to partnerships between governments, non-profits, and responsible tourism operators to develop ethical travel policies.
Mobile-based heritage tourism platforms and digital storytelling initiatives are gaining traction, with organizations like Local Purse and Atlas Obscura offering real-time engagement with artisans and cultural experts. The rise of carbon-neutral travel initiatives and regenerative tourism programs further drives market expansion.
Between 2020 and 2024, the ethno tourism and community-based ecotourism market expanded at a CAGR of 6.4%, driven by the post-pandemic shift toward nature-based and cultural travel experiences. The market, valued at USD 16.8 billion in 2024, is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.1% during 2025-2035, reaching USD 39.7 billion by 2035.
The main growth drivers are the rise in environmentally friendly tourism, the quest for authentic local experiences, and government-initiated policies of sustainable tourism. Firms are embracing digital storytelling solutions, AI-driven heritage conservation, and carbon footprint measurement to maximize visitor connections and sustainability outcomes.
Comparative Analysis: Ethno Tourism Vs Sustainable Travel & Regenerative Tourism
| Global Ethno Tourism Market | Sustainable Travel & Regenerative Tourism Market |
|---|---|
| 2020: USD 12.4 Billion (Rise in Local & Rural Tourism) | 2020: USD 8.3 Billion (Early Adoption of Responsible Tourism) |
| 2024: USD 16.8 Billion (Eco-Tourism & Heritage Travel Boom) | 2024: USD 11.6 Billion (Widespread Carbon-Neutral Initiatives) |
| 2025: USD 18.5 Billion (Government Policies Support Indigenous Tourism) | 2025: USD 13.1 Billion (Stronger Push for Ethical Travel) |
| 2035: USD 39.7 Billion (Mainstream Community-First Travel Experiences) | 2035: USD 28.9 Billion (Global Standardization of Sustainable Tourism) |
Comparative Analysis: Ethno Tourism vs. Community-Based Tourism
| Ethno Tourism | Community-Based Tourism |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2024A): USD 6.2 Billion | Market Size (2024A): USD 10.6 Billion |
| Projected Growth (CAGR 2025-2035): 7.9% | Projected Growth (CAGR 2025-2035): 8.4% |
| Focus: Promotes deep cultural experiences with indigenous and ethnic communities. | Focus: Engages local communities in tourism development for economic and social benefits. |
| Economic Impact: Generates USD 2.5 billion annually through cultural preservation and artisan markets. | Economic Impact: Contributes USD 4.1 billion to local economies by creating sustainable employment. |
| Sustainability: Focuses on preserving intangible cultural heritage and traditions. | Sustainability: Encourages responsible tourism that benefits host communities directly. |
| Government Role: Cultural ministries and heritage organizations fund and promote ethno tourism. | Government Role: Local governments and NGOs collaborate to enhance community-based initiatives. |
| Traveler Engagement: 65% of ethno tourists seek immersive cultural traditions, such as participating in ceremonies or festivals. | Traveler Engagement: 75% of community-based tourists engage in daily community activities, such as farming, fishing, and handicrafts. |
| Technology Integration: Digital storytelling platforms and virtual cultural workshops promote traditions. | Technology Integration: Online booking platforms and digital marketplaces connect travelers with local hosts. |
Ethno tourism and community-based tourism have developed considerably as tourists increasingly demand more in-depth cultural immersion and interaction with host communities. They are transforming the industry by highlighting authenticity, sustainability, and immediate local community engagement.
Ethno tourism is booming as tourists go beyond the act of sightseeing to become participants in indigenous and traditional cultures. In Peru, tourists hike with Quechua guides on the Inca Trail, learning about prehistoric farming techniques and Andean cosmology. In Mongolia, too, tourists live with nomadic families, sharing traditional horse-riding skills and throat singing. Governments and cultural institutions are going out of their way to safeguard these experiences by financing heritage tourism initiatives and supporting local artisans.
Community tourism is growing at a fast pace, and tourists are able to directly support local economies. In Guatemala, cooperatives such as Rupalaj K'istalin provide tourists the option to live with Mayan families, experience weaving workshops, and learn about traditional farming practices. In Thailand, sustainable homestays of the Karen Hill Tribe community provide travelers with opportunities to immerse themselves in their culture while ensuring economic gains are retained within the village. These projects empower the community by raising income, maintaining traditions, and generating jobs.
Technology is having a significant impact across both industries. Sites such as NotOnMap are linking travelers with off-grid village stays, so tourism dollars go directly to supporting local hosts. Virtual cultural workshops are also becoming a hit, allowing tourists to learn activities such as Japanese calligraphy or Moroccan tile-making from anywhere globally.
As the world's tourists seek greater immersion, responsible, and ethical tourism experiences, ethno and community-based tourism will increasingly determine the future of international travel. Such models ensure cultural conservation while stimulating economic development to deliver a more inclusive, sustainable, and tourism industry.
Cultural immersion is now the backbone of the ethno tourism industry, with tourists looking for real, experiential holidays that transcend traditional site-seeing. Tourists are more and more now taking part in festivals in the destination countries, artisan workshops, and community-led food activities. In Mongolia, for example, tourists live with nomad families, picking up traditional herding skills and horse riding, whereas in Japan's countryside villages, tourists learn historical kimono weaving and tea ceremonies.
Governments and nonprofits are actively advocating cultural immersion experiences. Peru's Ministry of Tourism has launched indigenous-guided Andean trekking programs, featuring local Quechua guides interpreting their history and spiritual practices in depth. Analogously, South Africa's Zulu people have established cultural heritage tours, during which tourists can take part in bead-making courses and storytelling exercises.
Companies are also integrating virtual cultural immersion experiences to make indigenous traditions accessible worldwide. Platforms like Local Purse and Atlas Obscura enable real-time interactions with artisans, allowing travelers to explore heritage crafts remotely before visiting destinations in person. As demand for deep, meaningful travel experiences grows, cultural immersion will continue to shape the future of ethno tourism.
Cultural aficionados are a critical niche within the ethno tourism market, with a focus on preserving heritage and experiential learning. These tourists seek out active interaction with indigenous customs, be it through tribal fairs, language courses, or historical reenactments. Cultural tourists at India's Rajasthan engage in Pushkar Camel Fair festivities, whereas in Turkey's Cappadocia, they visit subterranean cities and ancient cave settlements.
Organizations focused on cultural heritage conservation have launched volunteer-based tourism programs, allowing travelers to contribute directly to preservation efforts. In Italy’s Tuscany region, visitors work alongside artisans to restore historic frescoes, while in Ethiopia, cultural enthusiasts help document ancient scripts and oral histories.
Luxury travel brands have also tapped into this segment by offering high-end cultural experiences that support local artisans. Aman Resorts and Explora Lodges curate exclusive cultural itineraries, including private access to indigenous ceremonies and collaborations with master craftsmen. The growing demand for intellectual and heritage-rich travel ensures that cultural enthusiasts will remain a primary driver of community-based ecotourism expansion.
Ethno tourism and community tourism in India have seen a dramatic change as tourists increasingly look for experiential cultural experiences. The nation's rich traditions, ancient history, and native populations have fueled the development of locally-managed tourism programs.
In Rajasthan, heritage homestays have emerged as a popular alternative to conventional hotels. Families in villages like Chandelao and Samode host tourists in traditional havelis, offering them firsthand experiences of folk music, Rajasthani cuisine, and local craftsmanship. In Northeast India, tribal tourism has gained momentum, with Nagaland’s Hornbill Festival drawing thousands of visitors eager to learn about Naga customs, warrior traditions, and handicrafts.
India's government has actively pursued community-based tourism. The Rural Tourism Scheme, introduced by the Ministry of Tourism, has motivated villages such as Hodka in Gujarat and Mawlynnong in Meghalaya to be self-sufficient tourism destinations. These villages represent traditional ways of life, with eco-friendly accommodations and guided cultural tours.
The private sector has also been instrumental in promoting community-based tourism. Enterprises such as Grassroutes Journeys and Spiti Ecosphere have created sustainable travel initiatives in which tourists take part in farm work, local narratives, and conservation efforts. The high-altitude villages in Spiti Valley offer homestays in which tourists interact with Buddhist monks, assist with organic farming, and experience ancient Tibetan heritage.
Technology is redefining India's ethno tourism. Websites such as NotOnMap are bringing travelers into contact with isolated village homestays, guaranteeing that benefits from tourism trickle directly into the pockets of the locals. Virtual experiences have also caught on, with online interactive sessions on Madhubani painting and Kutch embroidery enabling global travelers to connect with craftsmen. With increasing demand for genuine travel, India's ethno tourism sector is developing further, combining tradition with sustainability to provide enriching and meaningful experiences.
Japan's community-based tourism and ethno tourism industry is changing as tourists look for more intensive exposure to traditional Japanese culture. Heritage towns and rural areas are being converted into culture immersion centers, providing tourists with genuine experiences beyond Japan's large cities.
In Shirakawa-go, a UNESCO World Heritage village, tourists live in centuries-old thatched-roof cottages, learning about traditional farming and local crafts. The government actively encourages this model, with the assurance that tourism income goes towards historic preservation and community development. Likewise, in Kyushu, samurai heritage villages provide interactive experiences where tourists can take sword-fighting lessons and participate in tea ceremonies with descendants of feudal warriors.
The private sector is also powering Japan's community-based tourism development. Satoyama Experience in Gifu Prefecture, for example, runs cycling tours across rural villages where tourists go to local sake breweries, rice fields, and washi paper mills. In Okinawa, tourism is led by the community and focuses on Ryukyuan culture, with tourists engaging in traditional dance performances and coral reef conservation activities.
Technology is driving Japan's ethno tourism sector. Sites such as TABICA bring tourists to rural hosts who can provide unusual cultural experiences, such as workshops for indigo dyeing and miso making. Virtual reality tours enable tourists to view Japan's historical sites prior to visiting them, creating interest in off-the-beaten-path locations.
As the Japanese government focuses on sustainable tourism and regional revitalization, the ethno tourism industry will keep growing. Tourists increasingly opt for meaningful, community-based experiences, so that Japan's rich cultural heritage continues to be a core component of its tourism industry.
The ecotourism and community-based ethno-tourism market has a dispersed market structure with many small and medium-sized operators fueling competition. Regional markets are dominated by local cooperatives, such as Thailand's Karen Hill Tribe Homestay initiative, and indigenous-led operations like Canada's Indigenous Tourism Association. Larger operators, such as G Adventures and Intrepid Travel, incorporate these activities into their overall tour packages, fueling competition. In contrast to mass tourism, barriers to entry are low with little capital needed, supporting ongoing new entrants. Differentiation based on genuine cultural experiences and sustainability efforts—such as Ecuador's Sani Lodge's indigenous ownership structure—dictates success in this extremely competitive and experience-based market.
Scope of the Report
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Forecast Period | 2025-2035 |
| Historical Data Available for | 2020-2024 |
| Market Analysis | USD Billion for Value |
| Key Regions Covered | North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia, Oceania, MEA |
| Key Segments Covered | Service Type, End User |
| Key Companies Profiled | Triple Canopy, Olive Group, Control Risks, UnitedHealthcare Global, MEDEX Global Solutions, GardaWorld, Constellis |
The global ethno-tourism and community-based ecotourism market is valued at approximately USD 16.8 billion in 2024. The market is projected to reach USD 18.5 billion in 2025 and expand to around USD 39.7 billion by 2035, with an estimated CAGR of 8.1%.
Rising demand for authentic cultural experiences, government-backed sustainable tourism initiatives, and increasing traveler interest in indigenous heritage and environmental conservation are fueling industry growth.
Notable players include G Adventures, Intrepid Travel, Responsible Travel, and local organizations such as Thailand’s CBT-I (Community-Based Tourism Institute) and Namibia’s conservancy-run lodges.
Online platforms like Airbnb Experiences and Fairbnb enable small communities to reach global travelers.
Certifications such as the Rainforest Alliance’s sustainable tourism badge and the Global Ecotourism Network’s accreditation boost credibility.
Tourists are actively choosing destinations that promote environmental conservation and cultural preservation.
Travelers are prioritizing immersive, locally-led experiences over commercialized tours.
Table 01: Capital Investment in Tourism (US$ Million)
Table 02: Total Tourist Arrivals (Million), 2022
Table 03: Total Spending (US$ Million) and Forecast (2018 to 2033)
Table 04: Number of Tourists (Million) and Forecast (2018 to 2033)
Table 05: Spending Per Traveler (US$ Million) and Forecast (2018 to 2033)
Figure 01: Total Spending (US$ Million) and Forecast (2023 to 2033)
Figure 02: Total Spending Y-o-Y Growth Projections (2018 to 2033)
Figure 03: Number of Tourists (Million) and Forecast (2023 to 2033)
Figure 04: Number of Tourists Y-o-Y Growth Projections (2018 to 2033)
Figure 05: Spending per Traveler (US$ Million) and Forecast (2023 to 2033)
Figure 06: Spending per Traveler Y-o-Y Growth Projections (2018 to 2033)
Figure 07: Current Market Analysis (% of demand), By Age, 2022
Figure 08: Current Market Analysis (% of demand), By Demographic, 2022
Figure 09: Current Market Analysis (% of demand), By Nationality, 2022
Figure 10: Current Market Analysis (% of demand), By Tour Type, 2022






Full Research Suite comprises of:
Market outlook & trends analysis
Interviews & case studies
Strategic recommendations
Vendor profiles & capabilities analysis
5-year forecasts
8 regions and 60+ country-level data splits
Market segment data splits
12 months of continuous data updates
DELIVERED AS:
PDF EXCEL ONLINE
Market Share Breakdown of Ethno & Community-Based Eco Tourism
Tourism Independent Contractor Model Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Tourism Industry Analysis in Japan - Size, Share, & Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Tourism Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Tourism Industry Big Data Analytics Market Analysis by Application, by End, by Region – Forecast for 2025 to 2035
Assessing Tourism Industry Loyalty Program Market Share & Industry Trends
Tourism Industry Loyalty Programs Sector Analysis by Program Type by Traveler Profile by Region - Forecast for 2025 to 2035
Market Share Insights of Tourism Security Service Providers
Tourism Security Market Analysis by Service Type, by End User, and by Region – Forecast for 2025 to 2035
Competitive Overview of Geotourism Market Share
Geotourism Market Insights - Growth & Trends 2025 to 2035
Global Ecotourism Market Insights – Growth & Demand 2025–2035
Agritourism Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Art Tourism Market Analysis by, by Service Category, by End, by Booking Channel by Region Forecast: 2025 to 2035
Analyzing War Tourism Market Share & Industry Leaders
War Tourism Market Insights - Size, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Dark Tourism Market Forecast and Outlook 2025 to 2035
Food Tourism Sector Market Size and Share Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Wine Tourism Market Analysis - Size, Share, and Forecast Outlook 2025 to 2035
Film Tourism Industry Analysis by Type, by End User, by Tourist Type, by Booking Channel, and by Region - Forecast for 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA