The Crohn’s disease treatment market is valued at USD 12.67 billion in 2025. According to FMI's analysis, the industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.3%, reaching USD 19.30 billion by 2035.
Pipeline progress, increasing adoption of biologics, and regulatory approvals drove changes in the Crohn’s disease or Crohn syndrome treatment industry in 2024. A study released by the FMI found that regulatory feedback was given to several late-stage studies for JAK inhibitors and anti-integrins. This gave people hope for new therapies.
FMI anticipates the use of biosimilars and price dynamics further evolving, resulting in increased access in North America and Europe. Meanwhile, regional healthcare policies in emerging industries increasingly promoted cost-effective biosimilar drugs, allowing improved access for patients.
According to FMI research, investments in personalized medicine and microbiome therapeutics surged in the beginning of 2025. Big pharma companies stepped up R&D on small-molecule drugs to fill holes in treatments.
According to FMI, industry growth will be driven by continuous advancements in advanced therapies, increased awareness, and strategic alliances to diversify treatment pipelines. In the next decade, the industry will advance, with AI-powered drug discovery unlocking efficiencies in clinical trials and the easing of regulatory strategies for the next-generation therapeutics.
Industry Forecast Table
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 12.67 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 19.30 billion |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 4.3% |
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
The industry for healthcare sector in crohn syndrome treatment is expected to show a steady growth, fueled by the widening use of biologics, biosimilars, and personalised therapies. According to research by FMI, established drug companies that rely on traditional treatments are likely to see their profits go down, while new drug companies that invest in new therapies and AI-based drug development will do well.
FMI believes that with speedier regulatory approvals and ease of access to treatment, both healthcare professionals and patients alike will gain from a larger pool of impactful therapies.
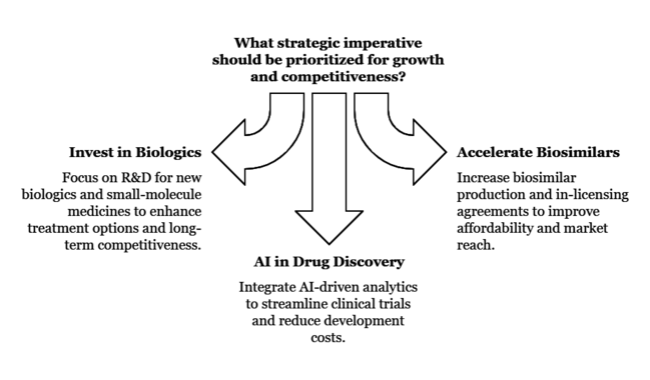
Invest in Next-Generation Biologics
Biopharma players should focus more on R&D for new biologics and small-molecule medicines to complement the shortcomings in available treatments and create long-term competitiveness.
Biosimilar Adoption and Industry Expansion
In response to healthcare policies favoring cost containment, companies must accelerate biosimilar production and establish in-licensing agreements to enhance affordability and industry reach.
Drive AI-powered drug discovery and clinical trials.
To optimize R&D pipelines and improve regulatory approval rates, firms should integrate AI-driven analytics into clinical trials to streamline drug development timelines and reduce costs.
| Risk | Probability & Impact |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Hurdles for Novel Therapies | High Probability - High Impact |
| Pricing Pressures from Biosimilars | Medium Probability - High Impact |
| Supply Chain Disruptions in Biologic Manufacturing | Medium Probability - Medium Impact |
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Accelerate Late-Stage Drug Approvals | Expedite regulatory submissions for novel therapies |
| Strengthen Biosimilar Industry Position | Expand partnerships with healthcare providers and insurers |
| Enhance AI Integration in R&D | Invest in AI-driven clinical trial optimization tools |
To stay ahead, companies must prioritise expedited drug approvals, biosimilar industry growth, and AI-based R&D efficacy in the evolving treatment landscape of this disease. An FMI analysis projects that organisations deploying AI in their clinical trials can develop cost-effective solutions and improve success rates, whereas selective biosimilar partnerships ensure cost-effectiveness and industry share.
FMI asserts that the leaders planning investment strategies must closely monitor regulatory changes and patient demand for targeted treatments to sustain growth and maintain a competitive edge.
According to FMI’s survey, key priorities for stakeholders in the industry include treatment efficacy, regulatory compliance, and access to new therapies.
Regional Variance:
According to FMI research, these therapeutic modalities are relatively new to the industry, with adoption rates varying among participants.
Price remains a significant factor affecting treatment access, FMI states, which has implications for investment and industry penetration.
In their research, FMI discovered that the industry was also investing in efficiency and innovation.
According to FMI, regulatory complexity would continue to be the top industry-secret concern in investment and entry strategies.
Key learnings: Divergence & Convergence
Consensus: Global challenges include rising treatment costs for patients, greater regulation, and a requirement to be creative with the drugs.
Key Regional Differences:
In North America, affordability and healthcare access are largely dictated by insurance coverage, while in Europe, government regulations drive cost control measures.
Strategic Outlook:
FMI anticipate that the era of uniform biologics is over, with USA innovation, European biosimilar expansion, and Asia-Pacific growth in low-cost oral therapies shaping the future industry.
| Country | Regulatory Impact & Mandatory Certifications |
|---|---|
| United States | The FDA oversees Crohn's disease therapies through the Biologics License Application (BLA) for biologics and New Drug Application (NDA) for small molecules. Accelerated approval pathways, like Breakthrough Therapy Designation, facilitate faster approaches to novel treatments. Pricing continues to be under debate, with state reform efforts demanding biosimilar price decreases. |
| United Kingdom | The Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) regulates post-Brexit approvals, following the guidelines of EMA but with the allowance for standalone biosimilar evaluations. NHS reimbursement policy supports biosimilars, inhibiting biologic pricing discretion. |
| France | The French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety (ANSM) requires rigorous pharmacovigilance for biologics. The government encourages biosimilar uptake through compulsory substitution policies to ensure cost containment. |
| Germany | The Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) regulates pricing and reimbursement with strict cost-benefit evaluations. Physicians are rewarded for prescribing biosimilars, speeding up their adoption. |
| Italy | The Italian Medicines Agency (AIFA) imposes regional price negotiations, frequently resulting in differences in biologic availability. AIFA promotes biosimilar substitution, but it's not mandatory. |
| South Korea | Due to government-backed healthcare cost reductions, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) regulates this area, focusing specifically on biosimilars. Firms are required to pass Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to enter the local industry. |
| Japan | The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has rigorous timelines for approval for biologics, which can delay industry entrance. Japan's National Health Insurance (NHI) system presses prices downward and restricts revenues for expensive drugs. |
| China | The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) is fast-tracking approvals under the Priority Review pathway. Yet, centralised volume-based procurement programs drive price reductions for biologics and biosimilars. |
| Australia-NZ | Approvals are overseen by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) and Medsafe, with Australia strongly supporting biosimilars through automatic substitution policies. Government subsidy under the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) places greater value on cost-effectiveness. |
| India | The Central Drug Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) controls biosimilars under the Biologics Guidelines, emphasizing affordability. Government healthcare programs ensure industry access, but quality issues continue due to differing manufacturing standards. |
Antibiotics occupy a secondary role in the management of Crohn's disease and are used mainly for the treatment of infections, such as in abscesses and fistulas. The immunomodulators segment by drug type is anticipated to occupy a significant share of 53% globally. While metronidazole and ciprofloxacin are standard prescriptions, their demand is plateauing as biologics and immunomodulators grow in popularity, according to FMI analysis.
Aminosalicylic acids, such as mesalamine, are still useful in mild cases, especially in Europe and Asia, as they are cheaper. But their importance is waning as biologics assume command of the serious cases.
Corticosteroids like prednisone and budesonide are still required for acute flare-ups, but long-term adverse effects hinder long-term use, dampening their growth. In the absence of biologics, immunomodulators such as azathioprine and methotrexate offer an inexpensive alternative and should lead to steady demand.
JAK inhibitors and microbiome therapy, belonging to the "Others" category, are the fastest-growing segments. New oral treatment products, according to FMI research, are changing how treatment solutions are given and will likely lead to more regulatory approvals, which will help the industry grow in the future. FMI expects new treatment options to play a significant role in the therapy landscape in the forecast period.
Hospital pharmacies prescribe the vast majority of all treatments, including biologics and corticosteroids, on physician-controlled pathways. According to FMI analysis, this segment will continue to expand significantly, driven by increased availability of infusion-based treatments. It is projected to hold a 27.3% share of the global industry from 2025 to 2035.
Retail pharmacies have a major share, providing oral medicines like aminosalicylates, immunomodulators, and corticosteroids. Yet while convenience and accessibility drive sales, pricing pressures and insurers preference for specialty networks could constrain long-term growth, an FMI analysis found. The fastest-growing segment is online pharmacies, driven by a greater uptake of digital health and desire for home delivery of maintenance therapies.
While access to biologics from online industries remains limited due to regulatory and storage-related issues, FMI analysis indicates that the segment is growing rapidly, particularly in industries with strong e-commerce infrastructure. According to FMI, the development of digital health will position online drugstores as key distributors of oral and biosimilar drugs.
FMI believes that the industry for treating Crohn's disease in the United States will expand at close to 4.6% CAGR from 2025 to 2035. The United States is still the leading within the industry, driven by robust healthcare infrastructure and quick uptake of biologics. FMI estimates that biosimilars are increasingly gaining popularity, with payers encouraging their adoption to reduce costs.
The FDA's expedited approval processes for new therapies drive industry expansion. However, the high cost of treatment is an issue, with inconsistency in insurance coverage affecting patient access.
Precision medicine and AI-driven drug discovery are revolutionising the industry, with digital health solutions playing a larger role in remote disease management. The USA will lead in clinical trials and new therapy approvals.
FMI estimates that the industry for treating Crohn's disease in the United Kingdom will grow at a near 3.8% CAGR during 2025 to 2035. NHS-led biosimilar uptake and cost-containment measures drive the industry in the UK. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) prefers cost-effective therapies and restricts premium pricing practices, according to FMI analysis.
Digital health products, especially remote monitoring solutions, are receiving increased NHS support. The post-Brexit regulatory environment streamlines approvals for clinical trials, positioning the UK as a favourable R&D destination.
However, economic factors constrain access to advanced biologics. Greater emphasis on microbiome treatments and personalised medicine will chart the future course of the industry, with UK biotech companies leading the charge in gut flora modulation innovations.
France The Crohn's disease treatment industry benefits from universal healthcare coverage, which ensures extensive availability of biosimilars and biologics and is likely to increase steadily with a 3.9% CAGR during the forecast period. FMI found that rigid price control regulations imposed by the French National Authority for Health (HAS) slow down the launch of new treatments.
Hospital-administered biologics are common in treatment paradigms, but subcutaneous versions are gaining momentum due to patient convenience. Spending on microbiome therapy is on the rise, with French biotech leaders in research. FMI thinks biosimilar adoption will increase further, as AI-based diagnosis and digital health technology enhance disease management.
FMI believes that Germany's Crohn's disease treatment industry will advance at nearly 4.1% CAGR from 2025 to 2035. It is defined by high biosimilar penetration and structured reimbursement. FMI analysis opines that 81% of physicians prefer biosimilars due to their cost-effectiveness. The Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) applies strict cost-effectiveness assessments, limiting access to expensive biologics.
Germany is the leader in AI-driven pharmaceutical development and microbiome testing, with biotechnology firms actively designing gut flora-modulating medicines.
Regional insurance variations affect treatment access. Government actions promoting digital health measures, like AI-supported patient monitoring, will drive industry growth. Germany remains the forerunner in new treatments but is fighting back with cost-containment measures.
Italy's Crohn's disease industry for treatment is expanding steadily at a CAGR of 3.6% during 2025 to 2035, with biosimilars gaining momentum in cost-aware public healthcare. Regional variations in healthcare spending had an effect on access to new treatments, FMI analysis revealed.
The Italian Medicines Agency (AIFA) tightly controls prices, with reimbursement approvals for new biologics delayed. Private healthcare centres, however, are increasingly offering specialized therapies for this disease.
Investment in microbiome-based therapies is on the rise, with government-funded research initiatives supporting alternative therapeutic pathways. Uptake of digital health is also on the rise, enhancing patient monitoring and adherence. Industry growth in Italy is driven by cost-containment measures and emerging biotech advances.
FMI opines that South Korea's Crohn's disease treatment industry will grow at a robust rate of 4.2% CAGR between 2025 and 2035. The industry is growing because of government investments in biosimilars and biologics. FMI research revealed that cost-saving biosimilars are preferred under reimbursement policies, with local pharmaceutical companies expanding capacity.
Precision medicine and AI-based diagnostics are picking up pace, with South Korean hospitals adopting predictive analytics for the management of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
However, price pressures constrain high-cost new biologics. The robust biotech ecosystem in the country is driving innovation, especially in microbiome-based therapy and regenerative medicine. FMI believes that South Korea's focus on digital health and personalised medicine will drive industry growth in the coming decade.
FMI believes that Japan's Crohn's disease treatment industry will expand at almost 3.7% CAGR during 2025 to 2035. Cost-conscious healthcare policies and sluggish biosimilar uptake hampered the industry. FMI estimates that patient preference for originator biologics is hindering the adoption of generics and biosimilars, despite government support.
R&D spending on gut microbiome therapy and regenerative medicine is shaping the industry, with Japan leading the way for alternative treatments. However, FMI feels that regulatory restrictions and price caps limit the size of the industry for costly therapies. Japan's increasing disease incidence and ageing population will drive steady demand as personalised medicine and AI-based diagnostics gain wider acceptance in clinical settings.
The treatment of Crohn's disease in China is growing at a rapid pace with a 5.1% CAGR over the forecast period, driven by government incentives for biologics production and rising disease incidence. FMI analysis identified that local pharmaceutical companies are ramping up biosimilar production to cut reliance on imports. The government's policy reforms, such as the National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL) updates, make treatment more accessible.
However, FMI attributes regional differences in healthcare infrastructure as a cause for inconsistency in the accessibility of novel treatments to patients. Expenditure in AI-driven diagnostics and microbiome therapeutics is increasing, with Chinese biopharmaceutical firms diversifying into emerging modes of therapy. Government campaigns and rising healthcare expenditures will drive the industry.
Universal healthcare and high biologic penetration rates support Australia's and New Zealand's Crohn's disease treatment industry. FMI believes that the industry will grow at nearly 3.9% CAGR during 2025 to 2035.
It also estimates that biosimilar adoption is picking up pace on the back of cost-containment strategies driven by governments. New treatments, however, remain out of reach due to high reimbursement scrutiny from the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS).
Digital healthcare products are growing in importance, with AI-based diagnostic capabilities improving the early detection of diseases and the management of ailments. Investment is increasing in microbiome treatments, particularly in the research institutions across Australia. Biosimilar adoption, innovative R&D, and increasing telemedicine solutions will ease growth in the regions, according to FMI.
The sales in India are witnessing robust growth at 5.4% CAGR during the forecast period due to rising awareness of the disease and improving healthcare penetration. The FMI study found that local pharma companies are leading the production of biosimilars, lowering the cost of treatment. Government initiatives, including enhanced insurance coverage under the Ayushman Bharat program, improve patient access to biologics.
However, FMI is of the opinion that inequality in healthcare infrastructure limits the accessibility of treatment in rural areas. Investment in microbiome therapy and AI-based diagnostics are increasing, with Indian biotech firms developing low-cost solutions. The industry will continue to grow based on increasing healthcare spending, increasing biologic penetration, and pharma innovation from within the country.
Industry leaders, including AbbVie, Johnson & Johnson, and Takeda, highlight their efforts to grow their biologic portfolios, particularly in terms of biosimilars, to maintain their industry-wide dominance in the future. As per FMI research, key growth drivers include mergers and acquisitions and licensing deals, with firms investing in new mechanisms, notably JAK inhibitors and microbiome therapies.
A priority has been to geographically expand into emerging industries, where alliances help facilitate regulatory clearance and distribution. FMI expects increased pricing competition over the coming years, as cost pressures and payer preference for biosimilars will create pressure to price aggressively.
AbbVie Inc.
Industry Share: ~35-40%
AbbVie ranks first, thanks to its extremely high revenue-generating Humira (adalimumab), despite the entry of competing biosimilars. To maintain its leadership position, AbbVie is focusing on newer biologics, Skyrizi (risankizumab) and Rinvoq (upadacitinib).
Johnson & Johnson (Janssen Pharmaceuticals)
Industry Share: ~20-25%
Janssen is well-positioned with Stelara (ustekinumab), which continues to generate strong sales and maintain industry dominance. To bolster its portfolio in Crohn's syndromee, the company is making investments in next-gen therapies that previous platforms couldn't offer, like Tremfya (guselkumab).
Takeda Pharmaceutical
Industry Share: ~15-20%
Takeda’s Entyvio (vedolizumab) remains a frontrunner because of its gut-selective action. To counter the threat of new entrants, the company is expanding its real-world evidence studies to strengthen the positioning of Entyvio.
Pfizer Inc.
Industry Share: ~10-15%
Pfizer is progressing its pipeline with etrasimod (oral S1P modulator), which achieved positive Phase 3 results in 2024. The firm aims to compete with existing biologics through this innovative oral treatment.
Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS)
Industry Share: ~5-10%
BMS will utilize Zeposia (ozanimod) for Crohn syndrome, following its success in ulcerative colitis. The company is conducting more trials to expand its label.
Amgen Inc.
Industry Share: ~5-10%
Amgen has Amiyvre (AMG 592, an IL-23 blocker) in late-stage development. The company also continues to add biosimilar competition with Abrilada (adalimumab-afzb).
AbbVie Skyrizi Adoption: AbbVie noted Q1 2024's strong adoption of Skyrizi in Crohn's disease following its 2023 FDA approval. AbbVie industries Skyrizi as a Humira replacement, emphasizing superior efficacy results in head-to-head clinical trials.
In 2024, Europe saw the launch of the first biosimilar for Stelara (ustekinumab), known as the Janseen Storm Warning. The company is accelerating lifecycle management initiatives to hold its ground.
Takeda’s Entyvio Subcutaneous - In February 2024, the FDA granted Takeda new approval for Entyvio to manufacture a subcutaneous formulation that is easier for patients to use and will provide more flexibility. This formulation can improve patient compliance and increase revenue.
Pfizer submitted a New Drug Application (NDA) for etrasimod in Crohn's disease in March 2024, following the reporting of positive Phase 3 results. If the drug gets the green light, it would be the first oral S1P modulator indicated for Crohn's.
Amgen's Phase 3 Initiation of AMG 592: Amgen announced a Phase 3 trial of AMG 592 in moderate-to-severe disease in Q1 2024 in competition against IL-23 inhibitors, including Skyrizi and Tremfya.
BMS Clip Label for Zeposia - Bristol Myers Squibb won EU approval for Zeposia in (QD dosing is key) in January 2024 following its success in ulcerative colitis. The firm is ramping up promotional activity.
Merck stopped developing evobrutinib, a BTK inhibitor, in 2024 after it failed Phase 2 trials, demonstrating the difficulty of introducing new treatment mechanisms.
Demand for treatments for Crohn's disease is boosted by improvements in biologics, increasing disease incidence and better diagnostic technologies.
The industry is expected to grow steadily due to the increased application of biosimilars, novel treatment techniques, and surging investments in precision medicine.
The major players in the industry are Abbvie Inc., Celgene Corporation, Genetech, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer Inc., Prometheus Laboratories Inc. (Nestle), Salix Pharmaceuticals Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Ltd, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Biogen, AstraZeneca, Merck & Co., Inc., UCB S.A., Celgene Corporation, Amgen Inc.
Due to their success and their increasing acceptance among patients, the biologics, particularly the anti-TNF agents and JAK inhibitors, will be the ones to watch.
The industry is projected to reach USD 19.30 billion by 2035, driven by steady annual growth.
The industry is segmented into antibiotics, amino salicylates, corticosteroids: Immunomodulators, and others.
It is segmented into hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies and online pharmacies
The industry is studied across North America, Latin America, Europe, South Asia, East Asia, Oceania, and Middle East & Africa.
Specialty Medical Chairs Market Trends - Size, Growth & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Surgical Drapes Market Overview - Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Super Resolution Microscope Market Insights - Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Large Molecule Bioanalytical Testing Services Market - Growth & Demand 2025 to 2035
Remote Healthcare Market – Growth & Innovations 2025 to 2035
Prosthetics and Orthotics Market - Growth & Future Trends 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.