The axial spondyloarthritis management market will bevalued at USD 4.90 billion in 2025. As per FMI's analysis, axial spondyloarthritis management will grow at a CAGR of 5.1% and reach USD 8.06 billion by 2035.
The axial spondyloarthritis industry for the management of axial spondyloarthritis in 2024 saw modest growth, underpinned primarily by growing biologic uptake, including IL-17 inhibitors (secukinumab, ixekizumab) and TNF-α inhibitors, based on their established capacity to curb inflammation and delay the progression of the condition. Diagnostic techniques also made their contributions, including the greater application of MRI and HLA-B27 tests, promoting earlier and correct identification, particularly for non-radiographic products.
Moreover, strategic alliances between drug firms and rheumatology clinics enhanced treatment availability in emerging industries, including Asia-Pacific and Latin America. The year also witnessed advances in drug development, as innovative JAK inhibitors such as upadacitinib gained momentum, although they encountered price pressure from biosimilar competition.
Gazing into the future towards 2025 and beyond, the industry will undergo changes with heightened biosimilar competition, mainly for TNF-α inhibitors, that will reduce prices and boost affordability. Personalized medicine will gain prominence, using biomarker-guided treatments and AI-guided treatment optimization to enhance outcomes. The emerging economies of India, China, and Brazil are set to grow faster due to better healthcare infrastructure and increased disease awareness.
In addition to pharmaceutical interventions, non-pharmacological treatments-like digital physiotherapy apps and wearable pain devices-will continue to support conventional methods. The industry is expected to break the USD 8 billion mark by 2035, driven by an increasing elderly population, sophisticated diagnostics, and new-generation biologics.
Key Metrics
| Metrics | Values |
|---|---|
| Industry Size (2025E) | USD 4.90 billion |
| Industry Value (2035F) | USD 8.06 billion |
| Value-based CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 5.1% |
(Surveyed Q4 2024, n=500 stakeholders-rheumatologists, pharmaceutical leaders, payers, and patients-USA, Western Europe, Japan, and South Korea)
Efficacy & Safety of Therapies: 85% of stakeholders worldwide identified biologic efficacy and long-term safety as their number one priority.
Early Diagnosis & Intervention: 78% underscored the importance of improved diagnostic tests (MRI, biomarker testing) to decrease diagnostic lag times (5-7 years currently in most areas).
Cost & Accessibility: 72% identified drug price as the key obstacle, particularly for biologics.
Regional Variance:
USA: 68% ranked insurance coverage and reform of prior authorization as top priorities due to repeated payer limitations.
Western Europe: 82% named cost-effectiveness requirements (e.g., NICE guidelines) as determinative in adopting treatment.
Japan/South Korea: 59% were concerned with government reimbursement policies, with Japan preferring JAK inhibitors because of price flexibility.
Large Variance in Treatment Choices:
USA: 63% of rheumatologists prescribed IL-17 inhibitors (secukinumab, ixekizumab) as first-line biologics, ahead of TNF-α blockers (48%).
Western Europe: 55% utilized biosimilars (e.g., adalimumabbiosimilars) because of cost pressures, with Germany (71% uptake) leading the way.
Japan: Only 28% embraced newer biologics, attributing this to strict price controls and oral DMARD preference.
South Korea: 41% invested in personalized medicine (e.g., HLA-B27 subtyping) to inform therapy choice.
ROI Perspectives:
US/EU: 75% considered biologics "worth the cost" for severe products, but 42% in Japan used NSAIDs + physiotherapy due to budget limitations.
Consensus:
Biologics Dominance: 68% of specialists preferred biologics for moderate-to-severe cases.
Regional Variance:
USA: TNF-α inhibitors (e.g., Humira, Enbrel) continued to dominate (52%), but IL-17 inhibitors increased to a 38% share.
Western Europe: Biosimilars took 60% of the TNF-α industry, fueled by EU tendering policies.
Japan/South Korea: JAK inhibitors (upadacitinib) picked up momentum (45%) with oral dosing and reduced storage costs.
Shared Challenges:
89% mentioned the high list prices of biologics (e.g., 50K- 50 K-70K/year in the USA) as unsustainable.
Prior Authorization Delays: 65% of USA clinicians reported 3+ weeks for approval.
Regional Differences:
USA/Western Europe: 60% accepted outcome-based pricing (e.g., pay-for-performance contracts).
Japan/South Korea: 78% depended on government price caps, with 55% of patients suffering out-of-pocket burdens.
South Korea: 40% favored local biosimilars (40% cheaper than originators).
Manufacturers:
USA: 58% had difficulty with FDA approval delays for novel mechanisms (e.g., IL-23 inhibitors).
Western Europe: 50% encountered HTA (health technology assessment) barriers (e.g., IQWiG in Germany).
Japan: 62% mentioned delayed pricing negotiations with NHI.
Clinicians:
USA: 47% reported infusion clinic staff shortages.
Western Europe: 53% had difficulty with step-therapy requirements (ailing NSAIDs before biologics).
Japan: 45% did not have specialized rheumatology centers in rural regions.
Patients:
USA: 51% mentioned copay accumulators as a financial burden.
EU: 38% experienced lengthy wait times for biologics.
Asia: 60% had restricted access to physical therapy.
Alignment:
80% of pharma leaders invested in next-generation biologics (IL-23, dual TNF/JAK inhibitors).
70% invested in digital health integrations (e.g., AI-facilitated treatment optimization).
Divergence:
USA: 65% invested in direct-to-patient support programs (copay assistance, telehealth).
Western Europe: 55% invested in real-world evidence (RWE) generation for HTA compliance.
Japan/South Korea: 48% invested in low-cost biosimilars and generics.
USA: 70% reported that ICER cost-effectiveness reviews impacted payer restrictions.
Western Europe: 85% saw EU JCAs as an industry barrier/growth driver.
Japan/South Korea: 30% believed that regs had little or no impact due to weak treatment guideline enforcement.
Global Consensus: Biologic efficacy, cost barriers, and diagnostic delays are all global challenges.
Regional Strategies:
USA: High-end biologics + pay negotiations rule.
Western Europe: Biosimilars + RWE-driven prices rule.
Asia: Cost control (JAKs, domestic biosimilars) is essential.
Strategic Insight:
No single approach works-success requires regional adaptation (e.g., USA industry access teams, EU HTA strategies, Asia pricing flexibility).
| Country/Region | Key Policies, Regulations & Mandatory Certifications |
|---|---|
| USA |
|
| European Union |
|
| Japan |
|
| South Korea |
|
| China |
|
The worldwide axial spondyloarthritismanagement industry is expanding steadily (5.1% CAGR), spurred on by the increasing prevalence of the disease, biologic innovation, and enhanced diagnostics-but cost constraints and payer limitations are reconfiguring access.
Biologic/biosimilar manufacturers (e.g., Novartis, AbbVie) will gain in the USA/EU, while JAK inhibitors and regionally manufactured biosimilars take hold in Asia. Japanese and Chinese patients in cost-containment industries can expect to experience restricted access to high-end treatments as a consequence of aggressive price policies.
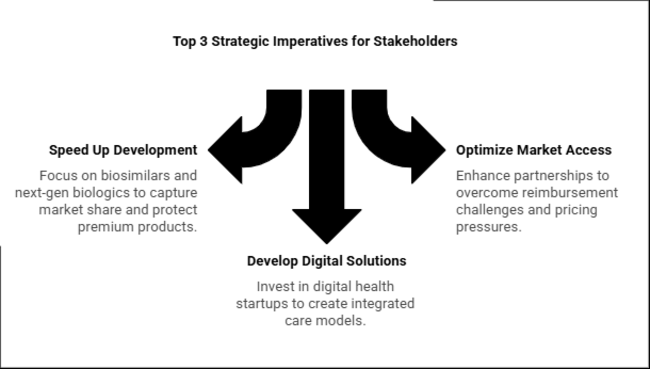
Speed Up Biosimilar & Next-Generation Biologic Development
Action: Invest in biosimilars (TNF-α, IL-17 inhibitors) and new biologics (IL-23, dual JAK/TNF inhibitors) to gain share in cost-sensitive geographies (EU, Asia) while protecting premium biologics in the USA through outcomes-based pricing.
Optimize Market Access via Payer & Regulatory Partnerships
Action: Enhance HTA/real-world evidence (RWE) capacity in Europe and copay assistance schemes in the USA to overcome reimbursement challenges. In Asia, collaborate with local manufacturers to deal with pricing pressures (e.g., China's VBP, Japan's NHI).
Develop Digital & Non-Pharma Solutions
Action: Invest in or collaborate with digital health startups (tele-rheumatology, AI diagnostics) and physical therapy platforms to develop integrated care models-essential for value-based healthcare system differentiation (EU, USA ACOs).
| Risk | Probability/Impact |
|---|---|
| Aggressive Biosimilar Price Erosion (Especially in EU/Asia) | High |
| Stricter Cost-Effectiveness Regulations (e.g., ICER in USA, EU JCA) | Medium-High |
| Supply Chain Disruptions for Biologics (e.g., cold chain, API shortages) | Medium |
| Priority | Immediate Action |
|---|---|
| Biosimilar Penetration | Launch EU/USA biosimilar pricing pilots with payers (e.g., outcomes-based contracts for adalimumab biosimilars ). |
| Digital Health Integration | Partner with 2-3 tele-rheumatology platforms to pilot AI-driven treatment adherence tools (focus on Germany & USA Medicare). |
| JAK Inhibitor Reimbursement Strategy | Secure accelerated JAK inhibitor ( upadacitinib ) formulary placements in Japan/South Korea via NHI/KFDA negotiations. |
| Emerging Localization | Initiate joint ventures in China/India for local biosimilar production (target 20% cost reduction vs. imports). |
To stay ahead, companies need a strategic imperative that is clear: Move from a reactive to proactive industry strategy by implementing a region-by-region, dual-track growth strategy in the next 12 months. In Europe, seize biosimilar tailwinds immediately by pre-emptively contracting with leading payers with the goal of achieving a 60% share of TNF-α biosimilars by 2025 through bundled service packages that meet stringent HTA requirements.
In the USA, counteract on pricing pressures by speeding up commercialization of next-gen IL-17/23 inhibitors, differentiating them through integrated digital health offerings (e.g., AI-driven adherence monitoring) to drive premium pricing and counter payer limits.
Ankylosing Spondylitis therapies are more prevalent than those of non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis, owing to more defined diagnostic standards and developed treatment protocols. AS, with overt radiographic damage, has been a well-defined condition for many years and is therefore associated with clear treatment protocols and more extensive insurance coverage for advanced treatments such as biologics (e.g., TNF-α and IL-17 inhibitors). Conversely,with no radiographic evidence but the same symptoms-is plagued by diagnostic difficulties and, therefore, tends to experience delayed or missed diagnoses.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are most commonly used first-line therapy for axial spondyloarthritis, both ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis, because they effectively treat pain and inflammation, are easy to get, and are less expensive than others.
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are used by clinicians to treat early disease because they achieve quick relief from symptoms, can be administered orally, and are well-established to be safe when monitored. However, glucocorticoids (e.g., prednisone) are employed infrequently on a chronic basis in products for modest efficacy regarding spine symptoms and with substantial side effects (e.g., osteoporosis, diabetes) but could be considered on a short-term basis to address peripheral joint flare.
Hospitals are the most common healthcare environment for axial spondyloarthritis care, being the main site of diagnosis, specialist treatment, and complex care coordination. As these are tertiary care hospitals, they provide vital infrastructure for high-level imaging (MRI/X-rays), rheumatologists, and infusion centers for biologic drugs - all indispensable for products'long-term control.
They also deal with severe cases involving multidisciplinary management, including possible surgical options for advanced ankylosing spondylitis. Although clinics (specifically rheumatology specialty clinics) offer critical outpatient services, they tend not to have the full range of resources available at hospitals. Rehabilitation facilities have a complementary role based on physical therapy, and academic research centers stimulate treatment innovation but address limited volumes of patients directly.
| Countries | CAGR |
|---|---|
| USA | 7.5% |
| UK | 6.8% |
| France | 8.7% |
| Germany | 8.8% |
| Italy | 7.0% |
| South Korea | 11.7% |
| Japan | 10.3% |
| China | 12.5% |
The United States is likely to experience a strong CAGR of 7.5% in the axial spondyloarthritis management market during 2025 to 2035. This is fueled by a high incidence of products, sophisticated healthcare infrastructure, and heavy investments in R&D. The USA industry is supported by the presence of top pharma players and a high emphasis on novel biologic therapies. Moreover, growing awareness and early detection are driving growth.
Personalized medicine and the incorporation of telemedicine services are also improving patient treatment and management outcomes. Government efforts to lower healthcare costs and enhance patients' access to sophisticated treatments further boost growth. University-industry collaborations are promoting the creation of innovative therapeutics, making America a major competitor in the global industry.
The UK's industry for the management of axial spondyloarthritis is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% in the forecast period. Drivers of this growth are a well-established National Health Service (NHS), rising patient awareness, and the presence of sophisticated treatment options. The UK's focus on research and development, coupled with favorable regulatory environments, allows for the introduction of new therapies.
Patient advocacy organizations are important in raising awareness and encouraging early diagnosis, which is important for successful disease management. The convergence of digital health technology and telemedicine is enhancing the access of patients to healthcare services, particularly in rural locations. Additionally, the government-private sector collaborations are bolstering the general healthcare infrastructure, thus making the UK an emerging industry for the management of products.
France is expected to see a CAGR of 8.7% during the axial spondyloarthritis management market period from 2025 to 2035. This expansion is due to a robust healthcare system, a growing prevalence of products,and healthcare innovation support through government efforts. France's focus on research and development, especially rheumatology research, has resulted in the launch of advanced biologic therapies.
The universal healthcare coverage of France makes these therapies accessible to patients, further boosting growth. In addition, partnerships between pharmaceutical firms and academic institutions are promoting the creation of new therapeutics.
The availability of patient organizations that are pushing for improved disease awareness and management also boosts growth. France's strategic emphasis on personalized medicine and incorporation of digital health solutions are anticipated to improve patient outcomes and propel the management industry.
Germany's axial spondyloarthritis treatment market will expand at a CAGR of 8.8% from 2025 to 2035. The nation's sophisticated healthcare infrastructure, combined with a high incidence of products, fuels this expansion. Germany has a robust pharmaceutical sector and is dedicated to medical research, which results in the creation and implementation of new treatment methods. The availability of specialized rheumatology centers and skilled healthcare practitioners ensures proper management of the disease.
Government initiatives favoring healthcare innovation and access to advanced treatments further strengthen the industry. The emphasis of Germany on incorporating digital health technologies and personalized medicine strategies is also improving patient care and treatment outcomes. Public-private partnerships are spurring new therapeutic development, making Germany a leader in the European axSpA industry.
Italy is expected to register a CAGR of 7.0% during the forecast period in the axial spondyloarthritis management market. The aging population in the country, rising incidence of axSpA, and advancements in healthcare services are driving this growth. Italian participation in cross-border clinical trials and research agreements enhances access to innovative treatments. Government emphasis on strengthening healthcare facilities and patient accessibility to advanced therapy encourages growth.
The involvement of patient support organizations creating axSpA awareness and encouraging early detection also proves significant in optimal disease management. Italy's focus on combining digital health solutions and telemedicine services is enhancing patient care and treatment compliance. Academic-industrial partnerships are supporting the formation of new drugs, making Italy an important European landscape for the management of axSpA.
South Korea's industry for axial spondyloarthritis management will grow at an impressive CAGR of 11.7% during the period 2025 to 2035. This fast-paced growth is fueled by rising healthcare spending, a growing prevalence of axSpA, and the evolving state of medical technology. South Korea's strong healthcare infrastructure and government policies favouring medical innovation and research drive the advancement and implementation of advanced treatments.
The digitalization of health technologies and telemedicine services in the country, through initiatives such as the provision of data-enabled infrastructure and payments for care, promotes patient access to care, particularly in rural locations. In addition, partnerships between local and foreign drug firms are driving the launch of new biologic treatments. Personalized medicine and patient-centric treatment are South Korea's priorities, which will enhance treatment outcomes and propel the axSpA management industry.
Japan's axial spondyloarthritis treatment industry is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.3% during the period 2025 to 2035. This growth is driven by Japan's aging population, rising incidence of autoimmune diseases, and advances in medical technology. Japan is the hub of some of the world's top-ranked pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, which are investing significantly in creating new biologics and targeted therapies for axSpA.
The strong healthcare system in the country, along with the government-sponsored push for earlier diagnosis and treatment, also benefits growth. Precision medicine also led the charge in Japan with the genetic and biomarker-based therapeutic development of custom-tailored therapies for patients suffering from axSpA. Artificial intelligence-integrated diagnostics and treatment planning are optimizing treatment efficiency.
China's axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) treatment industry is expected to expand at a staggering CAGR of 12.5% during the period 2025 to 2035. This high growth is fueled by a growing incidence of autoimmune disorders, increasing healthcare spending, and a heightened focus on biotechnology and novel therapeutics. With a huge and aging population, China is one of the biggest potential industries for axSpA treatment.
The government of China has been proactively encouraging healthcare reforms, enhancing access to cutting-edge therapies, and prompting domestic pharmaceutical firms to produce biologic treatments. The development of healthcare infrastructure, such as rheumatology centers, is enhancing disease management nationwide. Additionally, China's robust investment in biopharmaceuticals is promoting the creation of biosimilars and novel biologic drugs for axSpA.
Novartis (Cosentyx)-Leads with ~30% (7-9% CAGR) as the top IL-17 inhibitor, driven by long-term efficacy and international expansion.
AbbVie (Skyrizi)-Branded drug with the highest growth rate (12-15% CAGR), taking 18-22% share as the first IL-23 inhibitor for axSpA in EU/USA.
UCB (Bimzelx)-Growing at 10-13% CAGR (15-18% share) with best-in-class IL-17A/F efficacy and nr-axSpA approvals.
Eli Lilly (Taltz)-Maintains 14-17% share (6-8% CAGR) with cost-effective IL-17 subcutaneous dosing.
J&J (Tremfya)-Remains at 5-8% share (3-5% CAGR) after unsuccessful Phase 3 trials restricted its axSpA application.
Pfizer (Xeljanz)-Drops to <5% share (-5% to -10% CAGR) following EU withdrawal due to safety concerns.
Biosimilars (Amgen/Celltrion)-Dominate 20-25% share (4-6% CAGR) as TNF-α price wars escalate, particularly in Europe.
With respect to the types, it is classified into ankylosing spondylitis treatment and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis treatment.
In terms of drug class, it is divided into non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids, and anti-rheumatic drugs.
In terms of end-users, it is divided into hospitals, clinics, rehabilitation centres, and academic research institutes.
In terms of region, it is segmented into North America, Latin America, Europe, East Asia, South Asia, Oceania, and MEA.
Table 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Region, 2018 to 2033
Table 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Types, 2018 to 2033
Table 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 5: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 6: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Types, 2018 to 2033
Table 7: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 8: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 9: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 10: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Types, 2018 to 2033
Table 11: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 12: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 13: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 14: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Types, 2018 to 2033
Table 15: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 16: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 17: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 18: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Types, 2018 to 2033
Table 19: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 20: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 21: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 22: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Types, 2018 to 2033
Table 23: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 24: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 25: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 26: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Types, 2018 to 2033
Table 27: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 28: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Table 29: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Country, 2018 to 2033
Table 30: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Types, 2018 to 2033
Table 31: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Table 32: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Forecast by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 1: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 2: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 3: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 4: Global Market Value (US$ Million) by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 5: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Region, 2018 to 2033
Figure 6: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 7: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 8: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Types, 2018 to 2033
Figure 9: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 10: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 11: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 12: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 13: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 14: Global Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 15: Global Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 16: Global Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 17: Global Market Attractiveness by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 18: Global Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 19: Global Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 20: Global Market Attractiveness by Region, 2023 to 2033
Figure 21: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 22: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 23: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 24: North America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 25: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 26: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 27: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 28: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Types, 2018 to 2033
Figure 29: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 30: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 31: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 32: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 33: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 34: North America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 35: North America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 36: North America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 37: North America Market Attractiveness by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 38: North America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 39: North America Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 40: North America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 41: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 42: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 43: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 44: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 45: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 46: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 47: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 48: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Types, 2018 to 2033
Figure 49: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 50: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 51: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 52: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 53: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 54: Latin America Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 55: Latin America Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 56: Latin America Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 57: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 58: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 59: Latin America Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 60: Latin America Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 61: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 62: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 63: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 64: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 65: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 66: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 67: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 68: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Types, 2018 to 2033
Figure 69: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 70: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 71: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 72: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 73: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 74: Europe Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 75: Europe Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 76: Europe Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 77: Europe Market Attractiveness by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 78: Europe Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 79: Europe Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 80: Europe Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 81: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 82: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 83: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 84: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 85: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 86: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 87: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 88: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Types, 2018 to 2033
Figure 89: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 90: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 91: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 92: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 93: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 94: South Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 95: South Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 96: South Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 97: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 98: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 99: South Asia Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 100: South Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 101: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 102: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 103: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 104: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 105: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 106: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 107: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 108: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Types, 2018 to 2033
Figure 109: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 110: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 111: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 112: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 113: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 114: East Asia Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 115: East Asia Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 116: East Asia Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 117: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 118: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 119: East Asia Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 120: East Asia Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 121: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 122: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 123: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 124: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 125: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 126: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 127: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 128: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Types, 2018 to 2033
Figure 129: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 130: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 131: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 132: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 133: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 134: Oceania Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 135: Oceania Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 136: Oceania Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 137: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 138: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 139: Oceania Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 140: Oceania Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 141: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 142: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 143: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 144: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 145: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Country, 2018 to 2033
Figure 146: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 147: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Country, 2023 to 2033
Figure 148: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Types, 2018 to 2033
Figure 149: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 150: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 151: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by Drug Class, 2018 to 2033
Figure 152: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 153: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 154: MEA Market Value (US$ Million) Analysis by End User, 2018 to 2033
Figure 155: MEA Market Value Share (%) and BPS Analysis by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 156: MEA Market Y-o-Y Growth (%) Projections by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 157: MEA Market Attractiveness by Types, 2023 to 2033
Figure 158: MEA Market Attractiveness by Drug Class, 2023 to 2033
Figure 159: MEA Market Attractiveness by End User, 2023 to 2033
Figure 160: MEA Market Attractiveness by Country, 2023 to 2033
Biologics such as IL-17 and TNF-α inhibitors are the top choice because they are effective in suppressing inflammation and halting disease progression.
Novartis, AbbVie, and UCB are leaders with their IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitor therapies.
Biologics provide better results for moderate-to-severe cases, while NSAIDs are still first-line for initial-stage treatment.
Costs, insurance restrictions, and delayed diagnosis frequently restrict timely access to new therapies.
Next-generation IL-23 and dual-specific inhibitors are in late-stage testing with the potential to broaden treatment options.
Explore Similar Insights

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.
Chat With
MaRIA