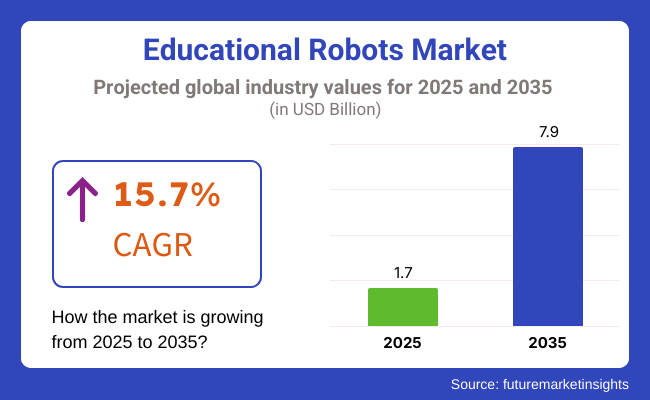
The high growth of the educational robots sector is attributed to the most potential application of artificial intelligence, robotics, and online learning technologies at both the higher and elementary levels of schools. The valuation is projected to be at USD 1.7 billion in 2025 and as high as USD 7.9 billion by 2035, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.7% over the period of time.
The educational robotics sector is on a steep uptrend, largely led by the soaring adoption of STEM within the curriculum, the growing need for personalized teaching, and government initiatives that promote learning robotics and coding in schools among other factors. These robots have made a significant impact on how students deal with complicated subjects, in this way they develop logical reasoning and problem-solving abilities.
Nevertheless, the huge start-up cost, limited manpower, and the barrier to entry faced by integration into traditional teaching methods can be the major hitches for many schools to incorporate them successfully. Regardless of these hurdles, the innovations in humanoid robots, strategic partnerships, and play-based learning are anticipated to lay down the groundwork for a considerable shift in the development of the market.
Furthermore, the implementation of hybrid models and the greater focus on remote schooling has allowed the use of robots for interactive and experiential learning to foster, and in this way, maintain the market stability. Adaptive learning which works on the principle of AI is one of the prominent trends indicating that these robots can employ artificial intelligence to set the lessons according to the individual tempo and patterns of learning of the students.
Machine learning algorithms are utilized that analyze the performance of students to give direct feedback and to work on personalized practices so as to augment the engagement as well as retention of the participants. Robotics specifically for AI education are also utilized in special education providing customized setups that increase the accessibility of the lessons. Such businesses as those that are into AI-powered robots development will secure a market niche in the future of this rapidly changing EdTech sector.
A newer trend observed in the market is the ever-increasing demand for STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) robotics sets, which augment project-based learning. Training centers and schools are being witnessed in the journey of increasing hybrid wall assemblies in teaching coding, mechanics and engineering through brainstorming.
The kits impart both technical knowledge and personality skills such as creativity and problem-solving which are required for jobs in the automation sector. On the other hand, incorporating STEAM robotics in corporate training programs is one of the many ways businesses train their employees in technical fields thus expanding the market's outreach.
The entry of these robots into the classrooms as well as the training programs is changing the conventional learning pattern. These robots by making the teaching more interactive and enjoyable are helping to create a balance between the theoretical knowledge and practical application. The focus on cross-curricular applications and modularity in robotics teaching has gained considerable interest from educational and corporate sectors alike.
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
Between 2020 and 2024, the market for education robots grew quickly as the uptake of STEM-focused learning and AI-enabled interactive teaching tools increased. Robotics was adopted by schools and universities to support problem-solving and coding skills. The growth in online and blended learning also created demand for tutoring robots powered by AI. These robots became less costly as robotics and 3D printing technologies improved and lowered production costs, making robots more affordable and accessible.
During 2025 to 2035, the market will evolve with greater emphasis on individualized education, AI-driven responsiveness, and greater emotional intelligence in robots. Augmented reality and virtual reality will facilitate immersive education. Growth in emerging economies will be driven by broad-based adoption, spearheaded by government programs promoting digital learning. In addition, sustainability will be the main feature leading to the design of eco-friendly robotic materials and power-saving mechanisms for long-lasting sustainability and least environmental impact.
Trend Analysis 2020 to 2024 VS 2025 to 2035
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| The industry experienced consistent growth as educational institutions and schools implemented robotic solutions for STEM learning. Early adopters were developed economies that made investments in experiential learning. | Growth will pick up pace as robots go mainstream across developing countries. Schools and industries will partner to create a workforce that is robotics and automation literate. |
| Robotics education was mostly centered on easy-to-code kits, mechanical construction, and low interactivity. Pre-programmed feedback with low adaptability dominated most systems. | Robots in the future will be smarter, using better Automotive SoC designs to deal with real-time information. The systems will provide an adaptive learning experience with customized feedback. |
| AI-driven teaching robots were in a nascent state, having basic cognitive capacity. They taught rigid lessons without adaptability according to varying learning rates. | In 2035, AI-driven educational robots will feature Automotive SoC components and offer seamless automation. They will customize curricula, provide vocational training, and fill education-to-industry gaps. |
| There were a handful of major robotics manufacturers dominating the industry, and usage was limited to K-12 and coding boot camps. | A larger ecosystem will form, with automotive and industrial companies investing in robotic education. Open-source platforms will open the way for new players to enter. |
| North America, Europe, and certain regions of Asia were the first to adopt, followed by developing nations because of infrastructure and cost issues. | Government policies and affordability will fuel growth into Latin America, Southeast Asia, and Africa, bringing robotic education within reach. |
| Exorbitant prices, shortage of technical expertise, and resistance from conventional instructors hindered uptake. Institutions experienced challenges with roll-out. | Attention will shift to cost-effectiveness, large-scale deployment, and effective industry-academia collaborations. Enterprises will invest in staff training through robotic learning. |
Adoption Gaps and White Space Opportunities for Educational Robot Developers
There are multiple competitive gaps and white space opportunities in the educational robotics market that companies can capitalise on to grow. A key gap here is regionalized robots that meet curriculum standards based on country or region. STEM education-related tools is limited in adoption in public schools in many countries because of the lack of curriculum to meet specific national education guidelines, for example the widely using Makeblock’s mBot. Localized content and understanding of different languages in specific regions will help not only develop engaging robots but also integrate these robots into formal education.
AI-driven personalized learning is another great opportunity. Although some robots provide a good level of student interactivity, few have adaptive learning models or real-time feedback for students. The talkative and learning robot known as Miko 3 utilizes AI and can talk to users and personalize learning experiences by recognizing when kids could benefit from different delivery methods or types of content, while many competing products are simply glorified toys with language, reading or math-learning preprogramming. Improving AI functionality for immediate evaluation and interaction monitoring could drastically enhance educational effectiveness.
This is particularly true in developing industries where affordability remains a deterrent. And if, like LEGO Mindstorms ($300+) all the good educational robots are priced out of the reach of most schools. Companies, such as Robotis Play, have provided low-cost alternatives, but high-quality, low-cost options aimed at budget-constrained schools are still wanted. Mid-and long-term commercialization efforts should consider expanding subscription-based pricing or government-funded partnerships to increase accessibility and contribute to higher adoption rates.
Supply Chain Analysis and Component Sourcing for Education Robot Manufacturing
Educational robots require advanced components to work such as AI chipsets, sensors (cameras, lidars, force sensors), and precision actuators that all have a huge impact on scalability and cost. Recent global chip shortages have highlighted the industry’s heavy dependence on a handful of top suppliers, lengthening lead times and jacking up costs for microcontrollers and AI processors. Top-tier materials do not come cheap, with multi-axis force sensors representing up to 15% of a humanoid robot’s total component cost.
However, as production ramps up and technology matures, many component prices are falling. The median prices of robotic arms, which correlate with actuator prices, fell by almost 46% during the five-year study period. In fact, one of the top manufacturers of LiDAR in China has announced a new model at half the cost of its previous offering, indicating rapid cost declines in sensing technology that can play a great role in educational robot designs.
Suppliers must employ diverse sourcing strategies to mitigate costs and supply risk. To avoid dependence on single suppliers, you can build relationships with various vendors from different regions to maintain stability at competitive costs. New players in emerging industries are interrupting legacy suppliers (like sharp Chinese companies that account for over half of the country’s precision gearbox market). Using open-source or off-the-shelf hardware rather than proprietary systems is another cost-saving strategy.
Built with a Raspberry Pi Zero and off-the-shelf sensors, the “WitBot” educational robot led to the realisation that inexpensive mass-market components could be used to achieve even the same functionalities as existing devices at a fraction of the price. When bought in bulk, these components substantially reduce costs, lowering the per-unit price and making robots more accessible. All these factors lead us to stable production, affordable pricing, and sustainable competition supported by strategic sourcing, diversified suppliers and lower technology costs.
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| AI Chip Supply Constraints | Large robotics companies are looking at developing their own AI chips in-house to be less reliant on Nvidia, Qualcomm, and TSMC |
| Battery Innovation & Second-Life Applications | Second life for EV batteries retrofitted for use in robotics to hit the price point and increase battery supply amid Lithium shortages. |
| Geopolitical Risks in Semiconductor Supply | Tensions between Taiwan and China are affecting semiconductor supply; robotics manufacturers are stockpiling essential components. |
| Rise of Non-Traditional Robotics Component Suppliers | Automotive and aerospace suppliers entering the robotics market, providing more robust supply chain alternatives. |
| Localized Manufacturing with Automation | Automation factories leveraging AI-driven automation will manufacture robotics in local regions, rather than reliance on low-cost regions. |
| Biodegradable & Sustainable Robotics Materials | Recent advancements in biodegradable polymers and recyclable electronics for sustainable robotics manufacturing |
| Cross-Industry Component Sourcing Strategies | Robotics companies tapping into supply chains of medical devices, industrial automation and consumer electronics for sourcing diversification |
Non-Humanoid academic bots such as coding kits, robotic arms are expected to enjoy stable growth. They are getting adopted more in School, Colleges, and corporate training environments into STEM education initiatives. One of the main benefits of these robots is to assist logical reasoning, building problem-solving skills via real-world simulations, putting an edge on learning.
The rise of non-humanoid robots marks a new era in the edtech industry as learning is gradually taking a turn towards engagement models, making it a lucrative venture for entrepreneurs and innovators in education technology.
Humanoid robots that imitate human appearance and behavior, which is expected to see dramatic growth due to demand for interactive and social smart teaching helps that can communicate with students in a natural manner, and offer personalized educational experiences. The main advantages of the humanoid robots are the extent of empathy, cooperation, and interaction with human-like interaction, which is a primary benefit for the younger students and special needs students.
With educational institutions and edtech companies focusing more on interactive and personalized learning, the demand for humanoid robots is expected to skyrocket. This will create profitable prospects for investors, robotics manufacturers, and AI developers working in the education sector.
The higher education segment is projected to lead the educational robots market during 2025 to 2035 driven by its growing adoption for research purposes, integration of artificial intelligence technology and hands-on learning approach.
The universities are using the programmable robots to run cutting-edge studies ranging from artificial intelligence to social sciences to environmental research. Other examples of these types of robots are Furhat, which has the ability to feel emotions and can talk to students, and Blueye X3, designed especially for deep-sea adventures.
As institutions emphasize more on the experiential and community of innovation learning, there will be a high demand for application-centric, AI-enabled robots. With this trend comes opportunities for robotics companies, technology developers, and investors to be involved in the growing demand for robots specialized for higher education and applications.
By 2025 to 2035, the primary education sector is anticipated to lead the educational robotics market due to the increasing use of robots for interactive and foundational learning in early school settings.
Robots are being utilized in elementary classrooms to teach basic skills like reading, math, and coding as well as to encourage creativity and critical thinking. Primary education is the area where the potential advantages of robots lie. Robots are also highly effective at teaching social and emotional skills, especially for children with special needs, by providing repetitive, predictable, and patient interaction.
With primary schools around the world incorporating technology in classrooms, there is expected to be continuing demand for these robots in the sector, and as such, great opportunities exist for edtech firms, robotics manufacturers, and investors.
The USA educational robots market is poised for dynamic expansion, projected to register a robust 14% CAGR growth from 2025 to 2035. This sustained momentum underscores rising investments in AI-driven learning tools, STEM-focused curricula as well as automation in education. Schools and enterprises are expected to increase investments in automation and will soon be prioritizing interactive, hands-on learning.
Smart robotics will witness inflating demand. Adoption will also be moved forward by government funding, technological innovation, and industry partnerships. Such businesses would empower themselves with immeasurable competitive advantages in that evolving, tech-centric education landscape. It is time to seize the transformative industry opportunity. FMI is of the opinion that the USA educational robots market is slated to grow at 14% CAGR during the study period.
Growth Factors in USA
| Key Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Strong STEM Education Initiatives | Government and private sector investments in STEM programs. |
| High R&D Investments | Major tech companies innovating in AI and robotics. |
| Integration in Schools & Universities | Increased adoption of robots in classrooms for hands-on learning. |
| Growing EdTech Industry | Expansion of digital learning tools, including robotics. |
The upsurge of China's educational robots market is a revolutionary growth, due in large part to government investments to infuse modern technology into the education system. Initiatives like the National Educational Policy emphasize the inclusion of robotics and AI in the school's curriculum in order to achieve quality learning outcomes.
Industries, such as Makeblock, are key players in developing educational robotics kits in sync with the educational policies of the country. More emphasis is laid on hands-on learning and problem-solving skill development among students, thus placing China ahead of the pack in the application of robotics.
Growth Factors in China
| Key Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Government Policies | Strong support for AI and robotics in education under "Made in China 2025." |
| High Demand for AI Learning | Emphasis on coding and AI education from early schooling. |
| Rising Disposable Income | Parents investing more in high-tech educational tools. |
| Large Manufacturing Base | Cost-effective production of robots. |
The integration of robotics into Japan's education system being continued means that the society in general has embraced these technologies. Humanoid robots are increasingly being employed by educational institutions to support interactive-learning activities for programming and engineering content.
Government supports now foster technological innovation within education while collaboration runs between schools and manufacturers of robotics, growing some fertility for the area. This collaboration aims to furnish students with the skills to adapt and flourish in a technology-imbued society.
Growth Factors in Japan
| Key Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Advanced Robotics Ecosystem | Leading country in humanoid and AI-powered robots. |
| Aging Population | Robotics used in lifelong learning and elderly education. |
| Government Support | Grants and policies encouraging robotics in education. |
| High-Tech Schooling | Robotics deeply integrated into school curriculums. |
South Korea highlights its commitment to enhancing STEM education through proactive actions in promoting educational robots. The government teaches policies supporting the pedagogy of creativity and technical capability through robotics.
These robots are being used from primary to higher learning institutions to enhance students' hands-on experience with some theoretical aspects of their knowledge. This has in one way or another strengthened South Korea's footprint in educational robotics by cooperating with educational institutions from the onset and through mutual input in defining the curriculum for robotic solutions.
Growth Factors in South Korea
| Key Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| AI & Robotics Leadership | South Korea is a global hub for robotics innovation. |
| Smart Education Policies | Government promotes coding and robotics in K-12 education. |
| Strong Tech Industry | Companies like LG & Samsung investing in educational robots. |
| High Digital Adoption | Students and educators comfortable with advanced tech. |
The UK sees its industry gain momentum as schools acknowledge that new forms for interactive learning tools are important in modern education. The supporting initiatives, which integrate robotics into the curriculum, promote digital literacy and prepare students for future technologies. In addition to coding, teaching with robots encompasses mathematics and science while engaging students in their own learning process.
Collaborations between educational entities and technologists are of prime importance in developing resources and training programs that would facilitate the use of robotics in the classrooms and enhance the educational experience altogether.
Growth Factors in UK
| Key Factors | Details |
|---|---|
| Coding & AI in Schools | UK curriculum emphasizes coding and AI education. |
| Government Grants | Funding available for EdTech startups and robotics programs. |
| EdTech Boom | Strong demand for interactive learning tools post-pandemic. |
| University Research | Leading universities developing AI-driven educational robots. |
The industry is becoming steadily concentrated, with only a handful of large companies shaping trends in the industry. Established tech corporations and specialized robotics companies acquire startups and add on them all their portfolio. Consolidation fortifies their positions in the industryso that they can provide solutions of commercial intelligence integrated with gamification and adaptive learning.
The competition gets heightened when the giants obtain huge institutional contracts with schools, universities, and edtech companies. Their wide distribution networks and research facilities enable them to set up the industry standards. It becomes very hard for the smaller companies to compete with the giants, which often focus on niche applications or regional industries.
Strategic partnerships drive the further concentration, with the top robotics companies partnering with educational institutions and software developers. These partnerships help them to refine the curricula, personalize the learning experiences, and secure long-term contracts. The industry now favors those well-funded innovators who can balance affordability, technological sophistication, and scalability.
Advancements in AI and automation, coupled with the growing push towards STEM-based education, are drastically shaping the landscape of the educational robots market. Softbank Robotics, known for its humanoid robots Pepper and NAO, these have been commonly adopted for interactive learning experiences. Makeblock from China presents an affordable option using an mBot for STEM coding and hands-on learning.
RobotLAB is another entity that specializes in distributing robots along with VR tools to institutions in support of robotics-based education. Pitsco Education stretches its development in fostering hands-on robotics and programming skills using TETRIX Robotics Kits. Headquartered in Taiwan, Techman Robot Inc. produces collaborative robots fitted with vision systems for technical education purposes. Danish Universal Robots supplies collaborative robots (cobots) for practical training in automation applications.
To remain competitive, companies are focusing on strategic growth plans. SoftBank Robotics aims to improve humanoid interaction, thereby increasing its appeal to educators. Makeblock emphasizes affordability as well as accessibility. RobotLAB partners with schools to offer programs integrating robotics into curricula.
Pitsco works with LEGO Education toward expanding STEM offerings. Techman Robot enhances AI vision for greater effectiveness in automation training. Universal Robots makes further investments in training platforms partnerships with third parties to form a robust robotics ecosystem. With increasing demand for robotics education, these companies are focused on innovating to preoccupy a share of the industry and design the future of learning.
Covariant
Launch in 2017, led by Pieter Abbeel and his team, Covariant is a venture-funded startup based out of Emeryville, California. The basic idea is to teach robots complicated new skills using artificial intelligence. The strategy of Covariant is to make one universal AI, which will allow the robots to see, reason, and act in their environment.
Covariant's foundation of combining deep imitation learning with deep reinforcement learning will work to create a robot that can do most of the activities across multiple sectors, thereby, increasing automation and operational efficiency in the respective fields.
Dobot
Dobot was set up in 2015. It primarily manufactures low-priced but high-precision robotic arms, mainly intended for educational purposes. The growth strategy of the organization consists of innovative versatile product development targeting education and industries. The acquisition of funds through successful crowdfunding campaigns has greatly helped Dobot not only diversify its product range but also reach out into markets emphasizing the practical applications of robotics in a learning environment.
The market is expected to reach USD 1.7 billion in 2025.
The educational robots market is expected to garner revenue of USD 7.9 billion by 2035.
The market growth is driven by the increasing adoption of AI-driven learning tools, rising demand for interactive and STEM-based education, and advancements in robotics technology.
Key players in the educational robots market include Aisoy Robotics, Hanson Robotics Limited, Modular Robotics, PAL Robotics, and Probotics America.
Humanoid and AI-powered educational robots are expected to command a significant share over the assessment period.
The industry is segmented based on type into humanoid and non-humanoid educational robots.
The application segmentation includes primary education, secondary education, higher education, and others.
Geographically, the industry is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
Remote Construction Market Analysis by Component, Application, End-use Industry and Region Through 2035
Security Inspection Market Insights – Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Procurement as a Service Market Trends – Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Massive Open Online Course Market Analysis – Growth, Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Tactical Radios Market Analysis by Type, Application, and Region Through 2025 to 2035
Healthcare Virtual Assistants Market Analysis by Product, End User and Region Through 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.