The Japan aircraft ground support equipment market is anticipated to be valued at USD 250.42 million in 2025. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% during the forecast period and reach a value of USD 478.98 million in 2035.
Key Metrics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Estimated Size in 2025 | USD 250.42 Million |
| Projected Size in 2035 | USD 478.98 Million |
| CAGR (2025 to 2035) | 6.7% |
In 2024, Japan aircraft ground support equipment market experienced steady growth, driven by fleet expansion by major carriers, the demand for maximizing aircraft turnaround efficiency, and modernization of airports. Another notable trend was the increased procurement of electric GSE by key airport hubs such as Haneda and Narita, aligning with Japan's decarbonization vision. Airlines have largely focused on automated baggage handling and advanced aircraft tugs while minimizing the use of conventional diesel units. Rising passenger traffic led to increased investment in passenger boarding bridges and catering trucks.
Sustained growth is expected from 2025 onward, driven by automation and electrification trends. Environmentally friendly aviation operations will be encouraged by regulatory support, which will propel GSE manufacturers towards energy-efficient technologies. AI-controlled and remotely operated equipment will enhance operational efficiency by 2035. At the same time, regional airport expansions and ramped-up activities by low-cost carriers will keep the demand for ground-handling solutions active.
Explore FMI!
Book a free demo
A recent survey conducted by FMI among key stakeholders in the industry revealed several critical trends shaping the industry. A majority of operators and airport authorities surveyed emphasized that electrification is getting much more important, with over 70% of respondents expecting to replace conventional diesel-operated GSE with electric options by the year 2030. This shift is driven by Japan's willingness to reduce the carbon footprint of the aviation sector with more government incentives for providing sustainable infrastructure investments.
Nearly 65% of stakeholders prioritized efficiency improvements, showing strong interest in AI-integrated baggage handling systems, remotely operated tugs, and automated passenger boarding bridges. Furthermore, in their discussions, stakeholders pointed out that workforce shortages specific to ground handling services are fast-tracking the introduction of such advanced solutions, particularly at airports with increasing traffic loads such as Haneda and Narita.
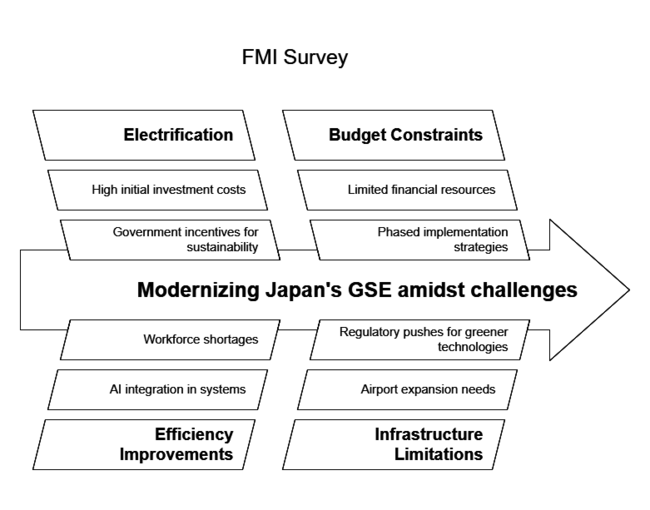
The survey showed further that budget constraints and infrastructure limitations continue to be among some of the greatest hurdles in modernizing GSE. Some 50% of respondents expressed that they were concerned about the high initial investment cost for electrification and automation. However, many airport operators and service providers are looking to develop partnerships with equipment manufacturers to allow phased implementation strategies and financial support models.
Despite challenges such as high initial investment costs, industry leaders anticipate steady long-term growth driven by regulatory incentives and technological advancements. The majority of respondents expect steady expansion in GSE procurement over the next decade, driven by increasing aircraft movements, airport expansions, and regulatory pushes for greener technologies. As the industry evolves, collaboration between airlines, airports, and GSE manufacturers will be critical to overcoming financial and operational barriers.
To gain deeper insights into Japan’s aircraft ground support equipment industry and explore strategic investment opportunities, connect with our experts today.
Stringent government regulations and sustainability initiatives shape the Japan aircraft ground support equipment industry. Policies promoting electrification, safety compliance, and efficiency enhancements are driving investments, while mandatory certifications ensure adherence to aviation standards for operational reliability and environmental responsibility.
| Country | Government Regulations & Certifications Impacting the GSE |
|---|---|
| Japan |
|
The airport service segment is expected to dominate the Japanese aircraft ground support equipment industry, holding a 54.3% share in 2024. Within this category, air start units play a crucial role in supporting aircraft operations at major airports. These units provide the necessary pneumatic power to start jet engines, ensuring seamless aircraft departures. The demand for air start units is rising with increasing flight frequencies at hubs like Haneda and Narita International Airports. Their adoption is further driven by airport modernization projects aimed at enhancing operational efficiency.
The electric segment is projected to account for 49.2% of the industry in 2024, driven by Japan’s push toward sustainable aviation solutions. Ground power units (GPUs) are among the fastest-growing electric GSE subsegments, replacing diesel-powered alternatives to reduce emissions and noise pollution. These units provide electricity to parked aircraft, improving energy efficiency and reducing fuel consumption. Advancements in battery technology are enhancing the reliability and operational longevity of electric GPUs, making them an attractive investment for airport authorities aiming to meet carbon reduction goals.
Leased GSE is emerging as the preferred ownership model, particularly for cost-intensive equipment like tugs and tractors. Airlines and ground-handling companies favor leasing to minimize capital investment while accessing the latest technology. Tugs and tractors play a vital role in maneuvering aircraft and baggage carts efficiently across airport grounds. The growing complexity of airport logistics and the need for flexible equipment solutions are encouraging operators to opt for leased tugs, ensuring uninterrupted ground handling services without high upfront costs.
The commercial segment remains dominant in the aircraft ground support equipment industry, with cargo handling operations witnessing significant growth. Cargo dollies, essential for efficient freight handling, enable smooth loading and unloading of cargo containers, reducing turnaround times for logistics providers. Rising air cargo volumes, particularly from international trade hubs, are accelerating investments in modern cargo dollies to improve supply chain efficiency and streamline airport logistics.
| 2020 to 2024 | 2025 to 2035 |
|---|---|
| The industry experienced a steady recovery following the COVID-19 pandemic, with increasing domestic and international flight operations driving demand for GSE. | Industry expansion is expected to accelerate due to growing air traffic, airport expansions, and technological advancements in GSE. |
| Electrification efforts began gaining traction, but adoption remained limited due to high costs and infrastructure constraints. | Widespread adoption of electric GSE is anticipated, supported by improved battery technology and government sustainability incentives. |
| Key airports such as Haneda and Narita focused on modernization, leading to increased procurement of advanced ground-handling equipment. | Further investments in automation, AI-integrated systems, and smart airport solutions will enhance operational efficiency. |
| Leasing and rental models gained popularity, particularly for high-cost equipment like tugs and tractors, as airlines sought cost-effective solutions. | Leasing and rental services will expand further, allowing operators to acquire advanced GSE without significant upfront investments. |
| Cargo handling GSE demand surged due to the rise in e-commerce and global trade, increasing the need for efficient logistics solutions. | Continued growth in air cargo traffic will drive further demand for specialized GSE, including automated cargo loaders and transporters. |
Japan’s aircraft ground support equipment industry falls under the aviation infrastructure and logistics equipment category, closely linked to air transport, airport modernization, and global trade. This sector is highly influenced by macroeconomic factors such as economic growth, international trade, tourism, and technological advancements in aviation.
Between 2020 and 2024, Japan's aviation sector witnessed a steady recovery from pandemic-induced disruptions, with passenger and cargo traffic rebounding. Government investments in airport expansions, including projects at Haneda and Narita International Airports, fueled demand for advanced GSE. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce bolstered air freight, further driving the need for cargo-handling equipment.
From 2025 to 2035, Japan’s GSE industry is expected to benefit from increased air travel demand, airline fleet expansion, and regulatory mandates for sustainable aviation. The shift toward electric and hybrid GSE aligns with Japan’s carbon neutrality goals, prompting significant infrastructure upgrades. Moreover, automation and AI-driven solutions will enhance operational efficiency, reducing turnaround times and labor costs.
Despite positive growth prospects, challenges such as high capital costs and supply chain disruptions may slow the pace of GSE modernization. However, strong government support, technological innovation, and increasing international connectivity will position Japan’s GSE sector for sustained long-term growth.
Expansion into Regional Airports
While Haneda and Narita remain key hubs, regional airports like Kansai and Chubu Centrair are emerging as significant growth areas for GSE deployment. Increasing low-cost carrier (LCC) operations are driving demand for cost-efficient GSE. Stakeholders should develop scalable, space-efficient solutions tailored for smaller airports to enhance ground handling efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Investment in Next-Generation Electric GSE
Japan's carbon neutrality goals are driving widespread adoption of electric GSE, with regulatory incentives supporting the transition from diesel-powered equipment. Stakeholders should explore advancements in battery technology, including potential solid-state solutions, while investing in fast-charging infrastructure to improve operational efficiency. Collaborations with airport authorities can support pilot projects for electric GPUs, tugs, and belt loaders, ensuring smooth integration of sustainable equipment into existing airport operations.
Leasing &Pay-Per-use Business Models
High upfront GSE costs limit adoption, especially for smaller operators. Manufacturers should expand leasing, rental, and pay-per-use models to improve industry accessibility. Offering flexible financing options will drive faster adoption of advanced GSE, benefiting ground-handling providers by reducing capital investment while ensuring access to modern, high-performance equipment.
The Japan aircraft ground support equipment market in 2024 has experienced steady growth, driven by increased air traffic, airport modernization projects, and the expansion of low-cost carriers. Key players such as JBT Corporation, TLD Group, Textron GSE, Toyota Industries Corporation, and Tug Technologies Corporation have been actively implementing strategies to strengthen their presence and cater to the evolving needs of the aviation industry.
In 2024, JBT Corporation maintained its leadership in Japan's GSE sector with an estimated domestic share of 22-25% and a revenue range of approximately USD 190-220 million from Japan operations. The company has focused on expanding its electric and hybrid GSE offerings, aligning with Japan's push for greener airport operations. JBT has also introduced advanced telematics systems for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of its equipment, enhancing operational efficiency for airport operators. Additionally, JBT has secured several contracts with major Japanese airports, including Narita and Haneda, to supply baggage handling systems and aircraft de-icing equipment.
TLD Group, a global leader in GSE manufacturing, holds a 20-23% share in Japan, with a revenue share of around USD 200 million. In 2024, TLD launched a new range of electric tow tractors and ground power units, targeting Japan’s stringent emissions regulations. The company has also partnered with local distributors to improve after-sales service and reduce delivery times. TLD’s focus on innovation and sustainability has helped it secure contracts with regional airports, including Kansai and Chubu, further solidifying its position.
Textron GSE, a subsidiary of Textron Inc., holds a 15-18% share and a revenue share of approximately USD 160 million in 2024. The company has introduced a new line of compact and lightweight GSE designed to meet the space constraints of smaller Japanese airports. Textron has also invested in digital solutions, such as remote diagnostics and fleet management software, to enhance customer experience. In March 2024, Textron GSE announced a partnership with a Japanese aviation services provider to supply electric baggage carts and pushback tractors, as reported by Aviation Pros. This collaboration has strengthened Textron's presence in the region.
Toyota Industries Corporation, a prominent player in Japan’s GSE industry, holds a 12-15% share and a revenue share of around USD 120 million. In 2024, Toyota leveraged its expertise in electric vehicle technology to develop a new range of battery-powered GSE, including aircraft refuelers and cargo loaders. The company also expanded its service network across Japan, ensuring timely maintenance and support for its equipment. Toyota’s strong brand reputation and focus on sustainability have made it a preferred choice for domestic airlines and airport operators.
Tug Technologies Corporation, with an 8-10% share and a revenue share of approximately USD 95 million, has been actively pursuing growth in Japan’s GSE sector. In 2024, Tug Technologies launched a new line of hybrid GSE, combining diesel and electric power for improved efficiency and reduced emissions. Other key players collectively hold the remaining 15-20% share. The company has also focused on enhancing the safety features of its equipment, such as advanced collision avoidance systems and ergonomic designs. Tug Technologies’ emphasis on innovation and customer satisfaction has helped it gain traction in the competitive Japanese landscape.
Japan’s GSE industry in 2024 has also seen increased collaboration between domestic and international players. For instance, in February 2024, TLD Group entered into a joint venture with a Japanese engineering firm to develop customized GSE solutions for regional airports, as reported by Airport Technology. This partnership enabled TLD to tap into the growing demand for specialized equipment in smaller airports across Japan.
Overall, Japan’s aircraft ground support equipment industry in 2024 is characterized by a strong focus on sustainability, innovation, and customer-centric strategies. Leading players are leveraging technological advancements and strategic partnerships to address the evolving needs of the aviation industry. With further growth expected, these companies are well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities and maintain their competitive edge.
Airport expansions, rising air traffic, increased cargo operations, and the shift toward electric and automated equipment for enhanced efficiency and sustainability fuel the demand.
Japan is prioritizing electric equipment due to stringent environmental policies, advancements in battery technology, and incentives promoting low-emission solutions at major airports.
Electric ground power units, tugs, and cargo loaders are growing rapidly due to their operational efficiency, cost savings, and alignment with sustainability goals.
High initial costs, infrastructure requirements for electric models, and the need for trained personnel to operate advanced equipment are key challenges.
Leasing minimizes upfront costs, provides access to the latest technology, and allows operators to upgrade equipment without major capital investment, making advanced GSE more accessible.
By equipment, the industry is segmented into airport service, cargo loading, and passenger services.
In terms of ownership, the sector is segmented into leased GSE, owned GSE, and rental GSE.
By power, the industry is segmented into electric, hybrid, and non-electric.
In terms of application, the sector is bifurcated into commercial and defense.
Diaphragm Coupling Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
HID Ballast Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
Fluid Conveyance Systems Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035
GCC Magnetic Separator Market Analysis by Over band/Cross Belt Separator and Magnetic Roller Separator through 2035
United Kingdom Magnetic Separator Market Analysis by Over band/Cross Belt Separator and Magnetic Roller Separator through 2035
Glass Door Merchandisers Market Growth - Trends & Forecast 2025 to 2035

Thank you!
You will receive an email from our Business Development Manager. Please be sure to check your SPAM/JUNK folder too.