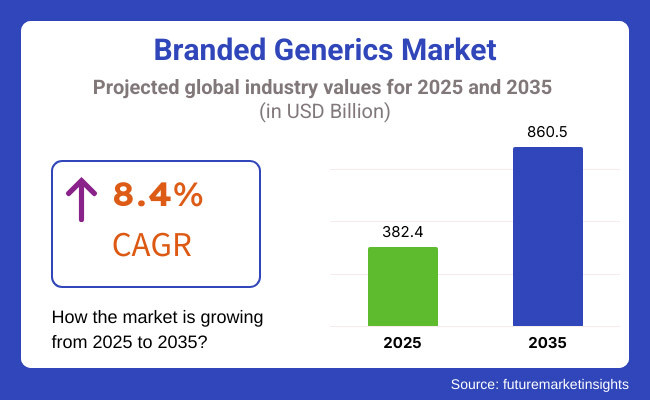
The sales of global branded generics are estimated to be worth USD 382.4 billion in 2025 and anticipated to reach a value of USD 860.5 billion by 2035. Sales are projected to rise at a CAGR of 8.4% over the forecast period between 2025 and 2035. The revenue generated by branded generics in 2024 was USD 353.7 billion.
The sales of branded generics have boosted owing to various organizational and industry based facts. Patent loss of innovator branded drugs is a primary driver as it enables drug companies to launch branded generics with strong brand recall at discounted prices. Policy incentives across most regions, including exclusivity periods for first-to-market generics, also push their use.
Pharmaceutical firms bank on physician confidence and brand loyalty to preserve market share even after a patent has expired. In contrast to unbranded generics, branded generics have some marketing and promotion support, guaranteeing sustained prescription levels. Vertical integration and manufacturing gains also allow pharmaceutical companies to make cost-effective substitutes while preserving quality.
Health systems and payers increasingly encourage cost-containment policies, preferring costly originator medications to branded generics. In addition, strategic collaborations and acquisitions facilitate companies to expand branded generic offerings, improving distribution channels and global presence.
At first, drug manufacturers concentrated on patent-protected medications, but once patents lapsed, companies looked for means to preserve market share with branded generics. In contrast to unbranded generics, the products continued to have brand identity and physician confidence, enabling companies to compete on more than price.
By the 2010s, consolidation was a top trend. Large pharma purchased generic makers to enhance their portfolios, taking advantage of economies of scale and far-reaching distribution systems. High out-of-pocket spending on healthcare nations, such as India and Latin America, experienced high branded generics growth because of cost-sensitive prescribing habits.
Presently, the market continues to be driven by regulatory adjustments, price competitiveness measures, and cost pressure for healthcare, thereby maintaining the position of branded generics as an essential area within the pharma business.
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
The global branded generics market compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) for the first half of 2024 and 2025 is compared in the table below. This analysis will help give the performance of the industry by putting emphasis on significant shifts and trends around revenue generation.
The first six months of the year is between January and June while the second half that is, H2, falls between July and December. In this case, business will be perceived to rise by 8.7% in the first half of the decade from 2024 and 2034 while growth is a bit modified at 9.1% in the second half of the same decade.
| Particular | Value CAGR |
|---|---|
| H1 | 8.7% (2024 to 2034) |
| H2 | 9.1% (2024 to 2034) |
| H1 | 8.4% (2025 to 2035) |
| H2 | 9.0% (2025 to 2035) |
Moving into the subsequent period, from H1 2025 to H2 2035, the CAGR is projected to decrease slightly to 8.4% in the first half and remain relatively lower at 9.0% in the second half. In the first half (H1) the industry witnessed a decrease of 30.00 BPS while in the second half (H2), the industry witnessed a decrease of 11.28 BPS.
Supply Chain Resilience Strategies Enhancing Branded Generics Sales
Supply chain resilience refers to essential players to ensure continuous availability of high-quality supply and products through recovery and response to disruptions. In the pharma space, companies producing branded generics are ramping up their investment in backup manufacturing facilities or regional hubs to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
This tactic has a direct effect on the branded generics industry by creating a consistent pipeline of drugs, even in international drug shortages. Branded generics enjoy robust, established, and diversified manufacturing platforms in contrast to fragmented supply networks without much duplication or backup plans enjoyed by unbranded generics.
With production units in different parts of the country or region, companies limit the reliance on one source and the resultant disturbance through regulatory backlog, raw materials unavailability, or geopolitical disruptions.
The capability to be consistently available increases the confidence in the market among healthcare providers, pharmacies, and distributors. Branded generics are more likely to be prescribed by physicians and pharmacists when they can be confident of an unbroken supply.
Such consistency improves brand loyalty and assurance, induces hospitals to make bulk purchases, and guarantees that insurers will continue to cover these drugs in reimbursement programs. Ultimately the supply chain resilience strategies are anticipated sales of branded generics while enhancing their competitive advantage against unbranded equivalents.
Increasing Competition from Unbranded Generics as a Sales Barrier
Unbranded generics are medicines that have the same active ingredients as branded generics but are sold without a particular brand name. They are usually cheaper in price, hence the preferred option for cost-saving healthcare systems. Governments and payers tend to adopt reimbursement policies that prefer unbranded generics by restricting coverage or financial incentives for branded counterparts.
This price competition pattern presents a strong challenge to branded generics manufacturers. As both types of products are therapeutically equivalent, doctors and pharmacists tend to opt for the less expensive one to keep costs low. In regions with automatic substitution laws in place, pharmacists must or are obligated to fill with the least expensive version, decreasing the market for branded generics even further.
For drug companies, it becomes challenging to justify the price premium for branded generics within such an environment. In the absence of significant differentiation in formulation, patient compliance advantage, or physician-preferred preference, sales of branded generics drop.
Rising Healthcare Expenditure in Emerging Markets and Its Impact on Branded Generics Sales
Healthcare spending is growing in emerging economies from past few years as governments invest in increasing medical infrastructure, enhancing insurance coverage, and widening access to vital medicines. India, Brazil, and China are among the countries seeing rapid increases in healthcare expenditure, motivated by increasing incomes, urbanization, and wider consciousness of medical interventions.
This situation presents real opportunities for branded generic manufacturers to increase market presence.
Branded generics tend to be more widely accepted in such areas than unbranded generics because they are perceived as superior in quality, reliability, and manufacturer reputation. Doctors, the key decision makers in prescribing, tend to use branded generics often because they carry the name of established drug manufacturers that maintain rigorous quality standards.
Patients, particularly those paying from their own pocket, are more likely to go for branded alternatives, perceiving them to have better efficacy and safety.
With increasing spending this has enables branded generics firms to gain a greater proportion of the growing pharmaceutical market while enjoying a price benefit over originator products. As healthcare access increases and more patients are treated for chronic and acute conditions, branded generics makers can solidify their distribution channels, launch new formulations, and build long-term brand loyalty, ensuring sustainable sales growth in these high-potential markets.
The global branded generics industry recorded a CAGR of 7.6% during the historical period between 2020 and 2024. The growth of branded generics industry was positive as it reached a value of USD 352.75 billion in 2024 from USD 264.18 billion in 2020.
For decades, branded generics have been called the stalwart of the pharma sector. This growth was spurred on by the expiration of patents on blockbuster drugs and an activated pharmaceuticals market where drug companies introduce cost-effective alternatives while maintaining their flagship brands. Branded generics took off in the early 2000s in places where doctors and patients cared about guaranteed quality and manufacturer reputation.
In developed markets, the segment grew steadily as healthcare systems everywhere sought to balance affordability with reliability. But in high-growth economies like India, Brazil, and China, branded generics grew the most because patients tend to prefer familiar pharmaceutical brands over unbranded ones. Pharmaceutical companies capitalized on this by diversifying offerings, solidifying distribution networks, and partnering strategically with local businesses.
The outlook for branded generic sales over the next few years is strong - particularly in those markets with increasing health care expenditure and the escalating burden of chronic disease treatment. With more patents on sales driven drugs expiring, more scope exists for firms to introduce branded generics via improved forms e.g. extended-release and fixed-dose combinations that can convey better therapeutic utility.
E-pharmacy and digital health technologies will also enhance access further by enabling companies to engage with consumers more effectively. Moreover, regulatory processes in most countries are changing to incorporate quicker approvals for branded generics to decrease time to market.
Tier 1 Companies are the real key players in this space and take away a whopping 41.5%. Companies like these generally have a broad therapeutic area and a great global reach and, therefore, are also able to take advantage of the different product lines at their disposal.
The enormous size of their operations and significant availability of financial strength permit them to invest massively in research-related activities, which is a solid foundation to reclaim competition. Second, another important reason that Tier 1 companies do strategic partnering and collaborations quite often.
Forming strategic partnerships and collaborations not only improve these companies' place in the market but also helps innovate better. With the consistent product quality and sound brand reputation enabled, keep providing trust among the customers leading the position high. Some of the big names in this tier are Bayer AG, Novartis, and Pfizer Inc., as they have had massive experience and impact in the pharmaceutical domain.
Tier 2 Companies consist of regional leaders or mid-sized players in the branded generics market. These companies maintain a market share of around 26.5%. While Tier 3 companies do not have a global footprint like their Tier 1 counterparts, they are concentrated in particular geographic markets or therapeutic areas, and have different strategies that align with the needs of their target populations.
By virtue of their local knowledge, such companies can both negotiate regulatory landscapes and react promptly to other regional market needs. Concentrating on particular segments, Tier 2 companies can build a strong brand loyalty and establish them as reliable sources of branded generics within their chosen markets.
Such companies include Lupin Ltd and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, both of which have gained significant recognition for their contribution to specific therapeutic fields and regional markets.
Tier 3 companies are smaller players with localized operations, focused on specific therapeutic areas, regions, or product categories. These companies rarely hold a large market share but can be agile and sensitive to the changing needs of their customers.
By concentrating on niche markets or special products, Tier 3 companies can provide targeted solutions that larger firms cannot easily offer. They have a tendency to develop strong connections with the service providers and consumers, which consequently enhances their customer loyalty.
Few of the examples of this level are Teva Pharmaceuticals, Zydus Lifesciences (Cadila), and Sanofi S.A. These are more modest in terms of size, but they make a significant value and option within niche therapeutic categories.
The market analysis for branded generics in various countries is covered in the section below. An analysis of different countries in Branded Generics Market of the world like United States, United Kingdom, China, India, Japan and South Korea are mentioned below. It is projected that the India leads the position, holding a value CAGR of 7.6%. In the Historic period of 2035, China is most likely to experience a CAGR of 6.6% in the Asia-Pacific region.
| Countries | CAGR Value (2025 to 2035) |
|---|---|
| United States | 4.1% |
| United Kingdom | 4.3% |
| Japan | 5.2% |
| China | 6.6% |
| South Korea | 5.7% |
| India | 7.6% |
The branded generics market in India is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.6% between 2025 and 2035. This places India as the leading player in the global branded generics market, which it already dominates with the largest market share.
India's pharma sector is facing drastic changes during the last twenty years, creating a conducive setup for the expansion of branded generics. The strengthening of manufacturing prowess, regulatory innovations, and increasing healthcare accessibility have cumulatively empowered the domestic market for branded generics.
The increased investment in drug manufacturing facilities is one of the main growth drivers. India is now an international pharmaceutical production center, where most modern drug plants conform to global regulatory norms, including the USFDA and EMA. All this has made it possible for companies to produce high-quality branded generics at competitive prices that now reach millions in domestic as well as global markets.
China is anticipated to reach a CAGR value of 6.6% between 2025 and 2035.
China's sales of branded generics are anticipated by extremely effective policies of the government and a well-rooted local pharma industry, which collectively dominate the market. The Chinese government has implemented healthcare reforms aimed at improving access to low-cost medicines while ensuring high quality standards.
Initiatives such as the Volume-Based Procurement (VBP) policy have significantly affected sales of branded generics in this time frame by reducing prices and benefiting local players with huge production capacities.
The domestic pharmaceuticals of China are dominated by domestic players with the support of government-inclined incentives, speedy regulatory approvals, and well-entrenched distribution channels.
In opposition to the Western countries in which the multinationals usually dominate, Sinopharm, Shanghai Pharmaceuticals, and Jiangsu Hengrui are among local majors that dominate branded generic manufacturing. They have scale economies without necessarily being high in costs, a capability to drive them into contesting the multination brands.
South Korea is expecting to show a CAGR of 5.7% between 2025 and 2035.
The branded generics sales in South Korea is mainly due to a strong regulatory framework, physician-prescription, and a domestic preference for local drug companies. The country’s health system is tightly constrained, with the state serving a significant role in determining drug prices, reimbursement policy and market access.
The core reasons for the brand-named generics being used in the country is that the country has a very rigorous approval process regulated by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS).
Though unbranded generics exist, the branded generics have a sense of superiority attached to them as people believe that they are better, they come with uniform potency, and guarantee that consistent manufacturing standards followed by South Korean regulators are maintained.
Another widespread player in South Korea is the doctor-driven prescription market. Compared to other countries where pharmacists have a larger role in substituting drugs, physicians in South Korea mainly determine the drugs that the patients receive.
Since doctors prefer proven pharmaceutical brands, branded generics compete more favorably with the unbranded generics. Furthermore, South Korean pharma companies dominate country's branded generics market locally by taking advantage of extensive domestic preference in addition to government backing.
The section contains information about the leading segments in the industry. Based on Drug class, the anti-hypertensive segment is expected to account for 29.0% of the global share in 2025.
| By Drug Class | Value Share (2025) |
|---|---|
| Anti-Hypertensive | 29.0% |
The Anti-Hypertensive segment is estimated to be a dominating segment in terms of revenue, accounting for almost 29.0% of the market share in 2025.
The sales for anti-hypertensive drugs had a dominated by drug class mainly grip on the basis of greater global prevalence of hypertension, improved cardiovascular disease awareness, and expanded access to medication.
Hypertension is a very common long-term condition among people all around the world across various age groups. Being the leading risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease, it involves regular medication usage, which automatically ensures steady demand in the market.
Also the anti-hypertensive drugs are the growth in the geriatric population. The elderly is more prone to hypertension, and thus the need for effective and safe treatment is increasing. Lifestyle factors like improper dietary lifestyle, high salt consumption, obesity, and physical inactivity have also placed increasingly more cases of hypertension on the market, further increasing demand for the drugs.
It is also driven by the continued advancement of drug delivery formulations, for example, fixed-dose combinations to improve compliance of patients.
| By Therapy Area | Value Share (2025) |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Diseases | 19.3% |
The increasing prevalence of cardiovascular disease has been a key driver supporting the predominance of anti-hypertensive products in branded generics. Since hypertension is one of the most important risk factors for heart disease, stroke and renal impairment, so its control is essential to prevent worse outcomes.
The relentless rise in the incidence of cardiovascular diseases across the globe ensures that demand for anti-hypertensive medication remains strong.
The presence of efficient therapies and combination regimens has also strengthened anti-hypertensive drugs' market share. Drug technology has seen fixed-dose combinations, which increase patient compliance as the number of pills per day decreases. They maximize treatment performance and enhance doctor preference for brand generics.
The branded generics market is intensely competitive, with multinational drug companies, regional players and local manufacturers vying with each other. Keyword: N/A Patented medicine are exclusively held, in contrast over patent protection life cycle branded generics need to encounter challenges from unbranded generics and other branded products making the market highly competitive.
Market leaders vary by geography, with multinationals such as Pfizer, Novartis, and Teva competing with strong local players like Sun Pharma in India, Sinopharm in China, and Hanmi Pharmaceutical in South Korea. Foreign players have struggled to gain a foothold as domestic players have a first-mover advantage in terms of regulatory clearances, distribution channels and doctor trust.
Recent Industry Developments in Branded Generics Industry Outlook
The global branded generics industry is projected to witness CAGR of 8.4% between 2025 and 2035.
The global branded generics industry stood at USD 353.7 billion in 2024.
The global Branded Generics industry is anticipated to reach USD 860.5 billion by 2035 end.
China is expected to show a CAGR of 6.6% in the assessment period.
The Key Players for branded generics industry are Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.(Viatris Inc.), Novartis AG, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc., Sun Pharmaceutical, Aspen Pharmacare Holding Ltd., Abbott Laboratories, Bausch Health Companies Inc. (Valeant Pharmaceuticals Inc.), GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Zydus Lifesciences Ltd. (CADILA), Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Sanofi S.A., AstraZeneca, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd., AbbVie Inc. (Allergan, Inc.), Bayer AG, Cipla Pharmaceuticals, Apotex Inc., Endo International Inc.
Water Testing Kit Market Analysis by Product, Test Type, Water Type, End User, and Region - Analysis for 2025 to 2035
Yeast Infection Treatment Market by Drug Type, Distribution Channel, End User, and Region, 2025 to 2035
Walking Aid Market Analysis by Product, Technology, End-user, and Region 2025 to 2035
Burns Treatment Market Overview – Growth, Demand & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Cardiovascular Ultrasound Market – Demand & Innovations 2025 to 2035
Biomaterial Market Analysis – Size, Share & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.