The celiac disease diagnostics market is valued at USD 343.29 million in 2025. As per FMI's analysis, the industry will grow at a CAGR of 8.3% and reach USD 740.65 million by 2035.
In 2024, the industry saw a meaningful increase in diagnostic activity, particularly in developed regions such as North America and Western Europe. Clinical adoption of tissue transglutaminase (tTG-IgA) and endomysial antibody (EMA) testing increased as more primary care providers included celiac screening for patients with persistent gastrointestinal symptoms and related autoimmune conditions.
There was a rise in testing among pediatric populations due to enhanced school-level awareness campaigns. Laboratories also expanded their offerings to include multi-marker panels for more accurate diagnosis.
Meanwhile, digital health platforms began integrating celiac risk assessment tools, making early detection more accessible. Despite these advancements, uptake in low- and middle-income countries remained limited due to lack of infrastructure and awareness, leading to under diagnosis.
In 2025 and beyond, the industry is expected to benefit from ongoing innovation in non-invasive diagnostics and home-based testing kits. Public health efforts aimed at increasing awareness and early diagnosis are likely to expand the tested population. Growth in gluten-free food industries may also contribute indirectly by encouraging more people to seek testing and understand their dietary needs.
Market Share Insights
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 343.29 million |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 740.65 million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 8.3% |
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
The celiac disease diagnostics industry is on a strong growth trajectory, driven by rising awareness, improved screening technologies, and increased diagnosis rates globally. Key drivers include advancements in non-invasive testing and broader physician adoption of routine screening, especially in high-risk populations. Diagnostic companies, digital health platforms, and specialized labs stand to benefit, while regions with limited healthcare access risk being left behind.
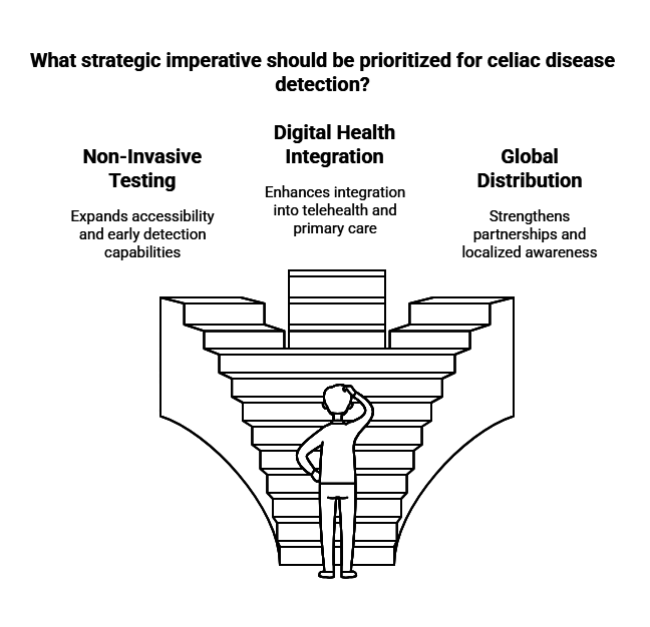
Expand Non-Invasive Testing Capabilities
Invest in the development and commercialization of non-invasive and home-based diagnostic tools to capture the growing demand for accessible and early-stage celiac disease detection.
Align with Digital Health Integration
Collaborate with digital health platforms to integrate celiac screening tools and risk assessment features into routine telehealth and primary care workflows, aligning with evolving patient and provider preferences.
Strengthen Global Distribution and Partnerships
Build strategic partnerships with regional labs, public health agencies, and healthcare providers-especially in underdiagnosed industries to expand reach, enhance distribution, and accelerate adoption through localized awareness campaigns.
| Risk | Probability - Impact |
|---|---|
| Limited diagnostic access in low-income regions | Medium - High |
| Reimbursement challenges and regulatory delays | High - Medium |
| Misdiagnosis due to inconsistent testing protocols | Medium - High |
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Expand Non-Invasive Test Portfolio | Conduct feasibility study on launching saliva- or stool-based test kits |
| Strengthen Provider Engagement | Initiate feedback loop with clinicians on diagnostic accuracy and usability |
| Boost Industry Penetration in Emerging Regions | Launch regional awareness and diagnostic training pilot with local partners |
To stay ahead, companies must prioritize innovation in non-invasive diagnostics and accelerate partnerships with digital health platforms to embed celiac screening into everyday care. This intelligence signals a shift toward earlier, decentralized testing and rising demand in currently underpenetrated industries.
Executives should realign their roadmap to focus on R&D for easy-to-use test kits, expand provider education programs, and pursue targeted geographic expansion through public-private partnerships. Acting now positions the company to lead in an industry that’s rapidly moving toward proactive, accessible celiac disease detection.
(Surveyed Q4 2024, n=500 stakeholder participants evenly distributed across diagnostic manufacturers, gastroenterologists, hospitals, and diagnostic labs across North America, Western Europe, India, and Japan)
| Countries | Policies and Regulations Impacting the Celiac Disease Diagnostics Industry |
|---|---|
| United States | The FDA regulates medical devices, including diagnostic tests for celiac disease, requiring preindustry approval or clearance. Additionally, the FDA defines "gluten-free" labeling standards for food products. |
| United Kingdom | The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) oversees the approval of diagnostic tests. The NHS provides gluten-free food prescriptions to diagnosed patients. |
| France | The French National Authority for Health (HAS) evaluates medical devices, including celiac disease diagnostics, for reimbursement eligibility. |
| Germany | The Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM) regulates diagnostic tests, ensuring compliance with EU directives. |
| Italy | Implemented a national pediatric screening program for type 1 diabetes and celiac disease in 2024, with allocated funding and a monitoring observatory. |
| South Korea | The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) regulates medical devices, including diagnostic tests, requiring approval before industry entry. |
| Japan | The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees the approval process for diagnostic tests, ensuring safety and efficacy. |
| China | The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) requires registration and approval of diagnostic tests, adhering to national standards. |
| Australia & New Zealand | The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) and Medsafe regulate diagnostic tests, ensuring compliance with stringent labeling laws for gluten-free products. |
Genetic rapid testing kits are expected to lead with the highest CAGR of 8.6% from 2025 to 2035. This growth is driven by increasing consumer preference for personalized medicine and the rising awareness of genetic predispositions toward celiac disease. These kits offer fast, accurate, and convenient home-based or clinical testing, which aligns with the growing demand for early diagnostics.
With advancements in genetic screening technology and the falling cost of genome testing, adoption is rising across both developed and emerging industrys. Compared to traditional serological testing, genetic kits provide more conclusive and lifelong diagnostic value, making them a future-proof choice for clinicians and end-users alike.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) holds the highest CAGR within the techniques segment at 8.7% for 2025 to 2035. ELISA continues to dominate due to its superior sensitivity and specificity in detecting celiac-related antibodies, especially transglutaminase and endomysial antibodies. Its application across both clinical laboratories and research settings is widespread, particularly in hospitals and diagnostic labs.
Increasing demand for high-throughput screening methods and the integration of ELISA into automated platforms further enhances its scalability and reliability. While lateral flow methods are popular for point-of-care, ELISA remains the gold standard in confirmatory diagnostics, thereby securing its stronghold in regulated and high-accuracy diagnostic environments.
Among sample types, blood serum is projected to grow at the highest CAGR of 8.4% over the forecast period. This is primarily due to its well-established role in detecting autoimmune responses through various serological markers in celiac disease. Blood serum remains the most preferred sample medium for ELISA-based and rapid serology kits, ensuring accuracy in both initial screening and follow-up tests.
Healthcare professionals trust blood serum analysis for its high reliability and compatibility with a range of testing techniques. As diagnostic infrastructure improves globally and access to laboratory services expands, serum-based testing is likely to continue its dominance in the diagnostic process.
Diagnostic laboratories will emerge as the fastest-growing end user category, with a CAGR of 8.5% from 2025 to 2035. The central role of diagnostic labs in performing confirmatory and high-complexity tests using ELISA or genetic testing methods has significantly increased their relevance. Rising referrals from hospitals and clinics, growing investment in lab infrastructure, and adoption of automation in testing processes are key contributors to this growth.
Additionally, labs offer centralized testing services that support both public and private healthcare institutions. Their ability to deliver accurate results on a large scale positions them as a backbone in the expanding diagnostics ecosystem for celiac disease detection.
Sales in the USA are anticipated to grow at 8.1% CAGR from 2025 to 2035 This increase is propelled by increased awareness of gluten intolerance, enhanced insurance coverage for diagnostics, and robust advocacy from groups like the Celiac Disease Foundation.
Widespread availability of point-of-care testing and growing acceptance of living a gluten-free lifestyle as a preventative measure has helped accelerate early detection rates.
The industry’s growth is further boosted by ongoing technological advancements and R&D investments from the prominent players in molecular diagnostics. However, it is fragmented, with regional disparities in availability of healthcare and differences in reimbursement models. Collaborating with primary care providers can help to increase diagnosis rates in resource-poor areas.
Sales in UK is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 8.7% during this time period. The NHS remains pivotal in early screening and diagnosing particularly in at-risks. The new Gluten Sensitivity recommendations, coupled with a burgeoning gluten-free product industry, offer policy-level support for eliminating diagnostic delays and increased awareness within the population.
Local biotech companies and diagnostic labs are working together on low-cost blood-based tests that can be turned around faster. In addition to this work, using AI in primary care to flag for symptoms is gaining significant traction. The UK is also a prominent place for clinical research into autoimmune conditions, offering further justification for diagnostic innovation in this area.
Sales in Germany is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 8.4% from 2025 to 2035. Germany benefits from a strong healthcare infrastructure and a highly aware consumer base. The German Celiac Society and other advocacy groups have intensified education and awareness campaigns targeting both consumers and healthcare providers.
In parallel, diagnostic labs are expanding their gluten sensitivity panels to detect both classical and non-classical presentations. German diagnostics firms are investing in multiplex immunoassays to capture a wider spectrum of autoimmune markers. Additionally, Germany’s emphasis on evidence-based medicine is pushing for standardization in diagnostic protocols, enhancing reliability and scalability.
France Sales in France is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% during the assessment period. The industry is driven by increasing awareness of gastrointestinal health and improved diagnostic coverage through public insurance.
Celiac disease remains underdiagnosed, but national screening recommendations for first-degree relatives are slowly changing this. Local labs are adopting ELISA and molecular technologies, while public health agencies run awareness campaigns targeting school-age children.
The rise of gluten-free diets, often driven by lifestyle choices, is prompting individuals to seek formal diagnosis. France’s integration of dietary and clinical management under a unified system ensures better patient retention and follow-up.
Sales in Italy are anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 8.8% during the forecast term. This aligns with Italy's status as one of the most advanced countries in terms of public policy and public health regarding celiac disease. The government reimburses individual celiac patients for specialized gluten-free foods, and most of the population has access to essential diagnostic testing.
Celicia Disease is a reportable condition for that early and accurate diagnosis. Rapid tests for use in primary care and pharmacies are seeing innovations in Italian diagnostics companies. In addition, increasing awareness of the resource, even among young patients, propelled by efforts to promote early diagnosis in schools, has led to an increase in pediatric screenings.
Sales in Japan are anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 7.0% from 2025 to 2035. While awareness of celiac disease remains relatively low compared to Western industrys, diagnostic interest is picking up in urban centers. Japan’s diet traditionally contains less gluten, which has historically masked prevalence.
However, Westernization of diets and increasing gastrointestinal complaints are pushing healthcare providers to consider celiac diagnostics. Industry entry for global diagnostics players is growing, though localization of tests and education campaigns are still needed.
Japan’s technological prowess offers room for innovation in minimally invasive diagnostics, but industry penetration will require long-term engagement and public health education.
Sales in China are anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 9.8% from 2025 to 2035. This represents one of the highest growth rates globally due to rapid urbanization, increasing adoption of Western diets, and growing gastrointestinal health concerns. Public health institutions are beginning to recognize gluten sensitivity as a significant concern, and diagnostic labs in major cities are scaling up testing capabilities.
Local startups are partnering with academic hospitals to pilot novel testing solutions like home-based kits and smartphone-enabled diagnostics. As middle-class health awareness grows, demand for clear diagnoses is rising. However, rural coverage remains a challenge, representing both a hurdle and an opportunity.
Sales in South Korea are anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 9.2% from within the assessment period. This high growth rate reflects rapid modernization of the healthcare sector and rising adoption of gluten-rich Western diets, particularly among youth. South Korean biotech firms are investing in advanced serological testing, often bundled with broader gastrointestinal panels.
The government’s investment in personalized health and diagnostics is also encouraging wider availability of celiac testing. Consumers are increasingly proactive about health, especially through mobile health apps and telemedicine platforms. Despite strong urban growth, the challenge lies in raising awareness among general practitioners and expanding diagnostics to regional clinics.
The industry in Australia and New Zealand is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 8.6% from 2025 to 2035. Both countries have long-standing recognition of celiac disease as a public health issue, with active involvement from national celiac societies. Primary care networks are well-equipped for early diagnosis, and school health programs include awareness education.
Diagnostic firms in the region are focusing on integrating AI-based risk scoring tools to streamline testing decisions. Reimbursement systems are favorable, and patient demand for quick, conclusive testing is fueling innovation. The industry also benefits from tight coordination between nutritionists, gastroenterologists, and diagnostics labs, leading to better outcomes.
In 2024, key developments in the Celiac Disease Diagnostics Industry included strategic moves by major players. Thermo Fisher Scientific expanded its diagnostic capabilities through acquisitions. Inova Diagnostics advanced its automated testing platform with FDA clearance for its Aptiva System.
EmpowerDx partnered with NIMA to expand access to genetic testing. Everlywell launched new at-home celiac testing solutions, aligning with the trend toward home diagnostics. Takeda, in collaboration with Zedira and Dr. Falk Pharma, progressed in developing a new therapeutic candidate.
These moves reflect a competitive landscape focused on innovation, accessibility, and expanding diagnostics across healthcare settings. (Sources: Future Industry Insights, GlobeNewswire)
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
Estimated Share: ~25-30%
The dominant global player offering EliA and Phadia systems for celiac antibody testing, with strong presence in clinical labs and automated diagnostics.
PRIMA Lab SA
Estimated Share: ~10-15%
Specializes in rapid at-home celiac tests with focus on European markets through easy-to-use antibody detection kits.
Biohit Oyj
Estimated Share: ~8-12%
A Finnish company focused on gastrointestinal diagnostics including celiac biomarker research and lab-based ELISA tests.
NanoRepro AG
Estimated Share: ~7-10%
German biotech firm known for quick celiac antibody tests available in pharmacies and direct-to-consumer channels.
AESKU.GROUP GmbH
Estimated Share: ~5-8%
Provides comprehensive autoimmune testing including celiac diagnostics with growing presence in emerging industry.
Imaware
Estimated Share: ~5-7%
Digital health company offering mail-order celiac screening with AI-driven personalized reports.
Biomerica, Inc.
Estimated Share: ~4-6%
Focuses on affordable celiac test kits for both healthcare providers and consumers in North America.
YORKTEST Laboratories
Estimated Share: ~3-5%
Known for food intolerance and celiac testing with strong direct-to-consumer model in UK and Europe.
J. Mitra & Co. Pvt. Ltd.
Estimated Share: ~3-5%
Leading Indian diagnostics company providing low-cost ELISA-based celiac tests for mass screening.
Glutenostics, Inc.
Estimated Share: ~2-4%
Specializes in gluten sensitivity and celiac diagnostics with innovative non-invasive tests in the USA industry.
The industry is valued at USD 343.29 million in 2025.
The industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.3% from 2025 to 2035.
North America and Western Europe are leading the adoption of celiac disease diagnostics.
Non-invasive testing, digital integration, and pediatric screening are key trends.
Limited infrastructure and low awareness continue to hinder diagnostic uptake.
The industry is bifurcated into serology rapid testing kits and genetic rapid testing kits.
The industry is bifurcated into immunochromatography (Lateral Flow) and ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay).
The industry is bifurcated into blood serum and body fluids.
The landscape is fragmented into hospitals, diagnostic laboratories, specialty clinics, and home care settings.
The industry studied across North America, Latin America, Europe, South Asia, East Asia, Oceania, and the Middle East and Africa (MEA).
The Intraoperative Radiation Therapy Systems Market Is Segmented by Disease Indication and End User from 2025 To 2035
The Cirrhosis Management Market is segmented by Corticosteroids, Analgesics and Dialysis from 2025 to 2035
The Soft Tissue Repair Market is segmented by Synthetic, Allograft, Xenograft and Alloplast from 2025 to 2035
Anti-hyperglycemic Agents Market: Growth, Trends, and Assessment for 2025 to 2035
Eyelid Scrub Market Analysis & Forecast by Product, Application and Region 2025 to 2035
CGRP Inhibitors Market Trends - Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.